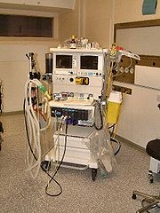
Anaesthetic machine
Encyclopedia
Anesthesiologist
An anesthesiologist or anaesthetist is a physician trained in anesthesia and peri-operative medicine....
s and nurse anaesthetist
Nurse anesthetist
A nurse anesthetist is a nurse who specializes in the administration of anesthesia.In the United States, a Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist is an advanced practice registered nurse who has acquired graduate-level education and board certification in anesthesia...
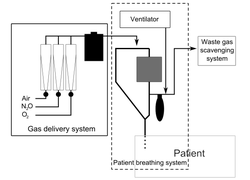
s to support the administration of anaesthesia. The most common type of anaesthetic machine in use in the developed world is the continuous-flow anaesthetic machine, which is designed to provide an accurate and continuous supply of medical gases (such as oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
and nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or sweet air, is a chemical compound with the formula . It is an oxide of nitrogen. At room temperature, it is a colorless non-flammable gas, with a slightly sweet odor and taste. It is used in surgery and dentistry for its anesthetic and analgesic...
), mixed with an accurate concentration of anaesthetic vapour (such as isoflurane
Isoflurane
Isoflurane is a halogenated ether used for inhalational anesthesia. Together with enflurane and halothane, it replaced the flammable ethers used in the pioneer days of surgery. Its name comes from being a structural isomer of enflurane, hence they have the same empirical formula...
), and deliver this to the patient at a safe pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
and flow. Modern machines incorporate a ventilator, suction unit, and patient-monitoring devices.
The original concept of Boyle's machine
Boyle's machine
In medicine, Boyle's machine is the name given to the continuous-flow apparatus used by anesthesiologists to administer general anesthesia to patients in operation theaters....
was invented by the British anaesthetist H.E.G. Boyle
Henry Edmund Gaskin Boyle
Henry Edmund Gaskin Boyle OBE was a pioneering anaesthetist best remembered for the development of early anaesthetic machines.-Early life:...
in 1917. Prior to this time, anaesthetists often carried all their equipment with them, but the development of heavy, bulky cylinder storage and increasingly elaborate airway equipment meant that this was no longer practical for most circumstances. The anaesthetic machine is usually mounted on anti-static wheels for convenient transportation.
Simpler anaesthetic apparatus may be used in special circumstances, such as the TriService Apparatus, a simplified anaesthesia delivery system invented for the British armed forces
Armed forces
The armed forces of a country are its government-sponsored defense, fighting forces, and organizations. They exist to further the foreign and domestic policies of their governing body, and to defend that body and the nation it represents from external aggressors. In some countries paramilitary...
, which is light and portable and may be used effectively even when no medical gases are available. This device has unidirectional valves which suck in ambient air which can be enriched with oxygen from a cylinder, with the help of a set of bellows. A large number of draw-over type of anaesthesia devices are still in use in India for administering an air-ether mixture to the patient, which can be enriched with oxygen. But the advent of the cautery has sounded the death knell to this device, due to the explosion hazard.
Many of the early innovations in U.S. anaesthetic equipment, including the closed circuit carbon-dioxide absorber (aka: the Guedel-Foregger Midget) and diffusion of such equipment to anaesthetists within the United States can be attributed to Dr. Richard von Foregger and The Foregger Company.
In dentistry
Dentistry
Dentistry is the branch of medicine that is involved in the study, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases, disorders and conditions of the oral cavity, maxillofacial area and the adjacent and associated structures and their impact on the human body. Dentistry is widely considered...
a simplified version of the anaesthetic machine, without a ventilator or anaesthetic vaporiser, is referred to as a relative analgesia machine
Relative analgesia machine
A relative analgesia machine is used by dentists to induce inhalation sedation in their patients. It delivers a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen. A relative analgesia machine is simpler than an anaesthetic machine, as it does not feature the additional medical ventilator and anaesthetic...
. By using this machine, the dentist can administer a mild inhalation sedation
Sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure...
with nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or sweet air, is a chemical compound with the formula . It is an oxide of nitrogen. At room temperature, it is a colorless non-flammable gas, with a slightly sweet odor and taste. It is used in surgery and dentistry for its anesthetic and analgesic...
and oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, in order to keep his patient in a conscious state while depressing the feeling of pain.
