
Amott index
Encyclopedia
The Amott test is one of the most widely used empirical wettability measurements for reservoir cores
in petroleum engineering
. The method combines two spontaneous imbibition
measurements and two forced displacement measurements. This test defines two different indices: the Amott water index (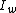 ) and the Amott oil index (
) and the Amott oil index (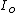 ).
).
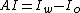
These two indices are obtained from special core analysis
(SCAL) experiments (porous plate or centrifuge
) by plotting the capillary pressure curve as a function of the water saturation as shown on figure 1:
with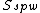 is the water saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the imbibition process,
is the water saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the imbibition process, 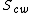 is the irreducible water saturation and
is the irreducible water saturation and 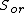 is the residual oil saturation after imbibition.
is the residual oil saturation after imbibition.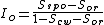
with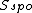 is the oil saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the secondary drainage process,
is the oil saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the secondary drainage process, 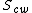 is the irreducible water saturation and
is the irreducible water saturation and 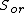 is the residual non-wetting phase saturation after imbibition.
is the residual non-wetting phase saturation after imbibition.
A rock is defined as:
Core sample
A core sample is a cylindrical section of a naturally occurring substance. Most core samples are obtained by drilling with special drills into the substance, for example sediment or rock, with a hollow steel tube called a core drill. The hole made for the core sample is called the "core hole". A...
in petroleum engineering
Petroleum engineering
Petroleum engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the activities related to the production of hydrocarbons, which can be either crude oil or natural gas. Subsurface activities are deemed to fall within the upstream sector of the oil and gas industry, which are the activities of...
. The method combines two spontaneous imbibition
Imbibition
'Imbibition' is defined as the displacement of one fluid by another immiscible fluid. This process is controlled and affected by a variety of factors...
measurements and two forced displacement measurements. This test defines two different indices: the Amott water index (
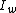 ) and the Amott oil index (
) and the Amott oil index (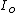 ).
).Amott–Harvey index
The two Amott indices are often combined to give the Amott–Harvey index. It is a number between 0 and 1 describing wettability of a rock in drainage processes. It is defined as: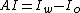
These two indices are obtained from special core analysis
Special core analysis
In the petroleum industry, special core analysis, often abbreviated SCAL or SPCAN, is a laboratory procedure for conducting flow experiments on core plugs taken from a petroleum reservoir...
(SCAL) experiments (porous plate or centrifuge
Centrifuge
A centrifuge is a piece of equipment, generally driven by an electric motor , that puts an object in rotation around a fixed axis, applying a force perpendicular to the axis...
) by plotting the capillary pressure curve as a function of the water saturation as shown on figure 1:
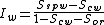
with
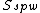 is the water saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the imbibition process,
is the water saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the imbibition process, 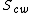 is the irreducible water saturation and
is the irreducible water saturation and 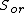 is the residual oil saturation after imbibition.
is the residual oil saturation after imbibition.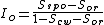
with
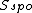 is the oil saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the secondary drainage process,
is the oil saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the secondary drainage process, 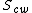 is the irreducible water saturation and
is the irreducible water saturation and 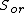 is the residual non-wetting phase saturation after imbibition.
is the residual non-wetting phase saturation after imbibition.A rock is defined as:
- Water wet when the Amott–Harvey index is between 0.3 and 1,
- Weakly water wet when the Amott–Harvey index is between 0 and 0.3,
- Weakly oil wet when the Amott–Harvey index is between -0.3 and 0,
- Oil wet when the Amott–Harvey index is between -1 and -0.3.
See also
- USBM index - an alternative wettability index
- Relative permeabilityRelative permeabilityIn multiphase flow in porous media, the relative permeability of a phase is a dimensionless measure of the effective permeability of that phase. It is the ratio of the effective permeability of that phase to the absolute permeability...
- Multiphase flowMultiphase flowIn fluid mechanics, multiphase flow is a generalisation of the modelling used in two-phase flow to cases where the two phases are not chemically related or where more than two phases are present In fluid mechanics, multiphase flow is a generalisation of the modelling used in two-phase flow to...
- Capillary pressure
- Leverett J-function
- ImbibitionImbibition'Imbibition' is defined as the displacement of one fluid by another immiscible fluid. This process is controlled and affected by a variety of factors...

