Basophil activation
Encyclopedia
Allergic symptoms are caused by an initial systemic histamine
release by activated basophiles and mast cell
s, that may lead to shock with laryngeal edema, lower-airway obstruction and hypotension
. This is why basophiles are considered with mast cells to be the key cells in allergic diseases.
) is a class of antibody (or immunoglobulin "isotype") that has only been found in mammals. It plays an important role in allergy, and is especially associated with type 1 hypersensitivity
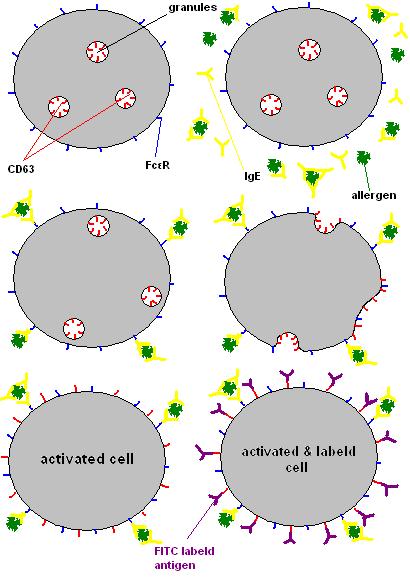
. There are receptors (FcεR) against the constant region of IgE, the Fc region, on several types of cells, including Mast cells and Basophils. Basophils contain many granules inside the cell, which are filled with a variety of active substance triggering an allergic response upon degranulation.
The cells get activated and start degranulation when the IgE antibody, bound to an allergen which can bind to the specific variable region of the IgE, the Fab region, bind to the Fc receptor
molecules on their outer cell membrane, hence the granules, which contain CD63 molecules on their inner surface, merged with the cell membrane. The inner cell surface of the granules becomes the outer cell surface of the basophile /mast cell during degranulation process.
is a valuable tool for analyzing large numbers of cells and for identifying cell populations, even at low concentrations, the percentage of basophiles activated after in vitro stimulation by allergens and expressing the CD63 marker can be determined. The CD63 marker is an FITC
labeled antigen which can bind to an CD63 protein and is used to sort the cells via FACS(Fluorescence activated cell sorting/sorter). This FITC labeled antigen emits light at a wavelength of 530 nm. As the emitted fluorescence intensity is proportional to the binding sites of each single cell, the intensity will increase according to the number of FITC- conjugated antibodies bound to CD63 expressing cells.
and an allergen
which is to be tested. The blood sample is added and the tube is incubated at 37°C for several minutes, to ensure that the allergens can bind to the IgE. By adding EDTA
to the test tube, the degranulation process is stopped immediately. After degranulation a CD63 marker (labeld antibodys) is added to the test tube. Several minutes at room temperature gives the marker time to bind to the CD63 proteins on the cell membrane of the basophil. A lysing step is performed to lyse the red blood cells. Because they outnumber by far the leucocytes they need to be removed to do a FACS analysis of the Basophils.
Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogen compound involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter. Histamine triggers the inflammatory response. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by...
release by activated basophiles and mast cell
Mast cell
A mast cell is a resident cell of several types of tissues and contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin...
s, that may lead to shock with laryngeal edema, lower-airway obstruction and hypotension
Hypotension
In physiology and medicine, hypotension is abnormally low blood pressure, especially in the arteries of the systemic circulation. It is best understood as a physiologic state, rather than a disease. It is often associated with shock, though not necessarily indicative of it. Hypotension is the...
. This is why basophiles are considered with mast cells to be the key cells in allergic diseases.

Activation process
Immunoglobulin E (IgEIGE
IGE was one of the largest services company buying and selling virtual currencies and accounts for MMORPG. During its peak time, it had offices in Los Angeles, China , and headquarters & customer service centre in Hong Kong. IGE was one of the main monopoly in virtual economy services, also known...
) is a class of antibody (or immunoglobulin "isotype") that has only been found in mammals. It plays an important role in allergy, and is especially associated with type 1 hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity refers to undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. These reactions may be damaging, uncomfortable, or occasionally fatal. Hypersensitivity reactions require a pre-sensitized state of the host. The four-group classification...