Components of a typical machine
- connections to piped hospital oxygenOxygenOxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, medical air, and nitrous oxideNitrous oxideNitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or sweet air, is a chemical compound with the formula . It is an oxide of nitrogen. At room temperature, it is a colorless non-flammable gas, with a slightly sweet odor and taste. It is used in surgery and dentistry for its anesthetic and analgesic...
. Pipeline pressure from the hospital medical gas system (wall outlet) should be around 50 psi. - reserve gas cylinderGas cylinderA gas cylinder is a pressure vessel used to store gases at above atmospheric pressure. High pressure gas cylinders are also called bottles. Although they are sometimes colloquially called "tanks", this is technically incorrect, as a tank is a vessel used to store liquids at ambient pressure and...
s of oxygen, air, and nitrous oxide attached via a specific yoke with a Bodok sealBodok sealThe Bodok seal is a specialised washer that ensures a gas-tight seal between the cylinder yoke or regulator of an anaesthetic machine or any medical device requiring a gas supply, and a gas cylinder...
. Older machines may have cylinder yokes and flow meters for carbon dioxideCarbon dioxideCarbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
and cyclopropaneCyclopropaneCyclopropane is a cycloalkane molecule with the molecular formula C3H6, consisting of three carbon atoms linked to each other to form a ring, with each carbon atom bearing two hydrogen atoms...
. Many newer machines only have oxygen reserve cylinders. The regulators for the cylinders are set at 300 kPa (45 psi; 3 atmospheres). If the cylinders are left on and the machine is plugged into the wall outlet, gas from the wall supply will be used preferentially, since it is at a higher pressure. In situations where pipeline gases are not available, machines may safely be used from cylinders alone, provided fresh cylinders are available. - a high-flow oxygen flush which provides pure oxygen at 30-75 litres/minute
- pressure gauges, regulators and 'pop-off' valves, to protect the machine components and patient from high-pressure gases (referred to as 'barotrauma').
- flow meters (rotameterRotameterA rotameter is a device that measures the flow rate of liquid or gas in a closed tube.It belongs to a class of meters called variable area meters, which measure flow rate by allowing the cross-sectional area the fluid travels through to vary, causing some measurable effect.-History:The first...
s) for oxygen, air, and nitrous oxide, which are used by the anaesthesiologist to provide accurate mixtures of medical gases to the patient. Flow meters are typically pneumatic, but increasingly electromagnetic digital flow meters are being used. - one or more anaesthetic vaporizers to accurately add volatile anaesthetics to the fresh gas flowFresh gas flowFresh gas flow refers to the mixture of medical gases and volatile anaesthetic agents which is produced by an anaesthetic machine. The flow rate and composition of the fresh gas flow is determined by the anaesthetist....
- a ventilatorMedical ventilatorA medical ventilator can be defined as any machine designed to mechanically move breatheable air into and out of the lungs, to provide the mechanism of breathing for a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently....
- a manual ventilation bag in combination with an Adjustable Pressure Limiting (APL) valve
- physiological monitors to monitor the patient's heart rateHeart rateHeart rate is the number of heartbeats per unit of time, typically expressed as beats per minute . Heart rate can vary as the body's need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide changes, such as during exercise or sleep....
, ECG, non-invasive blood pressure and oxygen saturationOxygen saturationOxygen saturation or dissolved oxygen is a relative measure of the amount of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium. It can be measured with a dissolved oxygen probe such as an oxygen sensor or an optode in liquid media, usually water.It has particular significance in medicine and...
(additional monitors are generally available to monitor end-tidal CO2, temperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, arterial blood pressure central venous pressureCentral venous pressureCentral venous pressure describes the pressure of blood in the thoracic vena cava, near the right atrium of the heart...
, etc.). In addition, the composition of the gases delivered to the patient (and breathed out) is monitored continuously. - breathing circuits, most commonly a circle attachment, or a Bain's breathing system, which are breathing hoses connected to an anaesthesia face mask
- a heat and moisture exchanger (HME) with or without bacteria-viral filter (HMEF).
- scavenging system to remove expired anaesthetic gases from the operating room. Scavenged gases should always be vented to the atmosphereAtmosphereAn atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
. - suction apparatus
There is generally a small work bench built into the machine where airway management equipment is kept within ready reach of the anaesthetist.
Safety features of modern machines
Based on experience gained from analysis of mishaps, the modern anaesthetic machine incorporates several safety devices, including:- an oxygen failure alarm (aka 'Oxygen Failure Warning Device' or OFWD). In older machines this was a pneumatic device called a Ritchie whistle which sounds when oxygen pressure is 38 psi decending. Newer machines have an electronic sensor.
