
Anonymous internet banking
Encyclopedia
Anonymous Internet banking is the proposed use of strong financial cryptography
to make electronic bank secrecy
(or more precisely pseudonymous
banking) possible. The bank issues currency in the form of electronic tokens that can be converted on presentation to the bank to some other currency. This concept has a long history in which free banking
institutions have issued their own paper currency often backed by a physical commodity.
algorithms. In this simple example we have Alice and Bob
and a banker. The banker generates an RSA public key with modulus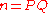 , where
, where 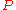 and
and  are large primes
are large primes
, making a semiprime
a semiprime
. As described in RSA operation, the bank also generates public key exponent and private key exponent
and private key exponent 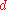 .
.
Bob asks the banker for a $100 deposit slip in anticipation of Alice wanting to transfer money to him. To generate a deposit slip the bank selects a large, globally unique random number
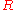 and encrypts it using the bank's public key; this means that it can only be decrypted with the bank's secret key:
and encrypts it using the bank's public key; this means that it can only be decrypted with the bank's secret key:
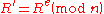
This encrypted value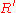 is sent to Bob with the promise to deposit $100 into his account when Bob sends the value
is sent to Bob with the promise to deposit $100 into his account when Bob sends the value 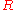 back to the bank. The bank is confident that Bob won't be able to break RSA to generate
back to the bank. The bank is confident that Bob won't be able to break RSA to generate 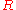 from
from 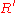 within the heat death of the universe
within the heat death of the universe
without knowledge of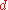 , so it does not worry about handing out the deposit slips without receiving anything from Bob.
, so it does not worry about handing out the deposit slips without receiving anything from Bob.
When Alice wants to pay Bob $100 she asks for the deposit slip and Bob sends her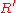 . Alice selects a large random value
. Alice selects a large random value 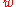 coprime with
coprime with  (so as to have an inverse modulo
(so as to have an inverse modulo  ) and uses it to blind
) and uses it to blind 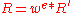 and sends it to the bank to be blind signed. The Bank charges Alice $100 for this operation and returns the blind signed value
and sends it to the bank to be blind signed. The Bank charges Alice $100 for this operation and returns the blind signed value  . Due to the symmetric properties of RSA, this provides her with
. Due to the symmetric properties of RSA, this provides her with 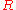 :
:
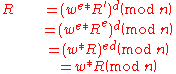
Because of the blinding process, the Bank is not able to associate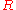 with
with 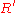 or
or  , so it is unable to determine that Bob and Alice are doing business together, preserving the anonymity of the transaction. Alice unblinds
, so it is unable to determine that Bob and Alice are doing business together, preserving the anonymity of the transaction. Alice unblinds 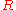 (by dividing it by
(by dividing it by 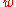 ) to generate the original value
) to generate the original value 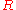 , which she sends to Bob.
, which she sends to Bob.
Bob verifies that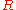 can be encrypted with the bank's public key by computing
can be encrypted with the bank's public key by computing 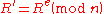 , which means that Alice has deposited $100 into the bank. Bob then sends this value to the bank and the bank checks its records to be sure that
, which means that Alice has deposited $100 into the bank. Bob then sends this value to the bank and the bank checks its records to be sure that  has not been already used. If it has not, it deposits $100 into his account and updates its database that the unique value
has not been already used. If it has not, it deposits $100 into his account and updates its database that the unique value 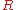 has been redeemed.
has been redeemed.
Different public keys can be used for different denominations of currency so this system doesn't take appreciably longer for large transactions.
Note that if neither Alice nor Bob wishes the bank to know that they performed a transaction with each other, then it is hard for the bank to find out. However, in order to ensure this is the case many people need to be making transactions at the same time. Otherwise the bank can figure it out by the timing of the transactions, using traffic analysis
.
Financial cryptography
Financial cryptography is the use of cryptography in applications in which financial loss could result from subversion of the message system.Cryptographers think of the field as originating in the work of Dr David Chaum who invented the blinded signature...
to make electronic bank secrecy
Bank secrecy
Bank secrecy is a legal principle in some jurisdictions under which banks are not allowed to provide to authorities personal and account information about their customers unless certain conditions apply...
(or more precisely pseudonymous
Pseudonymity
Pseudonymity is a word derived from pseudonym, meaning 'false name', and anonymity, meaning unknown or undeclared source, describing a state of disguised identity. The pseudonym identifies a holder, that is, one or more human beings who possess but do not disclose their true names...
banking) possible. The bank issues currency in the form of electronic tokens that can be converted on presentation to the bank to some other currency. This concept has a long history in which free banking
Free banking
Free banking refers to a monetary arrangement in which banks are subject to no special regulations beyond those applicable to most enterprises, and in which they also are free to issue their own paper currency...
institutions have issued their own paper currency often backed by a physical commodity.
