
Afocal system
Encyclopedia
In optics
an afocal system (a system without focus) is an optical system that produces no net convergence or divergence of the beam, i.e. has an infinite effective focal length. This type of system can be created with a pair of optical elements where the distance between the elements is equal to the sum of each element's focal length
(d = f1+f2). A simple example of an afocal optical system is an optical telescope
imaging a star, the light entering the system is at infinity and the image it forms is at infinity (the light is collimated). Although the system does not alter the divergence of a collimated beam, it does alter the width of the beam, increasing magnification
. The magnification of such a telescope is given by
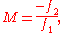
Afocal systems are used in laser optics, Infrared
and forward looking infrared
systems, camera zoom lens
es and telescopic lens attachments such as teleside converter
s, and photography setups combining cameras and telescopes (Afocal photography
).
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
an afocal system (a system without focus) is an optical system that produces no net convergence or divergence of the beam, i.e. has an infinite effective focal length. This type of system can be created with a pair of optical elements where the distance between the elements is equal to the sum of each element's focal length
Focal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light. For an optical system in air, it is the distance over which initially collimated rays are brought to a focus...
(d = f1+f2). A simple example of an afocal optical system is an optical telescope
Optical telescope
An optical telescope is a telescope which is used to gather and focus light mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum for directly viewing a magnified image for making a photograph, or collecting data through electronic image sensors....
imaging a star, the light entering the system is at infinity and the image it forms is at infinity (the light is collimated). Although the system does not alter the divergence of a collimated beam, it does alter the width of the beam, increasing magnification
Magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not in physical size. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification"...
. The magnification of such a telescope is given by
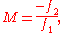
Afocal systems are used in laser optics, Infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
and forward looking infrared
Forward looking infrared
Forward looking infrared cameras, typically used on military aircraft, use an imaging technology that senses infrared radiation.The sensors installed in forward looking infrared cameras, as well as those of other thermal imaging cameras, use detection of infrared radiation, typically emitted from a...
systems, camera zoom lens
Zoom lens
A zoom lens is a mechanical assembly of lens elements for which the focal length can be varied, as opposed to a fixed focal length lens...
es and telescopic lens attachments such as teleside converter
Teleside converter
A teleside converter is a secondary lens which is mounted on the front of a photographic lens to increase the effective focal length of the lens they are attached to. They are used on cameras and video cameras with non–interchangeable lenses to increase the magnification of the image...
s, and photography setups combining cameras and telescopes (Afocal photography
Afocal photography
Afocal photography, also called afocal imaging or afocal projection is a method of photography where the camera with its lens attached is mounted over the eyepiece of another image forming system such as a optical telescope or optical microscope, with the camera lens taking the place of the human...
).