- Nitrous cut-off or oxygen failure protection device, OFPD: the flow of medical nitrous-oxide is dependent on oxygen pressure. This is done at the regulator level. In essence, the nitrous-oxide regulator is a 'slave' of the oxygen regulator. ie, if oxygen pressure is lost then the other gases can not flow past their regulators.
- hypoxicHypoxia (medical)Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is a pathological condition in which the body as a whole or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise...
-mixture alarms (hypoxy guards or ratio controllers) to prevent gas mixtures which contain less than 21-25% oxygen being delivered to the patient. In modern machines it is impossible to deliver 100% nitrous oxide (or any hypoxic mixture) to the patient to breathe. Oxygen is automatically added to the fresh gas flow even if the anaesthetist should attempt to deliver 100% nitrous oxide. Ratio controllers usually operate on the pneumatic principle or are chain linked (link 25 system). Both are located on the rotameter assembly, unless electronically controlled. - ventilator alarms, which warn of low or high airway pressures.
- interlocks between the vaporizers preventing inadvertent administration of more than one volatile agent concurrently
- alarms on all the above physiological monitors
- the Pin Index Safety SystemPin Index Safety SystemThe Pin Index Safety System, or PISS, is a safety system that uses geometric features on the yoke to ensure that pneumatic connections between a gas cylinder and a machine that uses pressurized gases are not connected to the wrong gas yoke. This system can be seen on an anesthesia machine.Each gas...
prevents cylinders being accidentally connected to the wrong yoke - the NIST (Non-Interchangeable Screw Thread) or Diameter Index Safety System, DISS system for pipeline gases, which prevents piped gases from the wall being accidentally connected to the wrong inlet on the machine
- pipeline gas hoses have non-interchangeable Schrader valveSchrader valveThe Schrader valve is a brand of pneumatic tire valve used on virtually every motor vehicle in the world today. The Schrader company, for which it was named, was founded in 1844 by August Schrader...
connectors, which prevents hoses being accidentally plugged into the wrong wall socket
The functions of the machine should be checked at the beginning of every operating list in a "cockpit-drill". Machines and associated equipment must be maintained and serviced regularly.
Older machines may lack some of the safety features and refinements present on newer machines. However, they were designed to be operated without mains electricity
Mains electricity
Mains is the general-purpose alternating current electric power supply. In the US, electric power is referred to by several names including household power, household electricity, powerline, domestic power, wall power, line power, AC power, city power, street power, and grid power...
, using compressed gas power for the ventilator and suction apparatus. Modern machines often have battery
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
backup, but may fail when this becomes depleted.
The modern anaesthetic machine still retains all the key working principles of the Boyle's machine (a cvBritish Oxygen Company
The BOC Group
The BOC Group plc was the official name of the multinational industrial gas and British based company more commonly known as BOC, and now a part of The Linde Group. In September 2004, BOC had over 30,000 employees on six continents, with sales of over £4.6 billion. BOC was a constituent of the...
trade name) in honour of the British anaesthetist H.E.G. Boyle (1875–1941). In India, however, the trade name 'Boyle' is registered with Boyle HealthCare Pvt. Ltd., Indore MP.
A two-person (Operating Theatre Practitioner and anaesthetist) pre-use check of the anaesthetic machine is recommended before every single case and has been shown to decrease the risk of 24-hour severe postoperative morbidity and mortality. Various regulatory and professional bodies have formulated checklists for different countries. A free transparent reality simulation of the checklist recommended by the United States Food & Drug Administration is available from the Virtual Anesthesia Machine web site ( see below) after registration which is also free. Machines should be cleaned between cases as they are at considerable risk of contamination with pathogens.
External links
- Virtual Anesthesia Machine (VAM) — a free transparent reality simulation of a generic anesthesia machine from the University of FloridaUniversity of FloridaThe University of Florida is an American public land-grant, sea-grant, and space-grant research university located on a campus in Gainesville, Florida. The university traces its historical origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its present Gainesville campus since September 1906...
- Various anesthesia-related simulations
- Virtual Anaesthesia Textbook
- FRCA UK — resources for UK anaesthetist in training
- History of Dr. Richard von Foregger and the Foregger Company — written by his son, Dr. R. Foregger, this website chronicles one of the leading manufacturers and developers of anesthesiology equipment in the early 20th century.

