
Alanine transaminase
Encyclopedia
Alanine transaminase or ALT is a transaminase
enzyme
. It is also called serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT) or alanine aminotransferase (ALAT).
ALT is found in serum
and in various bodily tissues, but is most commonly associated with the liver
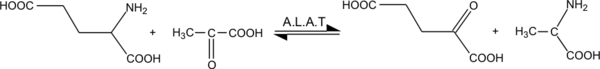
. It catalyzes the two parts of the alanine cycle
.
to a-ketoglutarate, the products of this reversible transamination
reaction being pyruvate and glutamate.
, to determine liver health. When used in diagnostics, it is almost always measured in international units/liter (U/L). While sources vary on specific normal range values, most show between 5-60 U/L as being normal. Alanine transaminase shows a marked diurnal variation.
, diabetes, congestive heart failure
, liver
damage, bile duct
problems, infectious mononucleosis
, or myopathy
. For this reason, ALT is commonly used as a way of screening for liver problems. However, elevated levels of ALT do not automatically mean that medical problems exist. Fluctuation of ALT levels is normal over the course of the day, and ALT levels can also increase in response to strenuous physical exercise.
When elevated ALT levels are found in the blood, the possible underlying causes can be further narrowed down by measuring other enzymes. For example, elevated ALT levels due to liver-cell
damage can be distinguished from biliary duct problems by measuring alkaline phosphatase
. Also, myopathy
-related ALT levels can be ruled out by measuring creatine kinase
enzymes. Many drugs may elevate ALT levels, including Zileuton
, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, cholesterol medications, and anti-convulsants. Consider advanced schizophrenia.
For years, the American Red Cross
used ALT testing as part of the battery of tests to ensure the safety of its blood supply by deferring donors with elevated ALT levels. The intent was to identify donors potentially infected with Hepatitis C because there was no specific test for that disease at the time. Prior to July 1992, widespread blood donation testing in the USA for Hepatitis C was not carried out by major blood banks. With the introduction of second-generation ELISA
antibody tests for Hepatitis C
, the Red Cross changed the ALT policy. , donors previously disqualified for elevated ALT levels and no other reason may be reinstated as donors by contacting the donor counseling department of their regional Red Cross organization.
Transaminase
In biochemistry, a transaminase or an aminotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes a type of reaction between an amino acid and an α-keto acid. To be specific, this reaction involves removing the amino group from the amino acid, leaving behind an α-keto acid, and transferring it to the...
enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
. It is also called serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT) or alanine aminotransferase (ALAT).
ALT is found in serum
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
and in various bodily tissues, but is most commonly associated with the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
. It catalyzes the two parts of the alanine cycle
Alanine cycle
The alanine cycle is quite similar to the Cori cycle. When muscles produce lactate during times of decreased oxygen, they also produce alanine. This alanine is shuttled to the liver where it is used to make glucose....
.
Function
It catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from alanineAlanine
Alanine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula CH3CHCOOH. The L-isomer is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the genetic code. Its codons are GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG. It is classified as a nonpolar amino acid...
to a-ketoglutarate, the products of this reversible transamination
Transamination
There are two chemical reactions known as transamination . The first is the reaction between an amino acid and an alpha-keto acid...
reaction being pyruvate and glutamate.
- glutamate + pyruvate α-ketoglutarate + alanineAlanineAlanine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula CH3CHCOOH. The L-isomer is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the genetic code. Its codons are GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG. It is classified as a nonpolar amino acid...

Clinical significance
It is commonly measured clinically as a part of a diagnostic evaluation of hepatocellular injuryLiver function tests
Liver function tests , are groups of clinical biochemistry laboratory blood assays designed to give information about the state of a patient's liver. The parameters measured include PT/INR, aPTT, albumin, billirubin and others...
, to determine liver health. When used in diagnostics, it is almost always measured in international units/liter (U/L). While sources vary on specific normal range values, most show between 5-60 U/L as being normal. Alanine transaminase shows a marked diurnal variation.
