
Armanen runes
Encyclopedia
The Armanen runes, or Armanen 'Futharkh' as Guido von List
referred to them, are a row of 18 runes that are closely based in shape (though not necessarily name, let alone interpretation) on the Younger Futhark
. They were "revealed to" the Austria
n occult
mysticist and Germanic revivalist Guido von List
in 1902, and subsequently published by him.
operation on both eyes in 1902. This vision in 1902 allegedly opened what List referred to as his "inner eye", via which the "Secret of the Runes" was revealed to him. List stated that his Armanen Futharkh were encrypted in the Rúnatal of the Poetic Edda
(stanzas 138 to 165 of the Hávamál
), with stanzas 147 through 165, where Odin enumerates eighteen wisdoms (with 164 being an interpolation), interpreted as being the "song of the 18 runes". List and many of his followers believed his runes to represent the "primal runes" upon which all historical rune rows were based.
List's row is based on the Younger Futhark, with the names and sound values mostly close to the Anglo-Saxon
Futhorc. The two final runes, Eh and Gibor, added to the Younger Futhark inventory, are taken from Anglo-Saxon Eoh and Gyfu. Apart from the two additional runes, and a displacement of the Man rune from 13th to 15th place, the sequence is identical to that of the Younger Futhark.
List noted in his book, The Secret of the Runes, that the "runic futharkh (= runic ABC) consisted of sixteen symbols in ancient times.".
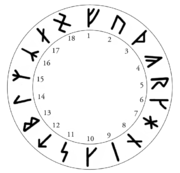 The first sixteen of von List's runes correspond to the sixteen Younger Futhark
The first sixteen of von List's runes correspond to the sixteen Younger Futhark
runes, with slight modifications in names (and partly mirrored shapes). The two additional runes are loosely inspired by the Anglo-Saxon Futhorc.
.
After World War II
, Karl Spiesberger
reformed the system, removing the racist aspects of the Listian
, Marbyan
and Kummerian
rune work and placing the whole system in a "pansophical", or eclectic
, context. In recent times Karl Hans Welz, Stephen E. Flowers, Adolf Schleipfer, Larry E. Camp and Victor Ordell L. Kasen have all furthered the effort to remove any racist connotations previously espoused by pre-war Armanen rune masters.
In German-speaking countries, the Armanen Runes have been influential among rune-occultists. According to Stephen E. Flowers they are better known even than the historical Elder Futhark
:
The Armanen runes are also having a significant impact in English language occultist literature.
Guido von List
Guido Karl Anton List, better known as Guido von List was an Austrian/German poet, journalist, writer, businessman and dealer of leather goods, mountaineer, hiker, dramatist, playwright, and rower, but was most notable as an occultist and völkisch author who is seen as one of the most important...
referred to them, are a row of 18 runes that are closely based in shape (though not necessarily name, let alone interpretation) on the Younger Futhark
Younger Futhark
The Younger Futhark, also called Scandinavian runes, is a runic alphabet, a reduced form of the Elder Futhark, consisting of only 16 characters, in use from ca. 800 CE...
. They were "revealed to" the Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
n occult
Occult
The word occult comes from the Latin word occultus , referring to "knowledge of the hidden". In the medical sense it is used to refer to a structure or process that is hidden, e.g...
mysticist and Germanic revivalist Guido von List
Guido von List
Guido Karl Anton List, better known as Guido von List was an Austrian/German poet, journalist, writer, businessman and dealer of leather goods, mountaineer, hiker, dramatist, playwright, and rower, but was most notable as an occultist and völkisch author who is seen as one of the most important...
in 1902, and subsequently published by him.
History and Runic revivalism
The row of 18 "Armanen runes", also known as the "Armanen futharkh" came to List while in an 11 month state of temporary blindness after a cataractCataract
A cataract is a clouding that develops in the crystalline lens of the eye or in its envelope, varying in degree from slight to complete opacity and obstructing the passage of light...
operation on both eyes in 1902. This vision in 1902 allegedly opened what List referred to as his "inner eye", via which the "Secret of the Runes" was revealed to him. List stated that his Armanen Futharkh were encrypted in the Rúnatal of the Poetic Edda
Poetic Edda
The Poetic Edda is a collection of Old Norse poems primarily preserved in the Icelandic mediaeval manuscript Codex Regius. Along with Snorri Sturluson's Prose Edda, the Poetic Edda is the most important extant source on Norse mythology and Germanic heroic legends, and from the early 19th century...
