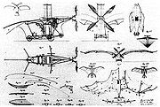
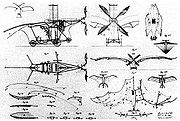
Ader Éole
Encyclopedia
Steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid.Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separate from the combustion products. Non-combustion heat sources such as solar power, nuclear power or geothermal energy may be...
-powered aircraft
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
. The Éole was named after the Greco-Roman wind god Aeolos. It was developed by Clément Ader
Clément Ader
Clément Ader was a French inventor and engineer born in Muret, Haute Garonne, and is remembered primarily for his pioneering work in aviation.- The inventor :...
in 1890. Unlike many early flying machines, the Éole did not attempt to fly by flapping its wings, but was to rely on the lift generated by its wings (mechanical copies of bat
Bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera "hand" and pteron "wing") whose forelimbs form webbed wings, making them the only mammals naturally capable of true and sustained flight. By contrast, other mammals said to fly, such as flying squirrels, gliding possums, and colugos, glide rather than fly,...
wings). Its steam engine was an unusually light weight design and drove a propeller
Propeller
A propeller is a type of fan that transmits power by converting rotational motion into thrust. A pressure difference is produced between the forward and rear surfaces of the airfoil-shaped blade, and a fluid is accelerated behind the blade. Propeller dynamics can be modeled by both Bernoulli's...
at the front of the aircraft. The machine lacked means for the pilot to control the direction of flight.
On October 9, 1890, the machine achieved a short flight of around 50 m (164 ft) at the Chateau d'Armainvilliers in Brie
Brie
Brie is a historic region of France most famous for its dairy products, especially Brie cheese. It was once divided into two sections ruled by different feudal lords: the western Brie française, corresponding roughly to the modern department of Seine-et-Marne in the Île-de-France region; the...
. It reached a height of around 20 cm (8 in). The poor power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement of actual performance of any engine or power sources...
of the steam engine and bad weather were felt to limit the flying height achieved. Ader later claimed to have flown the Éole again in September 1891, this time to a distance of 100 m (328 ft), but this claim is less substantiated.
The Éole is considered by some to be the first true aeroplane, given that it left the ground under its own power and carried a person through the air for a short distance; and therefore consider the event of October 9 to be the first flight. However, the lack of directional control and the dead-end that steam-powered aircraft were doomed to reach weigh against these claims. Ader's proponents have claimed that the Wrights' early airplanes required a catapult
Catapult
A catapult is a device used to throw or hurl a projectile a great distance without the aid of explosive devices—particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. Although the catapult has been used since ancient times, it has proven to be one of the most effective mechanisms during...
to take off; however, the Wrights did not use a catapult for their first flights in 1903, though they did for many flights in 1904 and later.
Modern attempts to recreate and evaluate the craft have met with mixed results. A full-size replica
Replica
A replica is a copy closely resembling the original concerning its shape and appearance. An inverted replica complements the original by filling its gaps. It can be a copy used for historical purposes, such as being placed in a museum. Sometimes the original never existed. For example, Difference...
built in 1990
1990 in aviation
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1990:- Events :*Pan American World Airways and Trans World Airlines, both in financial difficulty, transfer their coveted landing rights at London Heathrow Airport to American Airlines and United Airlines.-January:...
at the École Centrale Paris
École Centrale Paris
École Centrale Paris is a French university-level institution in the field of engineering. It is also known by its original name École centrale des arts et manufactures, or ECP. Founded in 1829, it is one of the oldest and most prestigious engineering schools in France and has the special status...
crashed on its first flight, injuring its pilot and leading to the termination of the experiment. Scale models, however, have been successfully flown.
Specifications (Éole)
See also
- Alexander Mozhaysky, a Russian inventor who also designed a steam-powered plane.