History
Whilst the academic study of trust relationships and systems has long been the forte of intelligence services such as the NSA, the growth of the Internet in the 1990s and the contemporary declassification of related knowledge allowed for greater public discussion of the potential for anonymous banking services by groups such as the cryptoanarchists and cypherpunks.Implemented systems
Examples of anonymous internet banking services and software that have already been implemented include:- eCacheECacheeCache is an anonymous bank operating through interfaces in the Tor network. The bank issues cryptographic certificates, digital bearer certificates, that can be exchanged among the bank's users. The certificates can be bought and sold for real money through the bank. The owners and operators of...
: an anonymous bank operating over the TorTor (anonymity network)Tor is a system intended to enable online anonymity. Tor client software routes Internet traffic through a worldwide volunteer network of servers in order to conceal a user's location or usage from someone conducting network surveillance or traffic analysis...
network. - BitcoinBitcoinBitcoin is a decentralized, peer-to-peer network over which users make transactions that are tracked and verified through this network. The word Bitcoin also refers to the digital currency implemented as the currency medium for user transactions over this network...
: a de-centralized, (Peer-to-peerPeer-to-peerPeer-to-peer computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads among peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application...
), digital currency - PecunixPecunixPecunix is a digital gold currency founded in 2002 by Simon Davis. Similar to competing systems such as e-gold, Pecunix allows for the instant transfer of gold between user accounts....
: an anonymous digital gold currency. - Yodelbank: an anonymous bank built on top of various digital gold currencies which ended operations during November 2005.
- Private Payments System: an anonymous digital currency(offshore registred).
The underlying mathematics
Anonymous internet banking depends on the mathematics of public key cryptography and blind signatureBlind signature
In cryptography a blind signature as introduced by David Chaum is a form of digital signature in which the content of a message is disguised before it is signed. The resulting blind signature can be publicly verified against the original, unblinded message in the manner of a regular digital...
algorithms. In this simple example we have Alice and Bob
Alice and Bob
The names Alice and Bob are commonly used placeholder names for archetypal characters in fields such as cryptography and physics. The names are used for convenience; for example, "Alice sends a message to Bob encrypted with his public key" is easier to follow than "Party A sends a message to Party...
and a banker. The banker generates an RSA public key with modulus
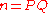 , where
, where 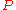 and
and  are large primes
are large primesPrime number
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. A natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime number is called a composite number. For example 5 is prime, as only 1 and 5 divide it, whereas 6 is composite, since it has the divisors 2...
, making
 a semiprime
a semiprimeSemiprime
In mathematics, a semiprime is a natural number that is the product of two prime numbers. The first few semiprimes are 4, 6, 9, 10, 14, 15, 21, 22, 25, 26, ... ....
. As described in RSA operation, the bank also generates public key exponent
 and private key exponent
and private key exponent 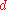 .
.Bob asks the banker for a $100 deposit slip in anticipation of Alice wanting to transfer money to him. To generate a deposit slip the bank selects a large, globally unique random number
Random number
Random number may refer to:* A number generated for or part of a set exhibiting statistical randomness.* A random sequence obtained from a stochastic process.* An algorithmically random sequence in algorithmic information theory....
 and encrypts it using the bank's public key; this means that it can only be decrypted with the bank's secret key:
and encrypts it using the bank's public key; this means that it can only be decrypted with the bank's secret key:
This encrypted value
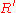 is sent to Bob with the promise to deposit $100 into his account when Bob sends the value
is sent to Bob with the promise to deposit $100 into his account when Bob sends the value  back to the bank. The bank is confident that Bob won't be able to break RSA to generate
back to the bank. The bank is confident that Bob won't be able to break RSA to generate  from
from 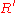 within the heat death of the universe
within the heat death of the universeHeat death of the universe
The heat death of the universe is a suggested ultimate fate of the universe, in which the universe has diminished to a state of no thermodynamic free energy and therefore can no longer sustain motion or life. Heat death does not imply any particular absolute temperature; it only requires that...
without knowledge of
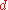 , so it does not worry about handing out the deposit slips without receiving anything from Bob.
