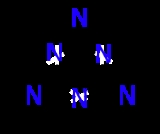
Altretamine
Encyclopedia
Altretamine is an antineoplastic agent. It was approved by the FDA in 1990.
.
It is not considered a first-line treatment, but it can be useful as salvage therapy. It also has the advantage of being less toxic than other drugs used for treating refractory ovarian cancer.
as an alkylating antineoplastic agent
.
This unique structure is believed to damage tumor
cells through the production of the weakly alkylating species formaldehyde
, a product of CYP450-mediated N-demethylation. Administered orally, altretamine is extensively metabolized on first pass, producing primarily mono- and didemethylated metabolites. Additional demethylation reactions occur in tumor cells, releasing formaldehyde
in situ before the drug is excreted in the urine. The carbinolamine (methylol) intermediates of CYP450-mediated metabolism also can generate electrophilic iminium species that are capable of reacting covalently with DNA guanine
and cytosine
residues as well as protein. Iminium-mediated DNA cross-linking and DNA-protein interstrand cross-linking, mediated through both the iminium intermediate and formaldehyde
, have been demonstrated, although the significance of DNA cross-linking on altretamine antitumor activity is uncertain.
, vomiting
, diarrhea
, renal toxicity, BMS
, sever orthostatic hypotension and neurotoxicity
. Toxicity can be decreased using pyridoxine.
Uses
It is used to treat refractory ovarian cancerOvarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous growth arising from the ovary. Symptoms are frequently very subtle early on and may include: bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty eating and frequent urination, and are easily confused with other illnesses....
.
It is not considered a first-line treatment, but it can be useful as salvage therapy. It also has the advantage of being less toxic than other drugs used for treating refractory ovarian cancer.
Mechanism
The precise mechanism by which altretamine exerts its anti-cancer effect is unknown but it is classified by MeSHMedical Subject Headings
Medical Subject Headings is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences; it can also serve as a thesaurus that facilitates searching...
as an alkylating antineoplastic agent
Alkylating antineoplastic agent
An alkylating antineoplastic agent is an alkylating agent used in cancer treatment that attaches an alkyl group to DNA.The alkyl group is attached to the guanine base of DNA, at the number 7 nitrogen atom of the purine ring....
.
This unique structure is believed to damage tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
cells through the production of the weakly alkylating species formaldehyde
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH2O. It is the simplest aldehyde, hence its systematic name methanal.Formaldehyde is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent odor. It is an important precursor to many other chemical compounds, especially for polymers...
, a product of CYP450-mediated N-demethylation. Administered orally, altretamine is extensively metabolized on first pass, producing primarily mono- and didemethylated metabolites. Additional demethylation reactions occur in tumor cells, releasing formaldehyde
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH2O. It is the simplest aldehyde, hence its systematic name methanal.Formaldehyde is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent odor. It is an important precursor to many other chemical compounds, especially for polymers...
in situ before the drug is excreted in the urine. The carbinolamine (methylol) intermediates of CYP450-mediated metabolism also can generate electrophilic iminium species that are capable of reacting covalently with DNA guanine
Guanine
Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine . In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with...
and cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
residues as well as protein. Iminium-mediated DNA cross-linking and DNA-protein interstrand cross-linking, mediated through both the iminium intermediate and formaldehyde
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH2O. It is the simplest aldehyde, hence its systematic name methanal.Formaldehyde is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent odor. It is an important precursor to many other chemical compounds, especially for polymers...
, have been demonstrated, although the significance of DNA cross-linking on altretamine antitumor activity is uncertain.
Side effects
Side effects include nauseaNausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
, vomiting
Vomiting
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
, diarrhea
Diarrhea
Diarrhea , also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having three or more loose or liquid bowel movements per day. It is a common cause of death in developing countries and the second most common cause of infant deaths worldwide. The loss of fluids through diarrhea can cause dehydration and...
, renal toxicity, BMS
BMS
BMS is a three letter acronym that may refer to:* Be-Music Script, a computer file format* Black Mesa * Borane-methylsulfide* Bristol Motor Speedway* Broadmeadows railway station, Melbourne...
, sever orthostatic hypotension and neurotoxicity
Neurotoxicity
Neurotoxicity occurs when the exposure to natural or artificial toxic substances, which are called neurotoxins, alters the normal activity of the nervous system in such a way as to cause damage to nervous tissue. This can eventually disrupt or even kill neurons, key cells that transmit and process...
. Toxicity can be decreased using pyridoxine.