(stanzas 138 to 165 of the Hávamál
Hávamál
Hávamál is presented as a single poem in the Poetic Edda, a collection of Old Norse poems from the Viking age. The poem, itself a combination of different poems, is largely gnomic, presenting advice for living, proper conduct and wisdom....
), with stanzas 147 through 165, where Odin enumerates eighteen wisdoms (with 164 being an interpolation), interpreted as being the "song of the 18 runes". List and many of his followers believed his runes to represent the "primal runes" upon which all historical rune rows were based.
List's row is based on the Younger Futhark, with the names and sound values mostly close to the Anglo-Saxon
Old English language
Old English or Anglo-Saxon is an early form of the English language that was spoken and written by the Anglo-Saxons and their descendants in parts of what are now England and southeastern Scotland between at least the mid-5th century and the mid-12th century...
Futhorc. The two final runes, Eh and Gibor, added to the Younger Futhark inventory, are taken from Anglo-Saxon Eoh and Gyfu. Apart from the two additional runes, and a displacement of the Man rune from 13th to 15th place, the sequence is identical to that of the Younger Futhark.
List noted in his book, The Secret of the Runes, that the "runic futharkh (= runic ABC) consisted of sixteen symbols in ancient times.".
List of runes

Younger Futhark
The Younger Futhark, also called Scandinavian runes, is a runic alphabet, a reduced form of the Elder Futhark, consisting of only 16 characters, in use from ca. 800 CE...
runes, with slight modifications in names (and partly mirrored shapes). The two additional runes are loosely inspired by the Anglo-Saxon Futhorc.
- Fa (an inverted FeFe (rune)The Fe rune represents the f-sound in the Younger Futhark and Futhorc alphabets. Its name means " wealth", cognate to English fee with the original meaning of "sheep" or "cattle" .The rune derives from the unattested but reconstructed Proto-Germanic...
) - UrUr (rune)The reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the Elder Futhark u rune is *Ūruz meaning "wild ox" or *Ûram "water". It may have been derived from the Raetic alphabet character u as it is similar in both shape and sound value...
- Thurs (as Anglo-Saxon Thorn) (also known as 'Dorn')
- Os (a mirrored Younger Futhark Os)
- Rit (as Reidh)
- KaKaunanThe k-rune is called Kaun in both the Norwegian and Icelandic rune poems, meaning "ulcer". The reconstructed Proto-Germanic name is *Kaunan. It is also known as Kenaz , based on its Anglo-Saxon name.The Elder Futhark shape is likely directly based on Old Italic c / Latin C...
(as in Younger Futhark) - HagalHagal (Armanen rune)Hagal is the 7th rune of Armanen Futharkh of Guido von List, derived from the Younger Futhark Hagal rune .Hagal is the "mother rune" of the Armanen system and also seen as such by List's contemporaries Jörg Lanz von Liebenfels, Adolf Schleipfer, Peryt Shou, Siegfried Adolf Kummer, Rudolf John...
(as Younger Futhark Hagall) - Nauth (as Younger Futhark Naud) (also known as Not)
- IsIsaz*Isaz is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the i-rune , meaning "ice". In the Younger Futhark it is called Iss in Icelandic and isa in Old Norse. As rune of the Anglo-Saxon futhorc, it is called is....
(as in Younger Futhark) - Ar (similar to short-twig Younger Futhark)
- SigSig RuneSig is the name given by Guido von List for the Sigel or s rune of the Armanen Futharkh, and is also used by Karl Maria Wiligut for his runes.-Nazism:...
(as Anglo-Saxon SigelSigelSigel may refer to:* Siȝel, the Old English for "Sun", see Sól ** the Old English name of the s-rune, see Sowilo rune-Surname:*Franz Sigel , Union general in the American Civil War...
) - TyrTiwaz runeThe t-rune is named after Týr, and was identified with this god. The reconstructed Proto-Germanic name is *Tîwaz or *Teiwaz.-Rune poems:Tiwaz is mentioned in all three rune poems...
- Bar (as Younger Futhark Bjarkan)
- Laf (as Younger Futhark Logr)
- Man (as Younger Futhark Madr)
- Yr (as in Younger Futhark, but with a sound value [i])
- Eh (the name is from Anglo-Saxon Futhork, the shape like Younger Futhark Ar)
- GiborGiborGibor is one of the Armanen runes devised by Guido von List in 1902 .There is no historical Gibor rune . Its shape is similar to that of the Wolfsangel symbol.List associated his Gibor rune with the final stanza of the Rúnatal Gibor is one of the Armanen runes devised by Guido von List in 1902...
