
Babinet's principle
Encyclopedia
In physics
, Babinet's principle is a theorem
concerning diffraction
that states that the diffraction pattern from an opaque body is identical to that from a hole of the same size and shape except for the overall forward beam intensity.
Diffraction patterns from apertures or bodies of known size and shape are compared with the pattern from the object to be measured. For instance, the size of red blood cell
s can be found by comparing their diffraction pattern with an array of small holes. One consequence of Babinet's principle is a paradox
that in the diffraction limit, the radiation removed from the beam due to a particle is equal to twice the particle's cross section
times the flux. This is because the amount of radiation absorbed
or reflected is the same as the amount diffracted.
The principle is most often used in optics
but it is also true for other forms of electromagnetic radiation
and is, in fact, a general theorem of diffraction and holds true for all waves. Babinet's principle finds most use in its ability to detect equivalence in size and shape.
. First place a thin (approx 0.1 mm) wire into the laser beam and observe the diffraction pattern. Then observe the diffraction pattern when the laser is shone through a narrow slit. The slit can be made either by using a laser printer
or photocopier
to print onto clear plastic film or by using a pin to draw a line on a piece of glass that has been smoked over a candle flame.
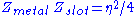 .
.
Where Zmetal and Zslot are input impedances of the metal and slot radiating pieces, and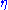 is the intrinsic impedance of the media in which the structure is immersed. In addition, Zslot is not only the impedance of the slot, but can be viewed as the complementary structure impedance (a dipole or loop in many cases). In addition, Zmetal is often referred to as Zscreen were the screen comes from the optical definition. It is noteworthy that the thin sheet or screen does not have to be metal, but rather any material that supports a
is the intrinsic impedance of the media in which the structure is immersed. In addition, Zslot is not only the impedance of the slot, but can be viewed as the complementary structure impedance (a dipole or loop in many cases). In addition, Zmetal is often referred to as Zscreen were the screen comes from the optical definition. It is noteworthy that the thin sheet or screen does not have to be metal, but rather any material that supports a 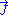 (current density vector) leading to a magnetic potential
(current density vector) leading to a magnetic potential 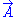 . One issue with this equation, is that the screen must be relatively thin to the given wavelength (or range thereof). If it is not, modes can begin to form or fringing fields may no longer be negligible.
. One issue with this equation, is that the screen must be relatively thin to the given wavelength (or range thereof). If it is not, modes can begin to form or fringing fields may no longer be negligible.
For a more general definition of Eta or intrinsic impedance, .
.
Please note that Babinet's principle does not account for polarization. In 1946, H.G. Booker published Slot Aerials and Their Relation to Complementary Wire Aerials to extend Babinet's principle to account for polarization (otherwise known as Booker's Extension). This information is drawn from, as stated above, Balanis's third edition Antenna Theory textbook.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, Babinet's principle is a theorem
Theorem
In mathematics, a theorem is a statement that has been proven on the basis of previously established statements, such as other theorems, and previously accepted statements, such as axioms...
concerning diffraction
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
that states that the diffraction pattern from an opaque body is identical to that from a hole of the same size and shape except for the overall forward beam intensity.
Explanation
Let B be the original diffracting body, and B' its complement, i.e., the body that is transparent where B is opaque, and opaque where B is transparent. The sum of the radiation patterns caused by B and B' must be the same as the radiation pattern of the undisturbed beam. In places where the undisturbed beam would not have reached, this means that the radiation patterns caused by B and B' must be opposite in phase, but equal in amplitude.Diffraction patterns from apertures or bodies of known size and shape are compared with the pattern from the object to be measured. For instance, the size of red blood cell
Red blood cell
Red blood cells are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate organism's principal means of delivering oxygen to the body tissues via the blood flow through the circulatory system...
s can be found by comparing their diffraction pattern with an array of small holes. One consequence of Babinet's principle is a paradox
Physical paradox
A physical paradox is an apparent contradiction in physical descriptions of the universe. While many physical paradoxes have accepted resolutions, others defy resolution and may indicate flaws in theory...
that in the diffraction limit, the radiation removed from the beam due to a particle is equal to twice the particle's cross section
Cross section (physics)
A cross section is the effective area which governs the probability of some scattering or absorption event. Together with particle density and path length, it can be used to predict the total scattering probability via the Beer-Lambert law....
times the flux. This is because the amount of radiation absorbed
Absorption (electromagnetic radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way by which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed to other forms of energy for example, to heat. The absorption of light during wave propagation is...
or reflected is the same as the amount diffracted.
The principle is most often used in optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
but it is also true for other forms of electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
and is, in fact, a general theorem of diffraction and holds true for all waves. Babinet's principle finds most use in its ability to detect equivalence in size and shape.
Demonstration experiment
The effect can be simply observed by using a laserLaser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
. First place a thin (approx 0.1 mm) wire into the laser beam and observe the diffraction pattern. Then observe the diffraction pattern when the laser is shone through a narrow slit. The slit can be made either by using a laser printer
Laser printer
A laser printer is a common type of computer printer that rapidly produces high quality text and graphics on plain paper. As with digital photocopiers and multifunction printers , laser printers employ a xerographic printing process, but differ from analog photocopiers in that the image is produced...
or photocopier
Photocopier
A photocopier is a machine that makes paper copies of documents and other visual images quickly and cheaply. Most current photocopiers use a technology called xerography, a dry process using heat...
to print onto clear plastic film or by using a pin to draw a line on a piece of glass that has been smoked over a candle flame.
Radio Engineer Useful Formula
Babinet Principle can be used to find complementary impedances. Babinet's Principle states (in optics) that when a field behind a screen with an opening is added to the field of a complementary structure (that is a shape covering the screen hole), then the sum is equal to the field where there is no screen. Demonstration can be found in any good optic or antenna book (such as Balanis, Krauss, Stuzman). The end result (corollary as a matter of fact) of practical interest for antenna engineers is the following formula: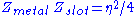 .
.Where Zmetal and Zslot are input impedances of the metal and slot radiating pieces, and
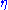 is the intrinsic impedance of the media in which the structure is immersed. In addition, Zslot is not only the impedance of the slot, but can be viewed as the complementary structure impedance (a dipole or loop in many cases). In addition, Zmetal is often referred to as Zscreen were the screen comes from the optical definition. It is noteworthy that the thin sheet or screen does not have to be metal, but rather any material that supports a
is the intrinsic impedance of the media in which the structure is immersed. In addition, Zslot is not only the impedance of the slot, but can be viewed as the complementary structure impedance (a dipole or loop in many cases). In addition, Zmetal is often referred to as Zscreen were the screen comes from the optical definition. It is noteworthy that the thin sheet or screen does not have to be metal, but rather any material that supports a 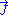 (current density vector) leading to a magnetic potential
(current density vector) leading to a magnetic potential 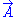 . One issue with this equation, is that the screen must be relatively thin to the given wavelength (or range thereof). If it is not, modes can begin to form or fringing fields may no longer be negligible.
. One issue with this equation, is that the screen must be relatively thin to the given wavelength (or range thereof). If it is not, modes can begin to form or fringing fields may no longer be negligible.For a more general definition of Eta or intrinsic impedance,
 .
.Please note that Babinet's principle does not account for polarization. In 1946, H.G. Booker published Slot Aerials and Their Relation to Complementary Wire Aerials to extend Babinet's principle to account for polarization (otherwise known as Booker's Extension). This information is drawn from, as stated above, Balanis's third edition Antenna Theory textbook.

