.gif)
Antiparallel (mathematics)
Encyclopedia
Definitions
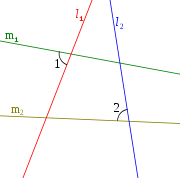
Given two lines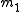 and
and 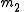 , lines
, lines 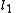 and
and 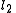 are anti-parallel with respect to
are anti-parallel with respect to 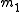 and
and 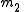 if
if 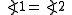 .
.
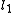 and
and 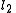 and are anti-parallel with respect to
and are anti-parallel with respect to 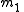 and
and 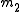 , then
, then 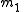 and
and 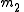 and are also anti-parallel with respect to
and are also anti-parallel with respect to 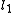 and
and 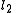 .
.In any quadrilateral
Quadrilateral
In Euclidean plane geometry, a quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides and four vertices or corners. Sometimes, the term quadrangle is used, by analogy with triangle, and sometimes tetragon for consistency with pentagon , hexagon and so on...
inscribed in a circle, any two opposite sides are anti-parallel with respect to the other two sides.
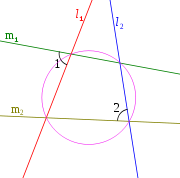
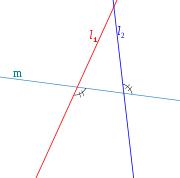
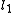 and
and 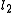 are said to be antiparallel with respect to the sides of an angle if they make the same angle
are said to be antiparallel with respect to the sides of an angle if they make the same angle 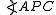 in the opposite senses with the bisector of that angle.
in the opposite senses with the bisector of that angle.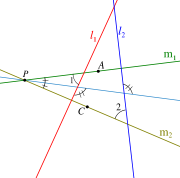
Antiparallel vectors
In a vector spaceVector space
A vector space is a mathematical structure formed by a collection of vectors: objects that may be added together and multiplied by numbers, called scalars in this context. Scalars are often taken to be real numbers, but one may also consider vector spaces with scalar multiplication by complex...
over
 (or some other ordered field
(or some other ordered fieldOrdered field
In mathematics, an ordered field is a field together with a total ordering of its elements that is compatible with the field operations. Historically, the axiomatization of an ordered field was abstracted gradually from the real numbers, by mathematicians including David Hilbert, Otto Hölder and...
),
two nonzero vectors are called antiparallel if they are parallel but have opposite directions.
In that case, one is a negative scalar
Scalar (mathematics)
In linear algebra, real numbers are called scalars and relate to vectors in a vector space through the operation of scalar multiplication, in which a vector can be multiplied by a number to produce another vector....
times the other.
Relations
- The line joining the feet to two altitudes of a triangle is antiparallel to the third side.
- The tangent to a triangle's circumcircle at a vertex is antiparallel to the opposite side.
- The radius of the circumcircle at a vertex is perpendicular to all lines antiparallel to the opposite sides.

