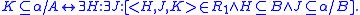Alpha recursion theory
Encyclopedia
In recursion theory
, α recursion theory is a generalisation of recursion theory
to subsets of admissible ordinal
s . An admissible ordinal is closed under
. An admissible ordinal is closed under 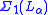 functions. Admissible ordinals are models of Kripke–Platek set theory
functions. Admissible ordinals are models of Kripke–Platek set theory
. In what follows is considered to be fixed.
is considered to be fixed.
The objects of study in recursion are subsets of
recursion are subsets of  . A is said to be
. A is said to be  recursively enumerable if it is
recursively enumerable if it is 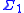 definable over
definable over 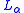 . A is recursive if both A and
. A is recursive if both A and 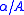 (its complement in
(its complement in  ) are
) are  recursively enumerable.
recursively enumerable.
Members of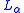 are called
are called  finite and play a similar role to the finite numbers in classical recursion theory.
finite and play a similar role to the finite numbers in classical recursion theory.
We say R is a reduction procedure if it is recursively enumerable and every member of R is of the form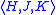 where H, J, K are all α-finite.
where H, J, K are all α-finite.
A is said to be α-recusive in B if there exist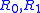 reduction procedures such that:
reduction procedures such that:
If A is recursive in B this is written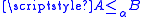 . By this definition A is recursive in
. By this definition A is recursive in  (the empty set
(the empty set
) if and only if A is recursive. However A being recursive in B is not equivalent to A being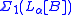 .
.
We say A is regular if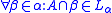 or in other words if every initial portion of A is α-finite.
or in other words if every initial portion of A is α-finite.
Results in
Shore's splitting theorem: Let A be  recursively enumerable and regular. There exist
recursively enumerable and regular. There exist  recursively enumerable
recursively enumerable 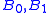 such that
such that 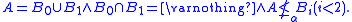
Shore's density theorem: Let A, C be α-regular recursively enumerable sets such that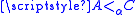 then there exists a regular α-recursively enumerable set B such that
then there exists a regular α-recursively enumerable set B such that 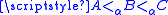 .
.
Recursion theory
Computability theory, also called recursion theory, is a branch of mathematical logic that originated in the 1930s with the study of computable functions and Turing degrees. The field has grown to include the study of generalized computability and definability...
, α recursion theory is a generalisation of recursion theory
Recursion theory
Computability theory, also called recursion theory, is a branch of mathematical logic that originated in the 1930s with the study of computable functions and Turing degrees. The field has grown to include the study of generalized computability and definability...
to subsets of admissible ordinal
Admissible ordinal
In set theory, an ordinal number α is an admissible ordinal if Lα is an admissible set ; in other words, α is admissible when α is a limit ordinal and Lα⊧Σ0-collection....
s
 . An admissible ordinal is closed under
. An admissible ordinal is closed under 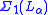 functions. Admissible ordinals are models of Kripke–Platek set theory
functions. Admissible ordinals are models of Kripke–Platek set theoryKripke–Platek set theory
The Kripke–Platek axioms of set theory are a system of axioms for axiomatic set theory developed by Saul Kripke and Richard Platek. The axiom system, written in first-order logic, has an infinite number of axioms because an infinite axiom schema is used.KP is weaker than Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory...
. In what follows
 is considered to be fixed.
is considered to be fixed.The objects of study in
 recursion are subsets of
recursion are subsets of  . A is said to be
. A is said to be  recursively enumerable if it is
recursively enumerable if it is 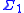 definable over
definable over 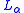 . A is recursive if both A and
. A is recursive if both A and 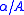 (its complement in
(its complement in  ) are
) are  recursively enumerable.
recursively enumerable.Members of
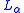 are called
are called  finite and play a similar role to the finite numbers in classical recursion theory.
finite and play a similar role to the finite numbers in classical recursion theory.We say R is a reduction procedure if it is recursively enumerable and every member of R is of the form
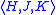 where H, J, K are all α-finite.
where H, J, K are all α-finite.A is said to be α-recusive in B if there exist
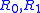 reduction procedures such that:
reduction procedures such that:If A is recursive in B this is written
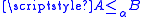 . By this definition A is recursive in
. By this definition A is recursive in  (the empty set
(the empty setEmpty set
In mathematics, and more specifically set theory, the empty set is the unique set having no elements; its size or cardinality is zero. Some axiomatic set theories assure that the empty set exists by including an axiom of empty set; in other theories, its existence can be deduced...
) if and only if A is recursive. However A being recursive in B is not equivalent to A being
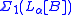 .
.We say A is regular if
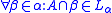 or in other words if every initial portion of A is α-finite.
or in other words if every initial portion of A is α-finite.Results in  recursion
recursion
Shore's splitting theorem: Let A be  recursively enumerable and regular. There exist
recursively enumerable and regular. There exist  recursively enumerable
recursively enumerable 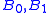 such that
such that 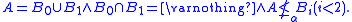
Shore's density theorem: Let A, C be α-regular recursively enumerable sets such that
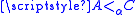 then there exists a regular α-recursively enumerable set B such that
then there exists a regular α-recursively enumerable set B such that 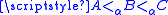 .
.