(the name similar to Anglo-Saxon Futhork GyfuGyfuGyfu is the name for the g-rune in the Anglo-Saxon rune poem, meaning "gift" or "generosity":The corresponding letter of the Gothic alphabet is g, called giba. The same rune also appears in the Elder Futhark, with a suggested Proto-Germanic name *gebô "gift". J. H...
)
Contemporary use
The Armanen runes are still used today in occultist and national socialist currents of Germanic neopaganismGermanic neopaganism
Germanic neopaganism is the contemporary revival of historical Germanic paganism. Precursor movements appeared in the early 20th century in Germany and Austria. A second wave of revival began in the early 1970s...
.
After World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, Karl Spiesberger
Karl Spiesberger
Karl Spiesberger was a German mystic, occultist, Germanic revivalist and Runosophist. He is most well known for his revivalism and usage of the Sidereal Pendulum for divination and dowsing and for his anti-racialist stance and revivalist usage of the Armanen Futharkh runic system after the second...
reformed the system, removing the racist aspects of the Listian
Guido von List
Guido Karl Anton List, better known as Guido von List was an Austrian/German poet, journalist, writer, businessman and dealer of leather goods, mountaineer, hiker, dramatist, playwright, and rower, but was most notable as an occultist and völkisch author who is seen as one of the most important...
, Marbyan
Friedrich Bernhard Marby
Friedrich Bernhard Marby was a German rune occultist and Germanic revivalist. He is abest known for his revivalism and use of the Armanen runes row. He was imprisoned during the Third Reich, which may have been due to a denunciation by Karl Maria Wiligut...
and Kummerian
Siegfried Adolf Kummer
Siegfried Adolf Kummer was a German mystic and Germanic revivalist. He is also most well known for his revivalism and use of the Armanen runes row...
rune work and placing the whole system in a "pansophical", or eclectic
Eclecticism
Eclecticism is a conceptual approach that does not hold rigidly to a single paradigm or set of assumptions, but instead draws upon multiple theories, styles, or ideas to gain complementary insights into a subject, or applies different theories in particular cases.It can sometimes seem inelegant or...
, context. In recent times Karl Hans Welz, Stephen E. Flowers, Adolf Schleipfer, Larry E. Camp and Victor Ordell L. Kasen have all furthered the effort to remove any racist connotations previously espoused by pre-war Armanen rune masters.
In German-speaking countries, the Armanen Runes have been influential among rune-occultists. According to Stephen E. Flowers they are better known even than the historical Elder Futhark
Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark is the oldest form of the runic alphabet, used by Germanic tribes for Northwest Germanic and Migration period Germanic dialects of the 2nd to 8th centuries for inscriptions on artifacts such as jewellery, amulets, tools, weapons and runestones...
:
"The personal force of List and that of his extensive and influential Armanen Orden was able to shape the runic theories of German magicians...from that time to the present day. [...] the Armanen system of runes...by 1955 had become almost 'traditional' in German circles"
The Armanen runes are also having a significant impact in English language occultist literature.
See also
- Rudolf John GorslebenRudolf John GorslebenRudolf John Gorsleben was a German Ariosophist, Armanist , journal editor and playwright.-Life:...
- Siegfried Adolf KummerSiegfried Adolf KummerSiegfried Adolf Kummer was a German mystic and Germanic revivalist. He is also most well known for his revivalism and use of the Armanen runes row...
- Jörg Lanz von Liebenfels
- Runic divination
- Peryt ShouPeryt ShouPeryt Shou was a German mysticist and Germanic pagan revivalist. He is mentioned briefly by Goodrick-Clarke as a writer of novels with occult themes and a significant figure in the post-World War I German occult movement...
- Karl Maria WiligutKarl Maria WiligutKarl Maria Wiligut was an Austrian Ariosophist- Biography :...
- Wiligut runesWiligut runesThe Wiligut runes are a runic row developed by Karl Maria Wiligut in 1934. Wiligut rejected Guido von List's Armanen runes and his overall philosophy.Wiligut claimed to have been initiated into "runic lore" by his grandfather Karl Wiligut ....
External links
- Armanen runes by S. Hawkins
- Armanen runes truetype font

