
Background Radiation Equivalent Time
Encyclopedia
Background Radiation Equivalent Time, or BRET, is a unit of measurement of ionizing radiation
dosage. One BRET is the equivalent of one day worth of average human exposure to background radiation
. The unit is also referred to as BERT (Background Equivalent Radiation Time).
BRET units are used as a measure of low level radiation exposure. The health hazards of low doses of ionizing radiation are unknown and controversial, because the effects, mainly cancer
and genetic damage, take many years to appear, and the incidence due to radiation exposure can't be statistically separated from the many other causes of these diseases. The purpose of the BRET measure is to allow a low level dose to be easily compared with a universal yardstick: the average dose of background radiation
, mostly from natural sources, that every human unavoidably receives during daily life. Background radiation level is widely used in radiological health fields as a standard for setting exposure limits. Presumably, a dose of radiation which is equivalent to what a person would receive in a few days of ordinary life will not increase his rate of disease measurably.
in sievert
s by dividing by the average annual background radiation
dose in Sv, and multiplying by 365:
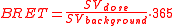
The definition of the BRET unit is apparently unstandardized, and depends on what value is used for the average annual background radiation dose, which differs in different countries and regions. The 2000 UNSCEAR estimate for worldwide background radiation dose is 2.4 mSv (240 mrem). Using this value each BRET unit equals 6.6 μSv.
BRET values range from 2 BRET for a dental
x-ray
to around 400 for a barium enema
study.
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation is radiation composed of particles that individually have sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. This ionization produces free radicals, which are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons...
dosage. One BRET is the equivalent of one day worth of average human exposure to background radiation
Background radiation
Background radiation is the ionizing radiation constantly present in the natural environment of the Earth, which is emitted by natural and artificial sources.-Overview:Both Natural and human-made background radiation varies by location....
. The unit is also referred to as BERT (Background Equivalent Radiation Time).
BRET units are used as a measure of low level radiation exposure. The health hazards of low doses of ionizing radiation are unknown and controversial, because the effects, mainly cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
and genetic damage, take many years to appear, and the incidence due to radiation exposure can't be statistically separated from the many other causes of these diseases. The purpose of the BRET measure is to allow a low level dose to be easily compared with a universal yardstick: the average dose of background radiation
Background radiation
Background radiation is the ionizing radiation constantly present in the natural environment of the Earth, which is emitted by natural and artificial sources.-Overview:Both Natural and human-made background radiation varies by location....
, mostly from natural sources, that every human unavoidably receives during daily life. Background radiation level is widely used in radiological health fields as a standard for setting exposure limits. Presumably, a dose of radiation which is equivalent to what a person would receive in a few days of ordinary life will not increase his rate of disease measurably.
Definition
The BRET corresponding to a dose of radiation is the number of days of average background dose it is equivalent to. It is calculated from the equivalent doseEquivalent dose
The equivalent absorbed radiation dose, usually shortened to equivalent dose, is a computed average measure of the radiation absorbed by a fixed mass of biological tissue, that attempts to account for the different biological damage potential of different types of ionizing radiation...
in sievert
Sievert
The sievert is the International System of Units SI derived unit of dose equivalent radiation. It attempts to quantitatively evaluate the biological effects of ionizing radiation as opposed to just the absorbed dose of radiation energy, which is measured in gray...
s by dividing by the average annual background radiation
Background radiation
Background radiation is the ionizing radiation constantly present in the natural environment of the Earth, which is emitted by natural and artificial sources.-Overview:Both Natural and human-made background radiation varies by location....
dose in Sv, and multiplying by 365:
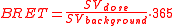
The definition of the BRET unit is apparently unstandardized, and depends on what value is used for the average annual background radiation dose, which differs in different countries and regions. The 2000 UNSCEAR estimate for worldwide background radiation dose is 2.4 mSv (240 mrem). Using this value each BRET unit equals 6.6 μSv.
BRET values range from 2 BRET for a dental
Dentistry
Dentistry is the branch of medicine that is involved in the study, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases, disorders and conditions of the oral cavity, maxillofacial area and the adjacent and associated structures and their impact on the human body. Dentistry is widely considered...
x-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
to around 400 for a barium enema
Barium enema
A lower gastrointestinal series, also called a barium enema, is a medical procedure used to examine and diagnose problems with the human colon . X-ray pictures are taken while barium sulfate fills the colon via the rectum.-Procedure:...
study.

