.gif)
Ashmont (MBTA station)
Encyclopedia
Ashmont is located on the Red Line
in Dorchester, Massachusetts
. It opened on September 1, 1928, and is the subway
terminal for the Red Line's Dorchester Branch. Ashmont is also the terminus of the light rail
Ashmont–Mattapan High Speed Line, which loops around on an elevated viaduct. Towards the end of the Ashmont renovations, new signs were put in that now read ASHMONT/PEABODY SQ., but this change will not appear on any new maps or publications.
 The first Ashmont Station was a simple building along the original Shawmut Branch of the Old Colony Railroad
The first Ashmont Station was a simple building along the original Shawmut Branch of the Old Colony Railroad
, which opened in 1872. That was when steam locomotives powered the passenger trains that continued into Boston with a stop at Fields Corner
. The current intermediate Shawmut Station was not created as a train stop until the Shawmut Branch of the steam railroad was adapted to electrified subway service in the late 1920s and placed underground as it approached Ashmont Station.
When first built in 1928, no buses served the station; all lines ran streetcars. Specifically, the following Boston Elevated Railway
streetcar lines operated to Ashmont (using post-1942 numbers), unloading on the east side and loading on the two west tracks on the west side: Ruggles
via Talbot Avenue Ruggles via Washington Street, Dorchester Mattapan Station via River St.
Eastern Massachusetts Street Railway
cars to Brockton
also used the station.
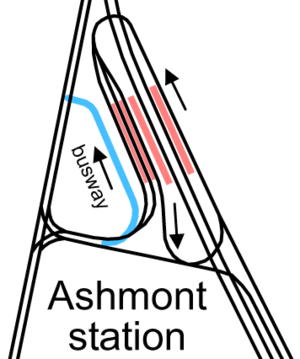
Two streetcar lines serving the area west of Ashmont were bustituted soon after opening, later becoming the and buses. They were rerouted to Ashmont for faster access to downtown. A new busway was built on the west side of the station in 1929; this has since been connected to the old streetcar ramps. The first section of the Mattapan High Speed Line (originally ) also opened in 1929, serving the easternmost track on the west side.
The Eastern Massachusetts Street Railway line converted to bus in 1932, using the busway. The was bustituted in 1933, and a new route serving the area east of the station was also added. Additionally the Eastern Mass started running buses over what are now the and routes.
The ramps were paved, and in 1949 the trolleybus
replaced the and lines.
service was interrupted for 18 months, but was restored in December 2007. The reconstruction was completed in 2009, while architectural work lasted until the summer of 2011. Highlights of the project included:
The station construction included of a first-of-its-kind transit oriented development (TOD) on the station site. The 116 units of mixed income housing represent the state, city, MBTA, community and a private developer's combined effort to provide housing adjacent to rapid transit, thereby reducing automobile usage.
In September 2011, a "HOLD" sign was installed on the trolley platform to allow an easier connection for those transferring from the Red Line.
-accessible for both the Red Line and the Ashmont-Mattapan trolley line. See MBTA accessibility
.
via Fields Corner - Forest Hills Sta.
via Morton St. - Ruggles Sta.
via Talbot Ave. - Ruggles Sta. via Washington St. - Mattapan Sta.
via River St. - Quincy Center Sta.
via W. Quincy - Avon Square or Holbrook/Randolph Commuter Rail Sta.
Other bus lines
Red Line (MBTA)
The Red Line is a rapid transit line operated by the MBTA running roughly north-south through Boston, Massachusetts into neighboring communities. The line begins west of Boston, in Cambridge, Massachusetts at Alewife station, near the intersection of Alewife Brook Parkway and Route 2...
in Dorchester, Massachusetts
Dorchester, Massachusetts
Dorchester is a dissolved municipality and current neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, United States. It is named after the town of Dorchester in the English county of Dorset, from which Puritans emigrated and is today endearingly nicknamed "Dot" by its residents. Dorchester, including a large...
