BPM 37093
Encyclopedia
BPM 37093 is a variable
white dwarf
star
of the DAV, or ZZ Ceti
, type, with a hydrogen
atmosphere and an unusually high mass of approximately 1.1 times the Sun
's. It is about 50 light-year
s from Earth, in the constellation Centaurus
, and vibrates; these pulsations cause its luminosity
to vary
. Like other white dwarfs, BPM 37093 is thought to be composed primarily of carbon and oxygen, which are created by thermonuclear fusion of helium
nuclei in the triple-alpha process
.
In the 1960s, it was predicted that as a white dwarf cools, its material should crystallize, starting at the center. When a star pulsates, observing its pulsations gives information about its structure. BPM 37093 was first observed to be a pulsating variable in 1992, and in 1995 it was pointed out that this yielded a potential test of the crystallization theory. In 2004, Antonio Kanaan and a team of researchers of the Whole Earth Telescope estimated, on the basis of these asteroseismological
observations, that approximately 90% of the mass of BPM 37093 had crystallized. Other work gives a crystallized mass fraction of between 32% and 82%. Any of these estimates would result in a total crystalline mass in excess of 5 kilograms.
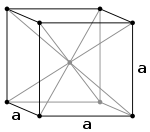 Crystallization of the material of a white dwarf of this type is thought to result in a body-centered cubic lattice of carbon and/or oxygen nuclei, which are surrounded by a Fermi sea of electrons. Since a diamond
Crystallization of the material of a white dwarf of this type is thought to result in a body-centered cubic lattice of carbon and/or oxygen nuclei, which are surrounded by a Fermi sea of electrons. Since a diamond
also consists of crystallized carbon, the star BPM 37093 has been nicknamed Lucy after The Beatles
's hit Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds
.
Variable star
A star is classified as variable if its apparent magnitude as seen from Earth changes over time, whether the changes are due to variations in the star's actual luminosity, or to variations in the amount of the star's light that is blocked from reaching Earth...
white dwarf
White dwarf
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored...
star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
of the DAV, or ZZ Ceti
Pulsating white dwarf
A pulsating white dwarf is a white dwarf star whose luminosity varies due to non-radial gravity wave pulsations within itself. Known types of pulsating white dwarfs include DAV, or ZZ Ceti, stars, with hydrogen-dominated atmospheres and the spectral type DA, pp. 891, 895; DBV, or V777 Her,...
, type, with a hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atmosphere and an unusually high mass of approximately 1.1 times the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
's. It is about 50 light-year
Light-year
A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres...
s from Earth, in the constellation Centaurus
Centaurus
Centaurus is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:...
, and vibrates; these pulsations cause its luminosity
Luminosity
Luminosity is a measurement of brightness.-In photometry and color imaging:In photometry, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance, which is the density of luminous intensity in a given direction. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre.The luminosity function...
to vary
Variable star
A star is classified as variable if its apparent magnitude as seen from Earth changes over time, whether the changes are due to variations in the star's actual luminosity, or to variations in the amount of the star's light that is blocked from reaching Earth...
. Like other white dwarfs, BPM 37093 is thought to be composed primarily of carbon and oxygen, which are created by thermonuclear fusion of helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
nuclei in the triple-alpha process
Triple-alpha process
The triple alpha process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions by which three helium-4 nuclei are transformed into carbon.Older stars start to accumulate helium produced by the proton–proton chain reaction and the carbon–nitrogen–oxygen cycle in their cores...
.
In the 1960s, it was predicted that as a white dwarf cools, its material should crystallize, starting at the center. When a star pulsates, observing its pulsations gives information about its structure. BPM 37093 was first observed to be a pulsating variable in 1992, and in 1995 it was pointed out that this yielded a potential test of the crystallization theory. In 2004, Antonio Kanaan and a team of researchers of the Whole Earth Telescope estimated, on the basis of these asteroseismological
Asteroseismology
Asteroseismology also known as stellar seismology is the science that studies the internal structure of pulsating stars by the interpretation of their frequency spectra. Different oscillation modes penetrate to different depths inside the star...
observations, that approximately 90% of the mass of BPM 37093 had crystallized. Other work gives a crystallized mass fraction of between 32% and 82%. Any of these estimates would result in a total crystalline mass in excess of 5 kilograms.

Diamond
In mineralogy, diamond is an allotrope of carbon, where the carbon atoms are arranged in a variation of the face-centered cubic crystal structure called a diamond lattice. Diamond is less stable than graphite, but the conversion rate from diamond to graphite is negligible at ambient conditions...
also consists of crystallized carbon, the star BPM 37093 has been nicknamed Lucy after The Beatles
The Beatles
The Beatles were an English rock band, active throughout the 1960s and one of the most commercially successful and critically acclaimed acts in the history of popular music. Formed in Liverpool, by 1962 the group consisted of John Lennon , Paul McCartney , George Harrison and Ringo Starr...
's hit Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds
Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds
"Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds" is a song written primarily by John Lennon and credited to Lennon–McCartney, for The Beatles' 1967 album Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band...
.
See also
- List of star extremes
- WASP-12bWASP-12bWASP-12b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star WASP-12, discovered by the SuperWASP planetary transit survey. Its discovery was announced on April 1, 2008. Due to its extremely close orbit to its star, it has one of the lowest densities for exoplanets...
, a "diamond planet" - PSR J1719-1438 b, the crystalline remnant of an evaporated white dwarf
External links
- BPM 37093 (Diamond Star)
- Largest diamond in galaxy predicts future of solar system, Pravda.ru, December 26, 2007.

