
Adolfas Jucys
Encyclopedia
Adolfas Jucys (12 September 1904 – 4 February 1974) was a Lithuania
n theoretical physicist and mathematician, member of the Lithuanian Academy of Sciences
in 1953. He graduated from Kaunas University in 1931 and later worked with both creators of the self-consistent field method – Douglas Hartree
in Manchester (in 1938) and Vladimir Fock
in Leningrad (1949–1951). Adolfas Jucys created the scientific school of theoretical physics in Vilnius, was the head of the Department of Theoretical Physics at Vilnius University
(1944–1971). He organized the first Institute of Physics and Mathematics in Lithuania and was its first director (1956–1963), later (1971–1974) the head of the Department of Quantum Mechanical Calculations of the Institute.
Jucys developed the theory of the electronic structure of atoms, formulated in a general form the multiconfiguration Hartree–Fock equations taking into account the correlation effects. He along with his co-workers obtained the first solutions of such equations and applied them in atomic structure calculations, later introduced and developed the extended method of calculation, as well as using non-orthogonal radial orbitals (see also, SEARCH FOR A.P.Jucys as an Author.)
Adolfas Jucys with his disciples developed the mathematical apparatus of many-electron atoms with open shells. The most known work in this field is the monograph, in which the original graphical method for the quantities of the angular momentum
theory was presented. In particular, Yutsis graphs (connected simple graphs which can be partitioned into two vertex-induced trees) are named after Adolfas Jucys.
Adolfas Jucys had an interest in the representation theory of Lie groups of different rank, but the Jucys–Murphy elements in the group algebra
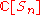 of the symmetric group
of the symmetric group
are named after his son Algimantas Adolfas Jucys
.
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
n theoretical physicist and mathematician, member of the Lithuanian Academy of Sciences
Lithuanian Academy of Sciences
The Lithuanian Academy of Sciences or LAS, founded in 1941 as the Lithuanian SSR Academy of Sciences , as an autonomous, state-subsidized establishment serving as a scientific advisory body to the government of Lithuanian SSR...
in 1953. He graduated from Kaunas University in 1931 and later worked with both creators of the self-consistent field method – Douglas Hartree
Douglas Hartree
Douglas Rayner Hartree PhD, FRS was an English mathematician and physicist most famous for the development of numerical analysis and its application to the Hartree-Fock equations of atomic physics and the construction of the meccano differential analyser.-Early life:Douglas Hartree was born in...
in Manchester (in 1938) and Vladimir Fock
Vladimir Fock
Vladimir Aleksandrovich Fock was a Soviet physicist, who did foundational work on quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics....
in Leningrad (1949–1951). Adolfas Jucys created the scientific school of theoretical physics in Vilnius, was the head of the Department of Theoretical Physics at Vilnius University
Vilnius University
Vilnius University is the oldest university in the Baltic states and one of the oldest in Eastern Europe. It is also the largest university in Lithuania....
(1944–1971). He organized the first Institute of Physics and Mathematics in Lithuania and was its first director (1956–1963), later (1971–1974) the head of the Department of Quantum Mechanical Calculations of the Institute.
Jucys developed the theory of the electronic structure of atoms, formulated in a general form the multiconfiguration Hartree–Fock equations taking into account the correlation effects. He along with his co-workers obtained the first solutions of such equations and applied them in atomic structure calculations, later introduced and developed the extended method of calculation, as well as using non-orthogonal radial orbitals (see also, SEARCH FOR A.P.Jucys as an Author.)
Adolfas Jucys with his disciples developed the mathematical apparatus of many-electron atoms with open shells. The most known work in this field is the monograph, in which the original graphical method for the quantities of the angular momentum
Angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
theory was presented. In particular, Yutsis graphs (connected simple graphs which can be partitioned into two vertex-induced trees) are named after Adolfas Jucys.
Adolfas Jucys had an interest in the representation theory of Lie groups of different rank, but the Jucys–Murphy elements in the group algebra
Group algebra
In mathematics, the group algebra is any of various constructions to assign to a locally compact group an operator algebra , such that representations of the algebra are related to representations of the group...
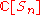 of the symmetric group
of the symmetric groupSymmetric group
In mathematics, the symmetric group Sn on a finite set of n symbols is the group whose elements are all the permutations of the n symbols, and whose group operation is the composition of such permutations, which are treated as bijective functions from the set of symbols to itself...
are named after his son Algimantas Adolfas Jucys
Algimantas Adolfas Jucys
Algimantas Adolfas Jucys was a Lithuanian theoretical physicist more prominent as a mathematician, a son of Lithuanian physicist Adolfas Jucys...
.

