
Banksia lindleyana
Encyclopedia
Banksia lindleyana, commonly known as the Porcupine Banksia, is a species of woody shrub in the genus Banksia
of the family Proteaceae
. It generally grows as a small shrub to 1 m (3 ft) high with long narrow serrated leaves, and bright yellow oval or round inflorescence
s. Flowering occurs in late summer, after which time the flower spikes age and turn to brown and then grey, and develop up to 70 follicles. It occurs in the vicinity of Kalbarri, Western Australia
. Found on sandy soils, the plant serves as a pollinator for a variety of bird and animal species.
in 1855, based on material collected by James Drummond
in 1850–1851 near the lower Murchison River
. Meissner did not give an etymology for the specific epithet, but it is accepted that the name honours John Lindley
. Initially, Meissner's only comment on the affinities of the species was that When he published his taxonomic arrangement of Banksia
the following year, in B. ser Salicinae
on account of its linear leaves with grey undersides, positioning it between B. cylindrostachya and B. marginata
.
When George Bentham
published his arrangement
in 1870, he abandoned Meissner's series, which were based on leaf characters and therefore unacceptably heterogeneous. Instead he erected four sections, placing B. lindleyana in B. sect. Orthostylis (now B. ser. Banksia
) because the styles, after they have been released from the perianth, are curved only at the base, and are otherwise, straight, rigid and erect. The species was positioned between B. caleyi
and B. elegans
.
A major disruption to Banksia nomenclature occurred in 1891, when Otto Kuntze
challenged Banksia L.f. on the grounds that Banksia J.R.Forst & G.Forst (now Pimelea
) had been published before it. Kuntze transferred all Banksia taxa to the new name Sirmuellera; thus B. lindleyana became Sirmuellera lindleyana (L.f.) Kuntze. Kuntze's transfer was rejected, andSirmuellera lindleyana is now considered a nomenclatural synonym of B. lindleyana.
In 1981, Alex George
published "The genus Banksia L.f. (Proteaceae)
", which presented the first taxonomic revision of Banksia for over a century. In George's taxonomic arrangement
, B. lindleyana was placed in B. ser. Cyrtostylis
, which was defined as containing those members of B. sect. Banksia
with slender flowers, a small pollen-presenter
, and beaked follicle
s. The species was placed near the middle of the series, between B. attenuata and B. ashbyi
, but George also acknowledged that some characters that were not typical of the series: an unusually large pollen-presenter, and some characters similar to those of B. ser. Tetragonae
.
George's arrangement stood unchallenged until 1996, when Kevin Thiele
and Pauline Ladiges published their revised arrangement
based on a cladistic analysis of the genus. They found George's B. ser. Cyrtostylis to be highly polyphyletic, and transferred a number of taxa into other series. B. lindleyana resolved as one of the most basal species of B. subg. Banksia
, after B. elegans
and a small clade consisting of B. elderiana
and B. ser. Tetragonae. Accordingly, it was placed alone in a new series, B. ser. Lindleyanae, which was placed between B. ser. Tetragonae and B. ser. Banksia.

Thiele and Ladiges' arrangement remained current only until 1999, when George's treatment of the genus for the Flora of Australia
series of monographs was published. George's 1999 arrangement
was essentially a revision of his 1981 arrangement, which took into account some of Thiele and Ladiges' data, but rejected their overall arrangement. Despite George describing B. ser. Cyrtostylis as "a rather heterogeneous series", his 1981 circumscription was restored with minimal changes, the most significant being the relocation of B. lindleyana to the end of the series, in recognition of the species' relationship with B. ser. Tetragonae:
Since 1998, Austin Mast
has been publishing results of ongoing cladistic analyses of DNA sequence
data for the subtribe Banksiinae. His analyses suggest a phylogeny that is very greatly different to George's arrangement, with B. lindleyana appearing in a clade with B. menziesii
, B. ashbyi
and B. sceptrum
. Early in 2007, Mast and Thiele initiated a rearrangement of Banksia by merging Dryandra
into it, and publishing B. subg. Spathulatae
for the taxa having spoon-shaped cotyledon
s; in this way they also redefined the autonym
B. subg. Banksia. They foreshadowed publishing a full arrangement once DNA sampling of Dryandra was complete; in the meantime, if Mast and Thiele's nomenclatural changes are taken as an interim arrangement, then B. lindleyana is placed in B. subg. Banksia.
