
Beam divergence
Encyclopedia
The beam divergence of an electromagnetic beam is an angular measure of the increase in beam diameter
or radius
with distance from the optical aperture
or antenna aperture
from which the electromagnetic beam emerges. The term is relevant only in the "far field", away from any focus
of the beam. Practically speaking, however, the far field can commence physically close to the radiating aperture, depending on aperture diameter and the operating wavelength.
Beam divergence is often used to characterize electromagnetic beams in the optical regime, for cases in which the aperture from which the beam emerges is very large with respect to the wavelength
. That said, it is also used in the Radio Frequency (RF) regime for cases in which the antenna is operating in the so-called optical region and is likewise very large relative to a wavelength.
Beam divergence usually refers to a beam of circular cross section, but not necessarily so. A beam may, for example, have an elliptical cross section, in which case the orientation of the beam divergence must be specified, for example with respect to the major or minor axis of the elliptical cross section.
The divergence of a beam can be calculated if one knows the beam diameter at two separate points (Di, Df), and the distance (l) between these points. The beam divergence, , is given by
, is given by
If the beam has been collimated
using a lens
or other focusing element, the divergence expected can be calculated from two parameters: the diameter,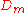 , of the narrowest point on the beam before the lens, and the focal length of the lens,
, of the narrowest point on the beam before the lens, and the focal length of the lens,  . The divergence is then given by
. The divergence is then given by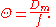
Like all electromagnetic beams, laser
s are subject to divergence, which is measured in milliradians (mrad) or degree
s. For many applications, a lower-divergence beam is preferable. Neglecting divergence due to poor beam quality, the divergence of a laser beam is proportional to its wavelength and inversely proportional to the diameter of the beam at its narrowest point. For example, an ultraviolet laser that emits at a wavelength of 308 nm will have a lower divergence than an infrared laser at 808 nm, if both have the same minimum beam diameter. The divergence of good-quality laser beams is modeled using the mathematics of Gaussian beam
s.
Gaussian laser beams are said to be diffraction limited when their radial beam divergence is close to the minimum possible value, which is given by
is close to the minimum possible value, which is given by
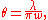
where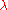 is the laser wavelength and w is the radius of the beam at its narrowest point, which is called the "beam waist". This type of beam divergence is observed from optimized laser cavities. Information on the diffraction-limited divergence of a coherent beam is inherently given by the N-slit interferometric equation
is the laser wavelength and w is the radius of the beam at its narrowest point, which is called the "beam waist". This type of beam divergence is observed from optimized laser cavities. Information on the diffraction-limited divergence of a coherent beam is inherently given by the N-slit interferometric equation
.
Beam diameter
The beam diameter or beam width of an electromagnetic beam is the diameter along any specified line that is perpendicular to the beam axis and intersects it. Since beams typically do not have sharp edges, the diameter can be defined in many different ways. Five definitions of the beam width are in...
or radius
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
with distance from the optical aperture
Aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture of an optical system is the opening that determines the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. The aperture determines how collimated the admitted rays are,...
or antenna aperture
Antenna aperture
In electromagnetics and antenna theory, antenna aperture or effective area is a measure of how effective an antenna is at receiving the power of radio waves. The aperture is defined as the area, oriented perpendicular to the direction of an incoming radio wave, which would intercept the same...
from which the electromagnetic beam emerges. The term is relevant only in the "far field", away from any focus
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by...
of the beam. Practically speaking, however, the far field can commence physically close to the radiating aperture, depending on aperture diameter and the operating wavelength.
Beam divergence is often used to characterize electromagnetic beams in the optical regime, for cases in which the aperture from which the beam emerges is very large with respect to the wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
. That said, it is also used in the Radio Frequency (RF) regime for cases in which the antenna is operating in the so-called optical region and is likewise very large relative to a wavelength.
Beam divergence usually refers to a beam of circular cross section, but not necessarily so. A beam may, for example, have an elliptical cross section, in which case the orientation of the beam divergence must be specified, for example with respect to the major or minor axis of the elliptical cross section.
The divergence of a beam can be calculated if one knows the beam diameter at two separate points (Di, Df), and the distance (l) between these points. The beam divergence,
 , is given by
, is given by
If the beam has been collimated
Collimated light
Collimated light is light whose rays are parallel, and therefore will spread slowly as it propagates. The word is related to "collinear" and implies light that does not disperse with distance , or that will disperse minimally...
using a lens
Lens (optics)
A lens is an optical device with perfect or approximate axial symmetry which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element...
or other focusing element, the divergence expected can be calculated from two parameters: the diameter,
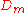 , of the narrowest point on the beam before the lens, and the focal length of the lens,
, of the narrowest point on the beam before the lens, and the focal length of the lens,  . The divergence is then given by
. The divergence is then given by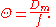
Like all electromagnetic beams, laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
s are subject to divergence, which is measured in milliradians (mrad) or degree
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
s. For many applications, a lower-divergence beam is preferable. Neglecting divergence due to poor beam quality, the divergence of a laser beam is proportional to its wavelength and inversely proportional to the diameter of the beam at its narrowest point. For example, an ultraviolet laser that emits at a wavelength of 308 nm will have a lower divergence than an infrared laser at 808 nm, if both have the same minimum beam diameter. The divergence of good-quality laser beams is modeled using the mathematics of Gaussian beam
Gaussian beam
In optics, a Gaussian beam is a beam of electromagnetic radiation whose transverse electric field and intensity distributions are well approximated by Gaussian functions. Many lasers emit beams that approximate a Gaussian profile, in which case the laser is said to be operating on the fundamental...
s.
Gaussian laser beams are said to be diffraction limited when their radial beam divergence
 is close to the minimum possible value, which is given by
is close to the minimum possible value, which is given by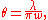
where
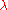 is the laser wavelength and w is the radius of the beam at its narrowest point, which is called the "beam waist". This type of beam divergence is observed from optimized laser cavities. Information on the diffraction-limited divergence of a coherent beam is inherently given by the N-slit interferometric equation
is the laser wavelength and w is the radius of the beam at its narrowest point, which is called the "beam waist". This type of beam divergence is observed from optimized laser cavities. Information on the diffraction-limited divergence of a coherent beam is inherently given by the N-slit interferometric equationN-slit interferometric equation
Quantum mechanics was first applied to optics, and interference in particular, by Paul Dirac. Feynman, in his lectures, uses Dirac’s notation to describe thought experiments on double-slit interference of electrons...
.

