Aspartylglucosaminuria
Encyclopedia
Aspartylglucosaminuria also called aspartylglycosaminuria, is a rare, autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder caused by deficient activity of the enzyme N-aspartyl-beta-glucosaminidase (aspartylglucosaminidase
). This enzyme normally cleaves long sugar chains known as oligosaccharides in the lysosome. When N-aspartyl-beta-glucosaminidase is deficient these long sugar chains build up and eventually lead to the clinical features of AGU. AGU is one of seven identified Glycoprotein Storage Diseases.
, ventral hernia and skeletal abnormalities. It is a member of Finnish disease heritage, a group of diseases or syndromes caused by mutation
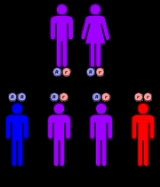
in a single gene
characterized by higher frequency in Finland
than the rest of the world.
 Deficiency of aspartylglucosaminidase (1-aspart-amido-beta-N-acetylglucosamine aminohydrase - E.C.3.5.1.26), an enzyme which cleaves the N-acetyl-glucosamine-asparagine linkage of oligosaccharide chains in glycoprotein and glycopeptide metabolism, causes Aspartylglycosaminuria. Biochemical tests show high urinary levels of aspartylglucosamine
Deficiency of aspartylglucosaminidase (1-aspart-amido-beta-N-acetylglucosamine aminohydrase - E.C.3.5.1.26), an enzyme which cleaves the N-acetyl-glucosamine-asparagine linkage of oligosaccharide chains in glycoprotein and glycopeptide metabolism, causes Aspartylglycosaminuria. Biochemical tests show high urinary levels of aspartylglucosamine
and low activity of aspartylglucosaminidase.
After trisomy 21 and fragile X syndrome
, this is the most frequent multiple congenital anomaly/mental retardation syndrome.
. Individuals with AGU also show increased upper respiratory infections. Development continues until about puberty, however, individuals at 13–16 years of age typically show mental and motor development similar to a 5-6 year old. Around puberty, a gradual decline in mental abilities and motor skills occurs. This progressive decline continues until about 25–28 years of age, when rapid impairment of abilities occurs, resulting in severe mental retardation.
Aspartylglucosaminidase
N--L-asparaginase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AGA gene.-Further reading:-External links:...
). This enzyme normally cleaves long sugar chains known as oligosaccharides in the lysosome. When N-aspartyl-beta-glucosaminidase is deficient these long sugar chains build up and eventually lead to the clinical features of AGU. AGU is one of seven identified Glycoprotein Storage Diseases.
Diagnosis
Clinical manifestations consist of psychomotor retardation, grotesque facial appearance, hepatosplenomegalyHepatosplenomegaly
Hepatosplenomegaly is the simultaneous enlargement of both the liver and the spleen . Hepatosplenomegaly can occur as the result of acute viral hepatitis or infectious mononucleosis, or it can be the sign of a serious and life threatening lysosomal storage disease...
, ventral hernia and skeletal abnormalities. It is a member of Finnish disease heritage, a group of diseases or syndromes caused by mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
in a single gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
characterized by higher frequency in Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
than the rest of the world.
Pathophysiology

Aspartylglucosamine
Aspartylglucosamine is a derivative of aspartic acid.Levels are elevated in aspartylglucosaminuria....
and low activity of aspartylglucosaminidase.
Epidemiology
Aspartylglycosaminuria is most common in patients of Finnish ancestry, affecting about 1 in 17,000 people in Finland.After trisomy 21 and fragile X syndrome
Fragile X syndrome
Fragile X syndrome , Martin–Bell syndrome, or Escalante's syndrome , is a genetic syndrome that is the most commonly known single-gene cause of autism and the most common inherited cause of intellectual disability...
, this is the most frequent multiple congenital anomaly/mental retardation syndrome.
Testing and Diagnosis
The diagnosis of AGU is made initially by demonstrating increased concentrations of oliogosaccharides, short chains of sugars, that accumulate in the urine. The diagnosis is then confirmed by measuring the activity of the enzyme aspartylglucosaminidase in the blood or in a skin biopsy. Mutations can be demonstrated in this gene and used to screen prenatally.Life Expectancy
Individuals with AGU typically have normal development in infancy. Around the age of 2–4 years, they begin showing signs of developmental delay, but development is still progressing. Initial symptoms may present as clumsiness and/or speech delaySpeech delay
Speech delay, also known as alalia, refers to a delay in the development or use of the mechanisms that produce speech. Speech, as distinct from language, refers to the actual process of making sounds, using such organs and structures as the lungs, vocal cords, mouth, tongue, teeth, etc...
. Individuals with AGU also show increased upper respiratory infections. Development continues until about puberty, however, individuals at 13–16 years of age typically show mental and motor development similar to a 5-6 year old. Around puberty, a gradual decline in mental abilities and motor skills occurs. This progressive decline continues until about 25–28 years of age, when rapid impairment of abilities occurs, resulting in severe mental retardation.