. It opened on September 1, 1928, and is the subway
Rapid transit
A rapid transit, underground, subway, elevated railway, metro or metropolitan railway system is an electric passenger railway in an urban area with a high capacity and frequency, and grade separation from other traffic. Rapid transit systems are typically located either in underground tunnels or on...
terminal for the Red Line's Dorchester Branch. Ashmont is also the terminus of the light rail
Light rail
Light rail or light rail transit is a form of urban rail public transportation that generally has a lower capacity and lower speed than heavy rail and metro systems, but higher capacity and higher speed than traditional street-running tram systems...
Ashmont–Mattapan High Speed Line, which loops around on an elevated viaduct. Towards the end of the Ashmont renovations, new signs were put in that now read ASHMONT/PEABODY SQ., but this change will not appear on any new maps or publications.
History


Old Colony Railroad
The Old Colony Railroad was a major railroad system, mainly covering southeastern Massachusetts and parts of Rhode Island. It operated from 1845 to 1893. Old Colony trains ran from Boston to points such as Plymouth, Fall River, New Bedford, Newport, Providence, Fitchburg, Lowell and Cape Cod...
, which opened in 1872. That was when steam locomotives powered the passenger trains that continued into Boston with a stop at Fields Corner
Fields Corner (MBTA station)
Fields Corner is a station on the rapid transit Red Line at Fields Corner in Dorchester, Massachusetts. It opened on November 5, 1927, serving as the south end of the line for about a year...
. The current intermediate Shawmut Station was not created as a train stop until the Shawmut Branch of the steam railroad was adapted to electrified subway service in the late 1920s and placed underground as it approached Ashmont Station.
When first built in 1928, no buses served the station; all lines ran streetcars. Specifically, the following Boston Elevated Railway
Boston Elevated Railway
The Boston Elevated Railway was a precursor first to the Metropolitan Transit Authority in Massachusetts, now the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority, operating rapid transit, streetcars and buses in the Boston, Massachusetts area. It was formerly known as the West End Street Railway.The...
streetcar lines operated to Ashmont (using post-1942 numbers), unloading on the east side and loading on the two west tracks on the west side: Ruggles
Ruggles (MBTA station)
Ruggles Station is a MBTA subway station on the Orange Line; it is also a MBTA commuter rail station serving the Providence/Stoughton, Franklin, and Needham Lines. It is located at the intersection of Ruggles and Tremont Streets, where the Roxbury neighborhood begins and borders with the nearby...
via Talbot Avenue Ruggles via Washington Street, Dorchester Mattapan Station via River St.
Eastern Massachusetts Street Railway
Eastern Massachusetts Street Railway
The Eastern Massachusetts Street Railway was a streetcar and later bus company in eastern Massachusetts, serving most suburbs of Boston, Massachusetts...
cars to Brockton
Brockton, Massachusetts
Brockton is a city in Plymouth County, Massachusetts, United States; the population was 93,810 in the 2010 Census. Brockton, along with Plymouth, are the county seats of Plymouth County...
also used the station.
Two streetcar lines serving the area west of Ashmont were bustituted soon after opening, later becoming the and buses. They were rerouted to Ashmont for faster access to downtown. A new busway was built on the west side of the station in 1929; this has since been connected to the old streetcar ramps. The first section of the Mattapan High Speed Line (originally ) also opened in 1929, serving the easternmost track on the west side.
The Eastern Massachusetts Street Railway line converted to bus in 1932, using the busway. The was bustituted in 1933, and a new route serving the area east of the station was also added. Additionally the Eastern Mass started running buses over what are now the and routes.
The ramps were paved, and in 1949 the trolleybus
Trolleybus
A trolleybus is an electric bus that draws its electricity from overhead wires using spring-loaded trolley poles. Two wires and poles are required to complete the electrical circuit...
replaced the and lines.
Reconstruction
In 2005, the MBTA awarded a $35.2 million contract for the complete reconstruction of the 75-year-old Ashmont station. The station was razed by September 2007 and the station was completely rebuilt. TrolleyTram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
service was interrupted for 18 months, but was restored in December 2007. The reconstruction was completed in 2009, while architectural work lasted until the summer of 2011. Highlights of the project included:
- New platforms and an elevated viaduct for the Ashmont-Mattapan High Speed LineAshmont-Mattapan High Speed LineThe Ashmont–Mattapan High Speed Line or also known as the "M-Line" in Boston and Milton, Massachusetts is considered to be part of the MBTA's Red Line, even though it uses different equipment and passengers have to change at Ashmont. The only MBTA line to run through a cemetery, the line opened on...