. There are receptors (FcεR) against the constant region of IgE, the Fc region, on several types of cells, including Mast cells and Basophils. Basophils contain many granules inside the cell, which are filled with a variety of active substance triggering an allergic response upon degranulation.
The cells get activated and start degranulation when the IgE antibody, bound to an allergen which can bind to the specific variable region of the IgE, the Fab region, bind to the Fc receptor
Fc receptor
An Fc receptor is a protein found on the surface of certain cells - including natural killer cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and mast cells - that contribute to the protective functions of the immune system....
in vitro allergy test method
In most cases, a positive skin test is used to identification of allergies, but the activation of basophilic granulocytes with anti-IgE, the expression of the CD63 antigen on the cell surface (plasma membrane) allows identification of the allergen responsible for the hypersensitivity reaction without performing the common scratch test. Only a little amount of blood is needed for this experiment, which makes it comfortable to use since one can perform it in parallel to a normal blood checkup.Degranulation
Degranulated cell expose CD63CD63
CD63 antigen is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD63 gene.CD63 is a good marker for flow cytometric quantification of in vitro activated basophils for diagnosis of IgE-mediated allergy. The test is commonly designated as basophil activation test -Interactions:CD63 has been shown to...
molecules on their outer cell membrane, hence the granules, which contain CD63 molecules on their inner surface, merged with the cell membrane. The inner cell surface of the granules becomes the outer cell surface of the basophile /mast cell during degranulation process.
| materials | purpose |
|---|---|
| BSB | basophil stimulation |
| IL-3 | basophil stimulation |
| allergen | |
| EDTA | degranulation stopper |
| marker | marks the basophils |
| lyse solution | lyses red blood cells |
| centrifuge | spin down red blood cells |
| PBS | washing away lyse solution |
| FACS | counting cells |
Labeling and sorting
As flow cytometryFlow cytometry
Flow cytometry is a technique for counting and examining microscopic particles, such as cells and chromosomes, by suspending them in a stream of fluid and passing them by an electronic detection apparatus. It allows simultaneous multiparametric analysis of the physical and/or chemical...
is a valuable tool for analyzing large numbers of cells and for identifying cell populations, even at low concentrations, the percentage of basophiles activated after in vitro stimulation by allergens and expressing the CD63 marker can be determined. The CD63 marker is an FITC
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
Fluorescein isothiocyanate is a derivative of fluorescein used in wide-ranging applications including flow cytometry. FITC is the original fluorescein molecule functionalized with an isothiocyanate reactive group , replacing a hydrogen atom on the bottom ring of the structure...
labeled antigen which can bind to an CD63 protein and is used to sort the cells via FACS(Fluorescence activated cell sorting/sorter). This FITC labeled antigen emits light at a wavelength of 530 nm. As the emitted fluorescence intensity is proportional to the binding sites of each single cell, the intensity will increase according to the number of FITC- conjugated antibodies bound to CD63 expressing cells.
Procedure
A test tube is prepared with basophile stimulation buffer (BSB) including Interleukin 3Interleukin 3
Interleukin 3, also known as IL-3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL3 gene.-Function:Interleukin-3 is an interleukin, a type of biological signal that can improve the body's natural response to disease as part of the immune system...
and an allergen
Allergen
An allergen is any substance that can cause an allergy. In technical terms, an allergen is a non-parasitic antigen capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivity reaction in atopic individuals....
which is to be tested. The blood sample is added and the tube is incubated at 37°C for several minutes, to ensure that the allergens can bind to the IgE. By adding EDTA
EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, widely abbreviated as EDTA , is a polyamino carboxylic acid and a colourless, water-soluble solid. Its conjugate base is named ethylenediaminetetraacetate. It is widely used to dissolve limescale. Its usefulness arises because of its role as a hexadentate ligand...
to the test tube, the degranulation process is stopped immediately. After degranulation a CD63 marker (labeld antibodys) is added to the test tube. Several minutes at room temperature gives the marker time to bind to the CD63 proteins on the cell membrane of the basophil. A lysing step is performed to lyse the red blood cells. Because they outnumber by far the leucocytes they need to be removed to do a FACS analysis of the Basophils.