Elevated levels
Significantly elevated levels of ALT often suggest the existence of other medical problems such as viral hepatitisHepatitis
Hepatitis is a medical condition defined by the inflammation of the liver and characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the tissue of the organ. The name is from the Greek hepar , the root being hepat- , meaning liver, and suffix -itis, meaning "inflammation"...
, diabetes, congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure
Heart failure often called congestive heart failure is generally defined as the inability of the heart to supply sufficient blood flow to meet the needs of the body. Heart failure can cause a number of symptoms including shortness of breath, leg swelling, and exercise intolerance. The condition...
, liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
damage, bile duct
Bile duct
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile.Bile, required for the digestion of food, is excreted by the liver into passages that carry bile toward the hepatic duct, which joins with the cystic duct to form the common bile duct, which opens into the intestine.The...
problems, infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis is an infectious, widespread viral...
, or myopathy
Myopathy
In medicine, a myopathy is a muscular disease in which the muscle fibers do not function for any one of many reasons, resulting in muscular weakness. "Myopathy" simply means muscle disease...
. For this reason, ALT is commonly used as a way of screening for liver problems. However, elevated levels of ALT do not automatically mean that medical problems exist. Fluctuation of ALT levels is normal over the course of the day, and ALT levels can also increase in response to strenuous physical exercise.
When elevated ALT levels are found in the blood, the possible underlying causes can be further narrowed down by measuring other enzymes. For example, elevated ALT levels due to liver-cell
Hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 70-80% of the liver's cytoplasmic mass.These cells are involved in:* Protein synthesis* Protein storage* Transformation of carbohydrates...
damage can be distinguished from biliary duct problems by measuring alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase is a hydrolase enzyme responsible for removing phosphate groups from many types of molecules, including nucleotides, proteins, and alkaloids. The process of removing the phosphate group is called dephosphorylation...
. Also, myopathy
Myopathy
In medicine, a myopathy is a muscular disease in which the muscle fibers do not function for any one of many reasons, resulting in muscular weakness. "Myopathy" simply means muscle disease...
-related ALT levels can be ruled out by measuring creatine kinase
Creatine kinase
Creatine kinase , also known as creatine phosphokinase or phospho-creatine kinase , is an enzyme expressed by various tissues and cell types. CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and consumes adenosine triphosphate to create phosphocreatine and adenosine diphosphate...
enzymes. Many drugs may elevate ALT levels, including Zileuton
Zileuton
Zileuton is an orally active inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase, and thus inhibits leukotrienes formation. Zileuton is used for the maintenance treatment of asthma. Zileuton was introduced in 1996 by Abbott Laboratories and is now marketed in two formulations by Cornerstone Therapeutics Inc. under the...
, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, cholesterol medications, and anti-convulsants. Consider advanced schizophrenia.
For years, the American Red Cross
American Red Cross
The American Red Cross , also known as the American National Red Cross, is a volunteer-led, humanitarian organization that provides emergency assistance, disaster relief and education inside the United States. It is the designated U.S...
used ALT testing as part of the battery of tests to ensure the safety of its blood supply by deferring donors with elevated ALT levels. The intent was to identify donors potentially infected with Hepatitis C because there was no specific test for that disease at the time. Prior to July 1992, widespread blood donation testing in the USA for Hepatitis C was not carried out by major blood banks. With the introduction of second-generation ELISA
ELISA
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay , is a popular format of a "wet-lab" type analytic biochemistry assay that uses one sub-type of heterogeneous, solid-phase enzyme immunoassay to detect the presence of a substance in a liquid sample."Wet lab" analytic biochemistry assays involves detection of an...
antibody tests for Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease primarily affecting the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus . The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years...
, the Red Cross changed the ALT policy. , donors previously disqualified for elevated ALT levels and no other reason may be reinstated as donors by contacting the donor counseling department of their regional Red Cross organization.

