
Appliance classes
Encyclopedia
In the electrical appliance manufacturing industry, the following IEC protection classes are used to differentiate between the protective-earth
connection requirements of devices.
 These appliances have no protective-earth connection and feature only a single level of insulation and were intended for use in dry areas. A single fault could cause an electric shock
These appliances have no protective-earth connection and feature only a single level of insulation and were intended for use in dry areas. A single fault could cause an electric shock
or other dangerous occurrence. Sales of these items have been banned in the UK since 1975.
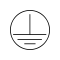 These appliances must have their chassis connected to electrical earth
These appliances must have their chassis connected to electrical earth
(US: ground) by an earth conductor (coloured
green/yellow in most countries, green in the U.S., Canada and Japan). A fault in the appliance which causes a live conductor to contact the casing will cause a current to flow in the earth conductor. This current should trip either an overcurrent device (fuse
or circuit breaker
(CB)) or a residual-current device
(RCD) also named as residual current circuit breaker (RCCB), or (ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI)) or also, residual current operated circuit-breaker with integral overcurrent protection (RCBO). which will cut off the supply of electricity to the appliance.

A Class II or double insulated electrical appliance is one which has been designed in such a way that it does not require a safety connection to electrical earth
(US: ground).
The basic requirement is that no single failure can result in dangerous voltage
becoming exposed so that it might cause an electric shock
and that this is achieved without relying on an earthed metal casing. This is usually achieved at least in part by having two layers of insulating
material surrounding live parts or by using reinforced insulation.
In Europe
, a double insulated appliance must be labelled Class II, double insulated, or bear the double insulation symbol (a square inside another square)..
 A Class III appliance is designed to be supplied from a separated/safety extra-low voltage (SELV) power source. The voltage from a SELV supply is low enough that under normal conditions a person can safely come into contact with it without risk of electrical shock. The extra safety features built into Class I and Class II appliances are therefore not required. For medical devices compliance with Class III is not considered sufficient protection.
A Class III appliance is designed to be supplied from a separated/safety extra-low voltage (SELV) power source. The voltage from a SELV supply is low enough that under normal conditions a person can safely come into contact with it without risk of electrical shock. The extra safety features built into Class I and Class II appliances are therefore not required. For medical devices compliance with Class III is not considered sufficient protection.
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be the reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured, or a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth....
connection requirements of devices.
Class 0

Electric shock
Electric Shock of a body with any source of electricity that causes a sufficient current through the skin, muscles or hair. Typically, the expression is used to denote an unwanted exposure to electricity, hence the effects are considered undesirable....
or other dangerous occurrence. Sales of these items have been banned in the UK since 1975.
Class 01
As Class 0 but appliance has an earth terminal which is unused since two core cable is used.Class I

Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be the reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured, or a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth....
(US: ground) by an earth conductor (coloured
IEC 60446
International standard IEC 60446 defines basic safety principles for identifying electrical conductors by colours or numerals, for example in electricity distribution wiring.-Permitted colours:...
green/yellow in most countries, green in the U.S., Canada and Japan). A fault in the appliance which causes a live conductor to contact the casing will cause a current to flow in the earth conductor. This current should trip either an overcurrent device (fuse
Fuse (electrical)
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is a type of low resistance resistor that acts as a sacrificial device to provide overcurrent protection, of either the load or source circuit...
or circuit breaker
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
(CB)) or a residual-current device
Residual-current device
A Residual Current Device is a generic term covering both RCCBs and RCBOs.A Residual-Current Circuit Breaker is an electrical wiring device that disconnects a circuit whenever it detects that the electric current is not balanced between the energized conductor and the return neutral conductor...
(RCD) also named as residual current circuit breaker (RCCB), or (ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI)) or also, residual current operated circuit-breaker with integral overcurrent protection (RCBO). which will cut off the supply of electricity to the appliance.
Class II

A Class II or double insulated electrical appliance is one which has been designed in such a way that it does not require a safety connection to electrical earth
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be the reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured, or a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth....
(US: ground).
The basic requirement is that no single failure can result in dangerous voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
becoming exposed so that it might cause an electric shock
Electric shock
Electric Shock of a body with any source of electricity that causes a sufficient current through the skin, muscles or hair. Typically, the expression is used to denote an unwanted exposure to electricity, hence the effects are considered undesirable....
and that this is achieved without relying on an earthed metal casing. This is usually achieved at least in part by having two layers of insulating
Electrical insulation
thumb|250px|[[Coaxial Cable]] with dielectric insulator supporting a central coreThis article refers to electrical insulation. For insulation of heat, see Thermal insulation...
material surrounding live parts or by using reinforced insulation.
In Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, a double insulated appliance must be labelled Class II, double insulated, or bear the double insulation symbol (a square inside another square)..
Class III

See also
- Mains power plug
- ElectricityElectricityElectricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
- Portable Appliance Test
- Test and taggingTest and taggingTest and tagging is a generic name given to the process of visually inspecting and electrically testing in-service electrical equipment for personal use and/or safety...