, so it does not worry about handing out the deposit slips without receiving anything from Bob.When Alice wants to pay Bob $100 she asks for the deposit slip and Bob sends her
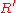 . Alice selects a large random value
. Alice selects a large random value  coprime with
coprime with  (so as to have an inverse modulo
(so as to have an inverse modulo  ) and uses it to blind
) and uses it to blind 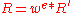 and sends it to the bank to be blind signed. The Bank charges Alice $100 for this operation and returns the blind signed value
and sends it to the bank to be blind signed. The Bank charges Alice $100 for this operation and returns the blind signed value  . Due to the symmetric properties of RSA, this provides her with
. Due to the symmetric properties of RSA, this provides her with  :
: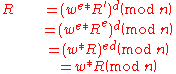
Because of the blinding process, the Bank is not able to associate
 with
with 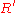 or
or  , so it is unable to determine that Bob and Alice are doing business together, preserving the anonymity of the transaction. Alice unblinds
, so it is unable to determine that Bob and Alice are doing business together, preserving the anonymity of the transaction. Alice unblinds  (by dividing it by
(by dividing it by  ) to generate the original value
) to generate the original value  , which she sends to Bob.
, which she sends to Bob.Bob verifies that
 can be encrypted with the bank's public key by computing
can be encrypted with the bank's public key by computing  , which means that Alice has deposited $100 into the bank. Bob then sends this value to the bank and the bank checks its records to be sure that
, which means that Alice has deposited $100 into the bank. Bob then sends this value to the bank and the bank checks its records to be sure that  has not been already used. If it has not, it deposits $100 into his account and updates its database that the unique value
has not been already used. If it has not, it deposits $100 into his account and updates its database that the unique value  has been redeemed.
has been redeemed.Different public keys can be used for different denominations of currency so this system doesn't take appreciably longer for large transactions.
Note that if neither Alice nor Bob wishes the bank to know that they performed a transaction with each other, then it is hard for the bank to find out. However, in order to ensure this is the case many people need to be making transactions at the same time. Otherwise the bank can figure it out by the timing of the transactions, using traffic analysis
Traffic analysis
Traffic analysis is the process of intercepting and examining messages in order to deduce information from patterns in communication. It can be performed even when the messages are encrypted and cannot be decrypted. In general, the greater the number of messages observed, or even intercepted and...
.
See also
- Bearer bondBearer bondA bearer bond is a debt security issued by a business entity, such as a corporation, or by a government. It differs from the more common types of investment securities in that it is unregistered – no records are kept of the owner, or the transactions involving ownership. Whoever physically...
- BitcoinBitcoinBitcoin is a decentralized, peer-to-peer network over which users make transactions that are tracked and verified through this network. The word Bitcoin also refers to the digital currency implemented as the currency medium for user transactions over this network...
- Electronic moneyElectronic moneyElectronic money is money or scrip that is only exchanged electronically. Typically, this involves the use of computer networks, the internet and digital stored value systems...
- Itex CorporationItex CorporationItex Corporation is an American company that provides a marketplace for cashless business transactions. The firm specializes in information technology and electronic funds transfer lifecycle management in an emerging niche market of cashless payment between firms...
- Online bankingOnline bankingOnline banking allows customers to conduct financial transactions on a secure website operated by their retail or virtual bank, credit union or building society.-Features:...
- Ripple monetary systemRipple monetary systemRipple is an open-source software project for developing and implementing a protocol for an open decentralized payment network. In its developed form , the Ripple network would be a peer-to-peer distributed social network service with a monetary honour system based on trust that already exists...
- Ven (currency)Ven (currency)Ven is a global virtual currency used by members of a social network service Hub Culture to buy, share and trade knowledge, goods and services globally. It can be spent at any Hub Culture Pavilion or used for micropayments on the Internet at large. The value of Ven is determined on the financial...
External links
- Open Transactions - Open-source software, including library, server, and client, providing untraceable digital cash and anonymous numbered accounts.
- The Digital Monetary Trust, Part 1 - Anonymous banking based on cryptography, not bankers & lawyers.
- The Digital Monetary Trust, Part 2 - The mathematical details of the anonymous banking system.
- David ChaumDavid ChaumDavid Chaum is the inventor of many cryptographic protocols, including blind signature schemes, commitment schemes, and digital cash. In 1982, Chaum founded the International Association for Cryptologic Research , which currently organizes academic conferences in cryptography research...
's Scientific American article on Achieving Electronic Privacy - Untraceable Digital Cash, Information Markets, and BlackNet by Timothy C. MayTimothy C. MayTimothy C. May, better known as Tim May, is a technical and political writer, and was an electronic engineer and senior scientist at Intel in the company's early history...