Among the Dryandra species transferred into Banksia by Mast and Thiele was Dryandra lindleyana; as the specific epithet "lindlayana" was already taken, D. lindleyana was given the name Banksia dallanneyi
, the new specific epithet being an anagram
of "lindleyana".
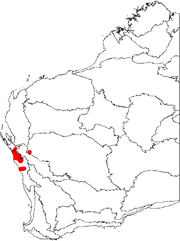 B. lindleyana mostly occurs on the Geraldton Sandplains
B. lindleyana mostly occurs on the Geraldton Sandplains
north of Geraldton toward Shark Bay
, but there is also a collection from well inland, on the western edge of the Murchison region
. It grows in shrubland
on deep yellow sand
, in the swales of coastal dunes and inland on flat sandplain.
Banksia
Banksia is a genus of around 170 species in the plant family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes and fruiting "cones" and heads. When it comes to size, banksias range from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up...
of the family Proteaceae
Proteaceae
Proteaceae is a family of flowering plants distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises about 80 genera with about 1600 species. Together with the Platanaceae and Nelumbonaceae they make up the order Proteales. Well known genera include Protea, Banksia, Embothrium, Grevillea,...
. It generally grows as a small shrub to 1 m (3 ft) high with long narrow serrated leaves, and bright yellow oval or round inflorescence
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Strictly, it is the part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed and which is accordingly modified...
s. Flowering occurs in late summer, after which time the flower spikes age and turn to brown and then grey, and develop up to 70 follicles. It occurs in the vicinity of Kalbarri, Western Australia
Kalbarri, Western Australia
Kalbarri is a coastal town in the Mid West region located 592 km north of Perth, Western Australia. The town is found at the mouth of the Murchison River and has an elevation of...
. Found on sandy soils, the plant serves as a pollinator for a variety of bird and animal species.
Description
It grows as a shrub up to 3 metres (9.8 ft) tall. Young branches are densely felted with hairs, but these are lost with age, and eventually replaced with a deeply fissured grey bark. The leaves are low and narrow (4 to 13 centimetres long but only 4 to 12 millimetres wide), with serrated edges and a blunt apex; like the young brances, young leaves are felted with hairs, but these are lost with age, except in small pits on the underside. The flowering season is from January to March; flowers are yellow, and occur in a characteristic Banksia flower spike. Oval to spherical in shape, this is from 5 to 9 centimetres (2-4 in) long, and occurs on a short, lateral branchlet arising from an older branch. After flowering, the styles wither but do not fall, giving the infructescence a hairy appearance. Infructescences may contain up to 70 follicles, each with two small winged seeds.Taxonomy
Commonly known as the Porcupine Banksia, B. lindleyana was first published by Carl MeissnerCarl Meissner
Carl Daniel Friedrich Meissner was a Swiss botanist.Born in Bern, Switzerland on 1 November 1800, he was christened Meisner but later changed the spelling of his name to Meissner. For most of his 40 year career he was Professor of Botany at University of Basel...
in 1855, based on material collected by James Drummond
James Drummond
James Drummond may refer to:*James Drummond, 1st Baron Maderty*James Drummond , Bishop of Brechin*James Drummond , Scottish-born botanist and naturalist, early settler in Western Australia....
in 1850–1851 near the lower Murchison River
Murchison River (Western Australia)
The Murchison River is the second longest river in Western Australia. It flows for about from the southern edge of the Robinson Ranges to the Indian Ocean at Kalbarri. It has a mean annual flow of about 200 million cubic metres.-Course:...
. Meissner did not give an etymology for the specific epithet, but it is accepted that the name honours John Lindley
John Lindley
John Lindley FRS was an English botanist, gardener and orchidologist.-Early years:Born in Catton, near Norwich, England, John Lindley was one of four children of George and Mary Lindley. George Lindley was a nurseryman and pomologist and ran a commercial nursery garden...
