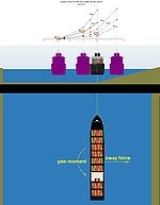
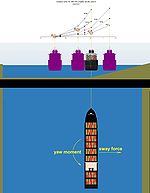
Bank effect
Encyclopedia
_nt.png)
Stern
The stern is the rear or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite of the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section...
of a ship
Ship
Since the end of the age of sail a ship has been any large buoyant marine vessel. Ships are generally distinguished from boats based on size and cargo or passenger capacity. Ships are used on lakes, seas, and rivers for a variety of activities, such as the transport of people or goods, fishing,...
to swing toward the near bank when operating in a river or constricted waterway
Waterway
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Waterways can include rivers, lakes, seas, oceans, and canals. In order for a waterway to be navigable, it must meet several criteria:...
.
The asymmetric flow around a ship induced by the vicinity of banks causes pressure differences (Bernoulli's principle
Bernoulli's principle
In fluid dynamics, Bernoulli's principle states that for an inviscid flow, an increase in the speed of the fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in pressure or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy...
) between port and starboard sides. As a result, a lateral force
Degrees of freedom (engineering)
In mechanics, degrees of freedom are the set of independent displacements and/or rotations that specify completely the displaced or deformed position and orientation of the body or system...
will act on the ship, mostly directed towards the closest bank, as well as a yawing moment pushing her bow towards the centre of the waterway. The squat effect
Squat effect
The squat effect is the hydrodynamic phenomenon by which a vessel moving quickly through shallow water creates an area of lowered pressure that causes the ship to be closer to the seabed than would otherwise be expected. This phenomenon is caused when water that should normally flow under the hull...
increases due to the decreased blockage.
This phenomenon depends on many parameters, such as bank shape, water depth, ship-bank distance, ship properties, ship speed and propeller action
Propeller
A propeller is a type of fan that transmits power by converting rotational motion into thrust. A pressure difference is produced between the forward and rear surfaces of the airfoil-shaped blade, and a fluid is accelerated behind the blade. Propeller dynamics can be modeled by both Bernoulli's...
. A reliable estimation of bank effects is important for determining the limiting conditions in which a ship can safely navigate a waterway.
This phenomenon has several different names, including bank suction, stern suction, and ship-bank interaction.
External links
- bank effects: Information on the largest test program on bank effects.

