
Anthocyanidin
Encyclopedia

- Not to be confused with anthocyaninAnthocyaninAnthocyanins are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that may appear red, purple, or blue according to pH...
s, their sugar-containing counterparts.
Anthocyanidins are common plant pigments. They are the sugar-free counterparts of anthocyanin
Anthocyanin
Anthocyanins are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that may appear red, purple, or blue according to pH...
s based on the flavylium ion or 2-phenylchromenylium, which is a type of oxonium ion
Oxonium ion
The oxonium ion in chemistry is any oxygen cation with three bonds. The simplest oxonium ion is the hydronium ion H3O+. Another oxonium ion frequently encountered in organic chemistry is obtained by protonation or alkylation of a carbonyl group e.g...
(chromenylium is referred also to as benzopyrylium). They form a large group of polymethine dye. In particular anthocyanidins are salt derivatives of the 2-phenylchromenylium cation, also known as flavylium cation. As shown in the figure below, the phenyl group at the 2-position can carry different substituent
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
s. The counterion
Counterion
A counterion is the ion that accompanies an ionic species in order to maintain electric neutrality. In table salt the sodium cation is the counterion for the chlorine anion and vice versa.In a charged transition metal complex, a simple A counterion is the ion that accompanies an ionic species in...
of the flavylium cation is mostly chloride
Chloride
The chloride ion is formed when the element chlorine, a halogen, picks up one electron to form an anion Cl−. The salts of hydrochloric acid HCl contain chloride ions and can also be called chlorides. The chloride ion, and its salts such as sodium chloride, are very soluble in water...
. With this positive charge, the anthocyanidins differ from other flavonoids.
pH
The stability of anthocyanidins is dependant on pHPH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
. At a low pH (acidic conditions), colored anthocyanidins are present, whereas at a higher pH (basic conditions) the colorless chalcones forms are present.
Classification
3-Deoxyanthocyanidin3-Deoxyanthocyanidin
The 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins and their glycosides are molecules with an anthocyanidins backbone lacking an hydroxyl group on carbon 3....
s are a class of anthocyanidins lacking an hydroxyl group on carbon 3.
| Anthocyanidin | Basic structure | R3' | R4' | R5' | R3 | R5 | R6 | R7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aurantinidin Aurantinidin Aurantinidin is a water soluble, red plant dye. It is a member of the class of compounds known as anthocyanidins and is a hydroxy derivative of pelargonidin. Aurantinidin has been reported to occur in Impatients aurantiaca , and also in cultivars from genus Alstroemeria.... |
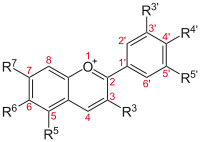 |
−H | −OH | −H | −OH | −OH | −OH | −OH |
| Cyanidin Cyanidin Cyanidin is a natural organic compound. It is a particular type of anthocyanidin . It is a pigment found in many red berries including but not limited to grapes, bilberry, blackberry, blueberry, cherry, cranberry, elderberry, hawthorn, loganberry, acai berry and raspberry... |
−OH | −OH | −H | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Delphinidin Delphinidin Delphinidin is an anthocyanidin, a primary plant pigment, and also an antioxidant. Delphinidin gives blue hues to flowers like violas and delphiniums... |
−OH | −OH | −OH | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Europinidin Europinidin Europinidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin. It is a water soluble, bluish red plant dye. It is a rare O-methylated flavonoid, a derivative of delphinidin. It can be found in species of Plumbago and Ceratostigma.-External links:* *... |
−OCH3 | −OH | −OH | −OH | −OCH3 | −H | −OH | |
| Luteolinidin Luteolinidin Luteolinidin is a chemical compound belonging to the 3-deoxyanthocyanidins and that can be found in Sorghum bicolor.-Glycosides:Luteolinidin 5-O-β-D-[3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-2-O-acetylglucopyranoside] Luteolinidin is a chemical compound belonging to the 3-deoxyanthocyanidins and that can be found in... |
−OH | −OH | −H | −H | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Pelargonidin Pelargonidin Pelargonidin is an anthocyanidin, a type of plant pigment. Like all anthocyanins, it is an antioxidant. It produces a characteristic orange color, and can be found in red geraniums, and ripe raspberries and strawberries, as well as blueberries, blackberries, plums and cranberries and pomegranates.... |
−H | −OH | −H | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Malvidin Malvidin Malvidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin. As a primary plant pigment, its glycosides are highly abundant in nature. It is responsible primarily for the color of red wine, Vitis vinifera being one of its sources... |
−OCH3 | −OH | −OCH3 | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Peonidin Peonidin Peonidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin, and a primary plant pigment. Peonidin gives purplish-red hues to flowers such as the peony, from which it takes its name, and roses. It is also present in some blue flowers, such as the morning glory.... |
−OCH3 | −OH | −H | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Petunidin Petunidin Petunidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin. It is a natural organic compound and a particular type of anthocyanidin. It is a dark-red or purple water-soluble pigment found in many redberries including chokeberries , Saskatoon berries or different species of grape , and... |
−OH | −OH | −OCH3 | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Rosinidin Rosinidin Rosinidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin. It is a pigment found in the flowers of Catharanthus roseus and, in lower concentration, in Primula rosea.... |
−OCH3 | −OH | −H | −OH | −OH | −H | −OCH3 |