. Initially, Meissner's only comment on the affinities of the species was that When he published his taxonomic arrangement of Banksia
Meissner's taxonomic arrangement of Banksia
Carl Meissner's taxonomic arrangement of Banksia was published in 1856, as part of his chapter on the Proteaceae in A. P. de Candolle's Prodromus systematis naturalis regni vegetabilis. It was the first attempt to provide an infrageneric classification for the genus, aside from Robert Brown's...
the following year, in B. ser Salicinae
Banksia ser. Salicinae
Banksia ser. Salicinae is a valid botanic name for a series of Banksia. First published by Carl Meissner in 1856, the name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Meissner:...
on account of its linear leaves with grey undersides, positioning it between B. cylindrostachya and B. marginata
Banksia marginata
Banksia marginata, commonly known as the Silver Banksia, is a species of tree or woody shrub in the plant genus Banksia found throughout much of southeastern Australia. It ranges from the Eyre Peninsula in South Australia, to north of Armidale, New South Wales, and across Tasmania and the islands...
.
When George Bentham
George Bentham
George Bentham CMG FRS was an English botanist, characterized by Duane Isely as "the premier systematic botanist of the nineteenth century".- Formative years :...
published his arrangement
Bentham's taxonomic arrangement of Banksia
George Bentham's taxonomic arrangement of Banksia was published in 1870, in Volume 5 of Bentham's Flora Australiensis. A substantial improvement on the previous arrangement, it would stand for over a century. It was eventually replaced by Alex George's 1981 arrangement, published in his classic...
in 1870, he abandoned Meissner's series, which were based on leaf characters and therefore unacceptably heterogeneous. Instead he erected four sections, placing B. lindleyana in B. sect. Orthostylis (now B. ser. Banksia
Banksia ser. Banksia
Banksia ser. Banksia is avalid botanic name for a series of Banksia. As an autonym, it necessarily contains the type species of Banksia, B. serrata . Within this constraint, however, there have been various circumscriptions.-According to Bentham:Banksia ser. Banksia originated in 1870 as...
) because the styles, after they have been released from the perianth, are curved only at the base, and are otherwise, straight, rigid and erect. The species was positioned between B. caleyi
Banksia caleyi
Banksia caleyi, commonly known as the red lantern banksia or Cayley's banksia, is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in southern Western Australia south and east of the Stirling Ranges through to around Jerramungup...
and B. elegans
Banksia elegans
The Elegant Banksia is a species of shrub or small tree in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs only over a 65 square kilometre area north and west of Eneabba, Western Australia.-Ecology:...
.
A major disruption to Banksia nomenclature occurred in 1891, when Otto Kuntze
Otto Kuntze
Otto Carl Ernst Kuntze was a German botanist.-Biography:Otto Kuntze was born in Leipzig.An apothecary in his early career, he published an essay entitled Pocket Fauna of Leipzig. Between 1863 and...
challenged Banksia L.f. on the grounds that Banksia J.R.Forst & G.Forst (now Pimelea
Pimelea
Pimelea is a genus of plants belonging to the family Thymelaeaceae. There are about 80 species in the genus, native to Australia and New Zealand. Many of the species are poisonous to cattle.Selected species...
) had been published before it. Kuntze transferred all Banksia taxa to the new name Sirmuellera; thus B. lindleyana became Sirmuellera lindleyana (L.f.) Kuntze. Kuntze's transfer was rejected, andSirmuellera lindleyana is now considered a nomenclatural synonym of B. lindleyana.
In 1981, Alex George
Alex George
Alexander Segger George is a Western Australian botanist. He is the authority on the plant genera Banksia and Dryandra...
published "The genus Banksia L.f. (Proteaceae)
The genus Banksia L.f. (Proteaceae)
The genus Banksia L.f. is a 1981 monograph by Alex George on the taxonomy of the plant genus Banksia. Published by the Western Australian Herbarium as Nuytsia 3, it presented George's taxonomic arrangement of Banksia, the first major taxonomic revision of the genus since George Bentham published...
", which presented the first taxonomic revision of Banksia for over a century. In George's taxonomic arrangement
George's taxonomic arrangement of Banksia
Alex George's taxonomic arrangement of Banksia was the first modern-day arrangement for that genus. First published in 1981 in the classic monograph The genus Banksia L.f. , it superseded the arrangement of George Bentham, which had stood for over a hundred years. It was overturned in 1996 by Kevin...