- Two new lobbies with access at the station
- An elevated busway that is level with the new lobbies
- Public access over the subway tunnel to Peabody Square
- Three new elevators and two new escalators
- CCTV security cameras and significantly enhanced lighting
- Charlie Card automated fare vending machines and fare gates
The station construction included of a first-of-its-kind transit oriented development (TOD) on the station site. The 116 units of mixed income housing represent the state, city, MBTA, community and a private developer's combined effort to provide housing adjacent to rapid transit, thereby reducing automobile usage.
In September 2011, a "HOLD" sign was installed on the trolley platform to allow an easier connection for those transferring from the Red Line.
Accessibility
After the reconstruction, the station is wheelchairWheelchair
A wheelchair is a chair with wheels, designed to be a replacement for walking. The device comes in variations where it is propelled by motors or by the seated occupant turning the rear wheels by hand. Often there are handles behind the seat for someone else to do the pushing...
-accessible for both the Red Line and the Ashmont-Mattapan trolley line. See MBTA accessibility
MBTA accessibility
Physical accessibility on the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority system is incomplete but improving, with accessibility on all buses , all Orange Line stations, all but 2 Red Line stations, and all but 2 Blue Line stations...
.
Bus connections
MBTA bus lines - Andrew Sta.Andrew (MBTA station)
Andrew is a station on the rapid transit Red Line at Dorchester Avenue at Andrew Square, by Southampton Street, Dorchester Street, and Boston Street in South Boston, Massachusetts...
via Fields Corner - Forest Hills Sta.
Forest Hills (MBTA station)
Forest Hills Station is a station on the MBTA Orange Line, located in Forest Hills in the southern part of the Jamaica Plain neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts at the intersections of Washington Street, Hyde Park Avenue, South Street, The Arborway and Morton Street.Forest Hills is the southern...
via Morton St. - Ruggles Sta.
Ruggles (MBTA station)
Ruggles Station is a MBTA subway station on the Orange Line; it is also a MBTA commuter rail station serving the Providence/Stoughton, Franklin, and Needham Lines. It is located at the intersection of Ruggles and Tremont Streets, where the Roxbury neighborhood begins and borders with the nearby...
via Talbot Ave. - Ruggles Sta. via Washington St. - Mattapan Sta.
Mattapan (MBTA station)
Mattapan or Mattapan Sq. is the southern terminus of the Ashmont-Mattapan High Speed Line in Boston, Massachusetts. It is in the Mattapan neighborhood of Boston. The station is a major transfer facility, served by several bus lines.- Reconstruction :...
via River St. - Quincy Center Sta.
Quincy Center (MBTA station)
Quincy Center is a station on the Red Line subway at 1300 Hancock Street and Washington Street, serving the Quincy Center area of Quincy, Massachusetts. Its other facilities include nearby stops on the MBTA Commuter Rail, Old Colony Lines, and bus connections at street level.-History:Quincy Center...
via W. Quincy - Avon Square or Holbrook/Randolph Commuter Rail Sta.
Holbrook/Randolph (MBTA station)
Holbrook/Randolph Station is a rail station on the MBTA Commuter Rail system in Randolph, Massachusetts. The station is located at the corner of Union and Center Streets near the Holbrook town line. Service to the station is provided by the Middleborough/Lakeville Line from Boston to Brockton,...
Other bus lines
- BAT12 - BrocktonBrockton, MassachusettsBrockton is a city in Plymouth County, Massachusetts, United States; the population was 93,810 in the 2010 Census. Brockton, along with Plymouth, are the county seats of Plymouth County...
(operated by Brockton Area TransitBrockton Area Transit AuthorityBrockton Area Transit Authority is a public, non-profit organization in Massachusetts, charged with providing public transportation to the Brockton area, consisting of the city of Brockton and the adjoining towns of Abington, Avon, Bridgewater, East Bridgewater, Easton, Stoughton, Canton, West...
)

