Aztlanolagus
Encyclopedia
Aztlanolagus is an extinct monotypic
genus
of rabbit
with a single species Aztlanolagus agilis. Differences among recovered fossils suggest that there were other species, however. The name of the genus refers to Aztlán
, the legendary place of origin of the Nahua peoples as recorded in the mythological accounts
of the Aztec
s and other Nahua groups. By some traditions, this legendary locale is placed in the border regions of the Southwestern United States
and adjacent northern Mexico
.
It is known only from the Pliocene
and Pleistocene
(Blancan
to Rancholabrean
North American land mammal ages). The known distribution is from southeastern Arizona
-(Madrean Sky Islands
region), to central Texas
and from central Colorado
to southern Chihuahua.
Monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group with only one biological type. The term's usage differs slightly between botany and zoology. The term monotypic has a separate use in conservation biology, monotypic habitat, regarding species habitat conversion eliminating biodiversity and...
genus
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
of rabbit
Leporidae
Leporids are the approximately 50 species of rabbits and hares which form the family Leporidae. The leporids, together with the pikas, constitute the mammalian order Lagomorpha. Leporids differ from pikas in having short furry tails, and elongated ears and hind legs...
with a single species Aztlanolagus agilis. Differences among recovered fossils suggest that there were other species, however. The name of the genus refers to Aztlán
Aztlán
Aztlán is the mythical ancestral home of the Nahua peoples, one of the main cultural groups in Mesoamerica. And, by extension, is the mythical homeland of the Uto-Aztecan peoples. Aztec is the Nahuatl word for "people from Aztlan".-Legend:...
, the legendary place of origin of the Nahua peoples as recorded in the mythological accounts
Aztec mythology
The aztec civilization recognized a polytheistic mythology, which contained the many deities and supernatural creatures from their religious beliefs. "orlando"- History :...
of the Aztec
Aztec
The Aztec people were certain ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries, a period referred to as the late post-classic period in Mesoamerican chronology.Aztec is the...
s and other Nahua groups. By some traditions, this legendary locale is placed in the border regions of the Southwestern United States
Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States is a region defined in different ways by different sources. Broad definitions include nearly a quarter of the United States, including Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas and Utah...
and adjacent northern Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
.
It is known only from the Pliocene
Pliocene
The Pliocene Epoch is the period in the geologic timescale that extends from 5.332 million to 2.588 million years before present. It is the second and youngest epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch...
and Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
(Blancan
Blancan
The Blancan North American Stage on the geologic timescale is the North American faunal stage according to the North American Land Mammal Ages chronology , typically set from 4,750,000 to 1,808,000 years BP, a period of .. It is usually considered to start in the early-mid Pliocene epoch and end...
to Rancholabrean
Rancholabrean
The Rancholabrean North American Stage on the geologic timescale is the North American faunal stage according to the North American Land Mammal Ages chronology , typically set from less than 240,000 years to 11,000 years BP, a period of . It is usually considered to overlap the Middle Pleistocene...
North American land mammal ages). The known distribution is from southeastern Arizona
Arizona
Arizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix...
-(Madrean Sky Islands
Madrean sky islands
The Madrean Sky Islands are enclaves of Madrean pine-oak woodlands, found at higher elevations in a complex of small mountain ranges in southern and southeastern Arizona, southwestern New Mexico, and northwestern Mexico. The sky islands are surrounded at lower elevations by the Sonoran and...
region), to central Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
and from central Colorado
Colorado
Colorado is a U.S. state that encompasses much of the Rocky Mountains as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the Great Plains...
to southern Chihuahua.
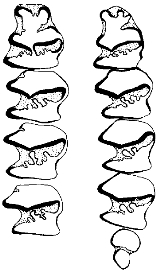
Aztlanolagus may be distinguished from all other known leporids as follows. Lower incisor terminates under diastema and well anterior to P3. Three reentrant folds present on trigonid of P3: an anterior reentrant fold, an anterointernal reentrant fold (rarely cut off to form an enamel lake), and an anteroexternal fold. At all growth stages, a posteroexternal reentrant fold extends approximately halfway across occlusal surface of P3 to a narrow enamel lake lying next to lingual border; enamel lake rarely joined to external reentrant to form the Lepus-type pattern (Hibbard, 1963). On P4 to M2, external fold extends to enamel of lingual wall. Anterior border of talonid on P4-M2 deeply convoluted, often with alternating series of major and minor enamel loops.... (Russell and Harris 1986:632-633)