, B. lindleyana was placed in B. ser. Cyrtostylis
Banksia ser. Cyrtostylis
Banksia ser. Cyrtostylis is a valid botanic name for a taxonomic series within the plant genus Banksia. First published at sectional rank by George Bentham in 1870, it was demoted to a series by Alex George in 1981. The name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Bentham:Bentham published B....
, which was defined as containing those members of B. sect. Banksia
Banksia sect. Banksia
Banksia sect. Banksia is one of four sections of Banksia subgenus Banksia. It contains those species of subgenus Banksia with straight or sometimes curved but not hooked styles. These species all have cylindrical inflorescences and usually exhibit a bottom-up sequence of flower anthesis...
with slender flowers, a small pollen-presenter
Pollen-presenter
A pollen-presenter is an area on the tip of the pistil in flowers of plants of the family Proteaceae. In this family, the anthers are difficult of access for potential pollination vectors such as bees, birds and nectariferous mammals....
, and beaked follicle
Follicle (fruit)
In botany, a follicle is a dry unilocular many-seeded fruit formed from one carpel and dehiscing by the ventral suture in order to release seeds, such as in larkspur, magnolia, banksia, peony and milkweed....
s. The species was placed near the middle of the series, between B. attenuata and B. ashbyi
Banksia ashbyi
The Ashby's Banksia is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in heath and spinifex country along the coast of Western Australia between Geraldton and Exmouth.-Description:...
, but George also acknowledged that some characters that were not typical of the series: an unusually large pollen-presenter, and some characters similar to those of B. ser. Tetragonae
Banksia ser. Tetragonae
Banksia ser. Tetragonae is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of three closely related species of erect shrub with pendulous inflorescences in section Banksia. These are B. lemanniana , B. caleyi and B. aculeata ....
.
George's arrangement stood unchallenged until 1996, when Kevin Thiele
Kevin Thiele
Kevin R. Thiele is curator of the Western Australian Herbarium. His research interests include the systematics of the plant families Proteaceae, Rhamnaceae and Violaceae, and the conservation ecology of grassy woodland ecosystems...
and Pauline Ladiges published their revised arrangement
Thiele and Ladiges' taxonomic arrangement of Banksia
Kevin Thiele and Pauline Ladiges' taxonomic arrangement of Banksia, published in 1996, was a novel taxonomic arrangement that was intended to align the taxonomy of Banksia more closely with the phylogeny that they had inferred from their cladistic analysis of the genus...
based on a cladistic analysis of the genus. They found George's B. ser. Cyrtostylis to be highly polyphyletic, and transferred a number of taxa into other series. B. lindleyana resolved as one of the most basal species of B. subg. Banksia
Banksia subg. Banksia
Banksia subg. Banksia is a valid botanic name for a subgenus of Banksia. As an autonym, it necessarily contains the type species of Banksia, B. serrata . Within this constraint, however, there have been various circumscriptions.-Banksia verae:B. subg...
, after B. elegans
Banksia elegans
The Elegant Banksia is a species of shrub or small tree in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs only over a 65 square kilometre area north and west of Eneabba, Western Australia.-Ecology:...
and a small clade consisting of B. elderiana
Banksia elderiana
The Swordfish Banksia , commonly known as the swordfish banksia or palm banksia, is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in two disjunct areas in the Goldfields-Esperance region of Western Australia...
and B. ser. Tetragonae. Accordingly, it was placed alone in a new series, B. ser. Lindleyanae, which was placed between B. ser. Tetragonae and B. ser. Banksia.

- BanksiaBanksiaBanksia is a genus of around 170 species in the plant family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes and fruiting "cones" and heads. When it comes to size, banksias range from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up...
- B. subg. IsostylisBanksia subg. IsostylisBanksia subg. Isostylis is a subgenus of Banksia. It contains three closely related species, all of which occur only in Southwest Western Australia. Members of subgenus Isostylis have dome-shaped flower heads that are superficially similar to those of B. ser...
