
Antenna efficiency
Encyclopedia
In electromagnetics, antenna efficiency or radiation efficiency is a figure of merit
for an antenna
. It measures the electrical losses that occur throughout the antenna while it is operating at a given frequency
, or averaged over its operation across a frequency band. It is expressed as a percentage, where 100% (or 1.0) is perfectly lossless and 0% (or 0.0) is perfectly lossy.
An antenna's efficiency is a component of its gain
; the other component is its directivity
.
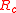 ), ground losses (
), ground losses (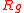 ), and other losses (
), and other losses (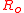 ) including ohmic and capacitive losses. The antenna's total resistance (
) including ohmic and capacitive losses. The antenna's total resistance (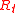 ) is the sum of these losses plus the radiation resistance (
) is the sum of these losses plus the radiation resistance ( ), which is the effective resistance representing emitted RF power:
), which is the effective resistance representing emitted RF power:

Antenna efficiency is the ratio between its radiation resistance and its total resistance:
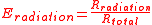
Antenna efficiency can also be expressed as the ratio between its input power and its radiated power:
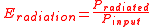
...again yielding a value between 0.0 and 1.0.
in the antenna's inductive coil(s). An ideal coil creates inductance
without also creating resistance; while a superconducting coil might someday achieve this, actual coils built from ordinary conductors do not. Coils are assessed a quality factor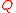 that expresses how much inductance they create versus how much resistance they impose:
that expresses how much inductance they create versus how much resistance they impose:
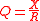
...where is the inductive reactance in ohms and
is the inductive reactance in ohms and  is the ohmic resistance in ohms.
is the ohmic resistance in ohms.
Laboratory coils may achieve a Q of 1000, but economic and geometric constraints keep typical antenna coils down to as little as 200. As well, the long slender coils chosen for lower wind resistance tend to have a lower Q than short fat coils.
and other ground-plane antennas, ground loss occurs due to ohmic resistance
in the antenna's connection to its ground plane/counterpoise, including its mast or stalk and its bonding connections, as well as the ohmic resistance within the ground plane.
in the conductors of the antenna's driven elements, and is usually small.
Capacitive loss is the loss into the stray capacitances between the antenna and any nearby conductive structures. Stray capacitance causes a loss because capacitor
s absorb part of the current and store it as an electric field
between their conductors. Capacitance forms between any two conductors separated by an insulator; in this case, one conductor is the antenna's driven element, the other conductor is a nearby conductive structure (a body panel, a water pipe, electrical wiring, etc.), and the insulator is the air between them. Although the resulting capacitance is very small (typically picofarads), it impacts antenna performance in direct proportion to frequency.

...where all variables are unitless values between 0.0 (100% loss) and 1.0 (0% loss).
variables are unitless values between 0.0 (100% loss) and 1.0 (0% loss).
Figure of merit
A figure of merit is a quantity used to characterize the performance of a device, system or method, relative to its alternatives. In engineering, figures of merit are often defined for particular materials or devices in order to determine their relative utility for an application...
for an antenna
Antenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
. It measures the electrical losses that occur throughout the antenna while it is operating at a given frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, or averaged over its operation across a frequency band. It is expressed as a percentage, where 100% (or 1.0) is perfectly lossless and 0% (or 0.0) is perfectly lossy.
An antenna's efficiency is a component of its gain
Antenna gain
In electromagnetics, an antenna's power gain or simply gain is a key performance figure which combines the antenna's directivity and electrical efficiency. As a transmitting antenna, the figure describes how well the antenna converts input power into radio waves headed in a specified direction...
; the other component is its directivity
Directivity
In electromagnetics, directivity is a figure of merit for an antenna. It measures the power density the antenna radiates in the direction of its strongest emission, versus the power density radiated by an ideal isotropic radiator radiating the same total power.An antenna's directivity is a...
.
Components of efficiency
Antenna efficiency depends on three kinds of loss: coil losses (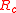 ), ground losses (
), ground losses (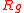 ), and other losses (
), and other losses (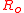 ) including ohmic and capacitive losses. The antenna's total resistance (
) including ohmic and capacitive losses. The antenna's total resistance (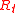 ) is the sum of these losses plus the radiation resistance (
) is the sum of these losses plus the radiation resistance ( ), which is the effective resistance representing emitted RF power:
), which is the effective resistance representing emitted RF power:
Antenna efficiency is the ratio between its radiation resistance and its total resistance:
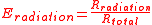
Antenna efficiency can also be expressed as the ratio between its input power and its radiated power:
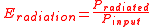
...again yielding a value between 0.0 and 1.0.
Coil loss
Coil loss is the loss due to ohmic resistanceElectrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
in the antenna's inductive coil(s). An ideal coil creates inductance
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
without also creating resistance; while a superconducting coil might someday achieve this, actual coils built from ordinary conductors do not. Coils are assessed a quality factor
 that expresses how much inductance they create versus how much resistance they impose:
that expresses how much inductance they create versus how much resistance they impose: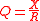
...where
 is the inductive reactance in ohms and
is the inductive reactance in ohms and  is the ohmic resistance in ohms.
is the ohmic resistance in ohms.Laboratory coils may achieve a Q of 1000, but economic and geometric constraints keep typical antenna coils down to as little as 200. As well, the long slender coils chosen for lower wind resistance tend to have a lower Q than short fat coils.
Ground loss
For monopoleMonopole antenna
A monopole antenna is a class of radio antenna consisting of a straight rod-shaped conductor, often mounted perpendicularly over some type of conductive surface, called a ground plane. The driving signal from the transmitter is applied, or for receiving antennas the output voltage is taken,...
and other ground-plane antennas, ground loss occurs due to ohmic resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
in the antenna's connection to its ground plane/counterpoise, including its mast or stalk and its bonding connections, as well as the ohmic resistance within the ground plane.
Ohmic and capacitive loss
Ohmic loss is the loss due to ohmic resistanceElectrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
in the conductors of the antenna's driven elements, and is usually small.
Capacitive loss is the loss into the stray capacitances between the antenna and any nearby conductive structures. Stray capacitance causes a loss because capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
s absorb part of the current and store it as an electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
between their conductors. Capacitance forms between any two conductors separated by an insulator; in this case, one conductor is the antenna's driven element, the other conductor is a nearby conductive structure (a body panel, a water pipe, electrical wiring, etc.), and the insulator is the air between them. Although the resulting capacitance is very small (typically picofarads), it impacts antenna performance in direct proportion to frequency.
Total efficiency
Total efficiency differs from antenna efficiency by including reflection efficiency, which expresses the percentage of power lost due to any impedance mismatch between the antenna and its feedline:
...where all
 variables are unitless values between 0.0 (100% loss) and 1.0 (0% loss).
variables are unitless values between 0.0 (100% loss) and 1.0 (0% loss).