(3 species) - B. elegansBanksia elegansThe Elegant Banksia is a species of shrub or small tree in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs only over a 65 square kilometre area north and west of Eneabba, Western Australia.-Ecology:...
(incertae sedis) - B. subg. BanksiaBanksia subg. BanksiaBanksia subg. Banksia is a valid botanic name for a subgenus of Banksia. As an autonym, it necessarily contains the type species of Banksia, B. serrata . Within this constraint, however, there have been various circumscriptions.-Banksia verae:B. subg...
- B. ser. TetragonaeBanksia ser. TetragonaeBanksia ser. Tetragonae is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of three closely related species of erect shrub with pendulous inflorescences in section Banksia. These are B. lemanniana , B. caleyi and B. aculeata ....
(4 species) - B. ser. Lindleyanae
- B. lindleyana
- B. ser. BanksiaBanksia ser. BanksiaBanksia ser. Banksia is avalid botanic name for a series of Banksia. As an autonym, it necessarily contains the type species of Banksia, B. serrata . Within this constraint, however, there have been various circumscriptions.-According to Bentham:Banksia ser. Banksia originated in 1870 as...
(2 subseries, 12 species) - B. baueriBanksia baueriThe Woolly Banksia is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in southwest Western Australia north and east of Albany. It has a distinctively large and hairy looking inflorescence which can be 300 mm or more long and up to 200 mm in diameter.It is placed alone in series...
(incertae sedis) - B. lullfitziiBanksia lullfitziiBanksia lullfitzii is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. A many-branched, spreading bush with golden-orange flowers, it occurs in scattered populations over a large area of the eastern goldfields of Western Australia...
(incertae sedis) - B. attenuataBanksia attenuataBanksia attenuata, commonly known as the candlestick banksia or slender banksia, is a species of plant in the proteaceae family. Commonly a tree, it reaches 10 m high, but is often a shrub in dryer areas 0.4 to 2 m high...
(incertae sedis) - B. ashbyiBanksia ashbyiThe Ashby's Banksia is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in heath and spinifex country along the coast of Western Australia between Geraldton and Exmouth.-Description:...
(incertae sedis) - B. coccineaBanksia coccineaBanksia coccinea, commonly known as the Scarlet Banksia, Waratah Banksia or Albany Banksia, is an erect shrub or small tree in the plant genus Banksia...
(incertae sedis) - B. ser. ProstrataeBanksia ser. ProstrataeBanksia ser. Prostratae is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of six closely related species in section Banksia, all endemic to Western Australia, with a prostrate habit.Banksia ser...
(8 species) - B. ser. CyrtostylisBanksia ser. CyrtostylisBanksia ser. Cyrtostylis is a valid botanic name for a taxonomic series within the plant genus Banksia. First published at sectional rank by George Bentham in 1870, it was demoted to a series by Alex George in 1981. The name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Bentham:Bentham published B....
(4 species) - B. ser. OchraceaeBanksia ser. OchraceaeBanksia ser. Ochraceae is a valid botanic name for a taxonomic series within the plant genus Banksia. It was published by Kevin Thiele in 1996, but discarded by Alex George in 1999.-Cladistics:...
(3 species, 2 subspecies) - B. ser. GrandesBanksia ser. GrandesBanksia ser. Grandes is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of two closely related species in section Banksia, both endemic to Western Australia. These are B. grandis and B. solandri ....
(2 species) - B. ser. SalicinaeBanksia ser. SalicinaeBanksia ser. Salicinae is a valid botanic name for a series of Banksia. First published by Carl Meissner in 1856, the name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Meissner:...
(2 series, 11 species, 4 subspecies) - B. ser. SpicigeraeBanksia ser. SpicigeraeBanksia ser. Spicigerae is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of the seven species in section Oncostylis that have cylindrical inflorescences. These range in form from small shrubs to tall trees. The leaves grow in either an alternate or whorled pattern, with various shape forms...
(3 series, 7 species, 6 varieties) - B. ser. QuercinaeBanksia ser. QuercinaeBanksia ser. Quercinae is avalid botanic name for a series of Banksia. First published by Carl Meissner in 1856, the name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Meissner:...
(2 species) - B. ser. DryandroideaeBanksia ser. DryandroideaeBanksia ser. Dryandroideae is a valid botanic name for a taxonomic series in the plant genus Banksia. First published by Carl Meissner in 1856, the name has had two circumscriptions. As presently circumscribed it is monotypic, containing only B. dryandroides.-According to Meissner:B. ser...
(1 species) - B. ser. AbietinaeBanksia ser. AbietinaeBanksia ser. Abietinae is avalid botanic name for a series of Banksia. First published by Carl Meissner in 1856, the name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Meissner:...
(4 subseries, 15 species, 8 varieties)
- B. ser. Tetragonae
- B. subg. Isostylis
Thiele and Ladiges' arrangement remained current only until 1999, when George's treatment of the genus for the Flora of Australia
Flora of Australia (series)
The Flora of Australia is a 59 volume series describing the vascular plants, bryophytes and lichens present in Australia and its external territories...
series of monographs was published. George's 1999 arrangement
George's taxonomic arrangement of Banksia
Alex George's taxonomic arrangement of Banksia was the first modern-day arrangement for that genus. First published in 1981 in the classic monograph The genus Banksia L.f. , it superseded the arrangement of George Bentham, which had stood for over a hundred years. It was overturned in 1996 by Kevin...
was essentially a revision of his 1981 arrangement, which took into account some of Thiele and Ladiges' data, but rejected their overall arrangement. Despite George describing B. ser. Cyrtostylis as "a rather heterogeneous series", his 1981 circumscription was restored with minimal changes, the most significant being the relocation of B. lindleyana to the end of the series, in recognition of the species' relationship with B. ser. Tetragonae:
- BanksiaBanksiaBanksia is a genus of around 170 species in the plant family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes and fruiting "cones" and heads. When it comes to size, banksias range from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up...
- B. subg. BanksiaBanksia subg. BanksiaBanksia subg. Banksia is a valid botanic name for a subgenus of Banksia. As an autonym, it necessarily contains the type species of Banksia, B. serrata . Within this constraint, however, there have been various circumscriptions.-Banksia verae:B. subg...
- B. sect. BanksiaBanksia sect. BanksiaBanksia sect. Banksia is one of four sections of Banksia subgenus Banksia. It contains those species of subgenus Banksia with straight or sometimes curved but not hooked styles. These species all have cylindrical inflorescences and usually exhibit a bottom-up sequence of flower anthesis...
- B. ser. SalicinaeBanksia ser. SalicinaeBanksia ser. Salicinae is a valid botanic name for a series of Banksia. First published by Carl Meissner in 1856, the name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Meissner:...
(11 species, 7 subspecies) - B. ser. GrandesBanksia ser. GrandesBanksia ser. Grandes is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of two closely related species in section Banksia, both endemic to Western Australia. These are B. grandis and B. solandri ....
(2 species) - B. ser. BanksiaBanksia ser. BanksiaBanksia ser. Banksia is avalid botanic name for a series of Banksia. As an autonym, it necessarily contains the type species of Banksia, B. serrata . Within this constraint, however, there have been various circumscriptions.-According to Bentham:Banksia ser. Banksia originated in 1870 as...
(8 species) - B. ser. CrocinaeBanksia ser. CrocinaeBanksia ser. Crocinae is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of four closely related species, all of which are endemic to Western Australia; namely B. prionotes , B. burdettii , B. hookeriana and B. victoriae...
(4 species) - B. ser. ProstrataeBanksia ser. ProstrataeBanksia ser. Prostratae is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of six closely related species in section Banksia, all endemic to Western Australia, with a prostrate habit.Banksia ser...
(6 species, 3 varieties) - B. ser. CyrtostylisBanksia ser. CyrtostylisBanksia ser. Cyrtostylis is a valid botanic name for a taxonomic series within the plant genus Banksia. First published at sectional rank by George Bentham in 1870, it was demoted to a series by Alex George in 1981. The name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Bentham:Bentham published B....
- B. mediaBanksia mediaThe Southern Plains Banksia , also known as Golden Stalk Banksia, is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs on the south coast of Western Australia between Albany and Israelite Bay, where it is a common plant....
- B. praemorsaBanksia praemorsaThe Cut-leaf Banksia is a species of shrub or tree in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in a few isolated populations on the south coast of Western Australia between Albany and Cape Riche. Seeds do not require any treatment, and take 30 to 49 days to germinate.-References:...
- B. epicaBanksia epicaBanksia epica is a shrub that grows on the south coast of Western Australia. A spreading bush with wedge-shaped serrated leaves and large creamy-yellow flower spikes, it grows up to 3½ metres high. It is known only from two isolated populations in the remote south east of the state, near the...
- B. pilostylisBanksia pilostylisThe Marsh Banksia is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs on the south coast of Western Australia around Esperance. Seeds do not require any treatment, and take 18 to 49 days to germinate.-External links:...
- B. attenuataBanksia attenuataBanksia attenuata, commonly known as the candlestick banksia or slender banksia, is a species of plant in the proteaceae family. Commonly a tree, it reaches 10 m high, but is often a shrub in dryer areas 0.4 to 2 m high...
- B. ashbyiBanksia ashbyiThe Ashby's Banksia is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in heath and spinifex country along the coast of Western Australia between Geraldton and Exmouth.-Description:...
- B. benthamianaBanksia benthamianaBentham's Banksia is a species of shrub or tree in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in scattered populations in the Wheatbelt region of Western Australia, one near Mullewa and the other near Dalwallinu.-Description:...
- B. audaxBanksia audaxBanksia audax is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs over a large area in the central south of Western Australia.-Description:...
- B. lullfitziiBanksia lullfitziiBanksia lullfitzii is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. A many-branched, spreading bush with golden-orange flowers, it occurs in scattered populations over a large area of the eastern goldfields of Western Australia...
- B. elderianaBanksia elderianaThe Swordfish Banksia , commonly known as the swordfish banksia or palm banksia, is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in two disjunct areas in the Goldfields-Esperance region of Western Australia...
- B. laevigataBanksia laevigataBanksia laevigata is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in Western Australia's semi-arid shrubland from Southern Cross south to the Fitzgerald River National Park. It is composed of two closely related subspecies, B. laevigata subsp. laevigata and B. laevigata...
(2 subspecies) - B. elegansBanksia elegansThe Elegant Banksia is a species of shrub or small tree in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs only over a 65 square kilometre area north and west of Eneabba, Western Australia.-Ecology:...
- B. lindleyana
- B. media
- B. ser. TetragonaeBanksia ser. TetragonaeBanksia ser. Tetragonae is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of three closely related species of erect shrub with pendulous inflorescences in section Banksia. These are B. lemanniana , B. caleyi and B. aculeata ....
(3 species) - B. ser. Bauerinae (1 species)
- B. ser. QuercinaeBanksia ser. QuercinaeBanksia ser. Quercinae is avalid botanic name for a series of Banksia. First published by Carl Meissner in 1856, the name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Meissner:...
(2 species)
- B. ser. Salicinae
- B. sect. Coccinea (1 species)
- B. sect. OncostylisBanksia sect. OncostylisBanksia sect. Oncostylis is one of four sections of subgenus Banksia subg. Banksia. It contains those Banksia species with hooked pistils. All of the species in Oncostylis also exhibit a top-down sequence of flower anthesis, except for Banksia nutans which is bottom-up.Banksia sect...
(4 series, 22 species, 4 subspecies, 11 varieties)
- B. sect. Banksia
- B. subg. IsostylisBanksia subg. IsostylisBanksia subg. Isostylis is a subgenus of Banksia. It contains three closely related species, all of which occur only in Southwest Western Australia. Members of subgenus Isostylis have dome-shaped flower heads that are superficially similar to those of B. ser...
(3 species)
- B. subg. Banksia
Since 1998, Austin Mast
Austin Mast
Austin R. Mast is a research botanist. Born in 1972, he obtained a Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 2000. He is currently an associate professor within the Department of Biological Science at Florida State University , and has been director of FSU's since August 2003.One of his...
has been publishing results of ongoing cladistic analyses of DNA sequence
DNA sequence
The sequence or primary structure of a nucleic acid is the composition of atoms that make up the nucleic acid and the chemical bonds that bond those atoms. Because nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are unbranched polymers, this specification is equivalent to specifying the sequence of...
data for the subtribe Banksiinae. His analyses suggest a phylogeny that is very greatly different to George's arrangement, with B. lindleyana appearing in a clade with B. menziesii
Banksia menziesii
Banksia menziesii, commonly known as firewood banksia, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Banksia. It is a gnarled tree up to 10 m tall, or a lower spreading 1–3 m shrub in the more northern parts of its range. The serrated leaves are dull green with new growth a paler grey...
, B. ashbyi
Banksia ashbyi
The Ashby's Banksia is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in heath and spinifex country along the coast of Western Australia between Geraldton and Exmouth.-Description:...
and B. sceptrum
Banksia sceptrum
Banksia sceptrum, the Sceptre Banksia, occurs in Western Australia near the central west coast from Geraldton north through Kalbarri to Hamelin Pool. It extends inland almost to Mullewa....
. Early in 2007, Mast and Thiele initiated a rearrangement of Banksia by merging Dryandra
Dryandra
Banksia ser. Dryandra is a series of 94 species of shrub to small tree in the plant genus Banksia. It was considered a separate genus named Dryandra until early 2007, when it was merged into Banksia on the basis of extensive molecular and morphological evidence that Banksia was paraphyletic with...
into it, and publishing B. subg. Spathulatae
Banksia subg. Spathulatae
Banksia subg. Spathulatae is a valid botanic name for a subgenus of Banksia. It was published in 2007 by Austin Mast and Kevin Thiele, and defined as containing all those Banksia species having spathulate cotyledons...
for the taxa having spoon-shaped cotyledon
Cotyledon
A cotyledon , is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant. Upon germination, the cotyledon may become the embryonic first leaves of a seedling. The number of cotyledons present is one characteristic used by botanists to classify the flowering plants...
s; in this way they also redefined the autonym
Autonym (botany)
In botanical nomenclature, autonyms are automatically created names, as regulated by the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature . Autonyms are cited without an author. Relevant provisions are in articles 6.8, 22.1-3 and 26.1-3....
B. subg. Banksia. They foreshadowed publishing a full arrangement once DNA sampling of Dryandra was complete; in the meantime, if Mast and Thiele's nomenclatural changes are taken as an interim arrangement, then B. lindleyana is placed in B. subg. Banksia.
Among the Dryandra species transferred into Banksia by Mast and Thiele was Dryandra lindleyana; as the specific epithet "lindlayana" was already taken, D. lindleyana was given the name Banksia dallanneyi
Banksia dallanneyi
Banksia dallanneyi, commonly known as Couch Honeypot, is a prostrate shrub endemic to Western Australia. It grows to a height and width of up to 0.5 m, although it is very common for many plants to be growing side by side; thus the clump may be several metres across.It was known as Dryandra...
, the new specific epithet being an anagram
Anagram
An anagram is a type of word play, the result of rearranging the letters of a word or phrase to produce a new word or phrase, using all the original letters exactly once; e.g., orchestra = carthorse, A decimal point = I'm a dot in place, Tom Marvolo Riddle = I am Lord Voldemort. Someone who...
of "lindleyana".
Distribution and habitat

Geraldton Sandplains
Geraldton Sandplains is an Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia region in Western Australia and part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion.It has two sub regions: -* Geraldton Hills sub region* Lesuer sub region...
north of Geraldton toward Shark Bay
Shark Bay
Shark Bay is a World Heritage listed bay in Western Australia. The term may also refer to:* the locality of Shark Bay, now known as Denham* Shark Bay Marine Park* Shark Bay , a shark exhibit at Sea World, Gold Coast, Australia* Shire of Shark Bay...
, but there is also a collection from well inland, on the western edge of the Murchison region
Murchison (biogeographic region)
Murchison is an Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia region in Western Australia and part of the Western Australian Mulga shrublands ecoregion .-Further reading:...
. It grows in shrubland
Shrubland
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub or brush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally or be the result of human activity...
on deep yellow sand
Sand
Sand is a naturally occurring granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles.The composition of sand is highly variable, depending on the local rock sources and conditions, but the most common constituent of sand in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal...
, in the swales of coastal dunes and inland on flat sandplain.

