Acyloin condensation
Encyclopedia
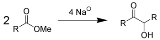
Acyloin condensation is a reductive
coupling of two carboxylic ester
s using metallic sodium
to yield an α-hydroxyketone, also known as an acyloin.
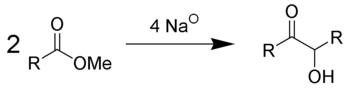 The reaction is most successful when R is aliphatic
The reaction is most successful when R is aliphatic
and inert
. To achieve the condensation, the reaction is performed in an aprotic solvent
s with a high boiling point
, such as benzene
and toluene
. Usage of protic solvents results in the Bouveault-Blanc reduction
of the separate esters rather than condensation. Depending on ring size and steric properties, but independent from high dilution, the acyloin condensation of diesters favours intramolecular cyclisation over intermolecular polymerisation.
as a trapping reagent; by this, competing reactions are efficiently subdued. Generally, yields increase considerably. The hydrolytic cleavage of the silylether gives the acyloin. To achieve a mild cleavage methanol can be used in several cases.
 Usually toluene
Usually toluene
, dioxane, tetrahydrofuran
or acyclic dialkylethers are employed as solvents. Advantageously also N-methyl-morpholine
has been used. It allowed in some cases a successful reaction, in which otherwise the reaction failed in less polar media.
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
coupling of two carboxylic ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
s using metallic sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
to yield an α-hydroxyketone, also known as an acyloin.

Aliphatic compound
In organic chemistry, aliphatic compounds are acyclic or cyclic, non-aromatic carbon compounds.Thus, aliphatic compounds are opposite to aromatic compounds.- Structure :...
and inert
Inert
-Chemistry:In chemistry, the term inert is used to describe a substance that is not chemically reactive.The noble gases were previously known as inert gases because of their perceived lack of participation in any chemical reactions...
. To achieve the condensation, the reaction is performed in an aprotic solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
s with a high boiling point
Boiling point
The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid....
, such as benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
and toluene
Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
. Usage of protic solvents results in the Bouveault-Blanc reduction
Bouveault-Blanc reduction
The Bouveault-Blanc reduction is a chemical reaction in which an ester is reduced to primary alcohols using absolute ethanol and sodium metal.This reaction is an inexpensive and large-scale alternative to lithium aluminium hydride reduction of esters....
of the separate esters rather than condensation. Depending on ring size and steric properties, but independent from high dilution, the acyloin condensation of diesters favours intramolecular cyclisation over intermolecular polymerisation.
Mechanism
The mechanism consists on four steps:- (1) Oxidative ionizationIonizationIonization is the process of converting an atom or molecule into an ion by adding or removing charged particles such as electrons or other ions. This is often confused with dissociation. A substance may dissociate without necessarily producing ions. As an example, the molecules of table sugar...
of two sodium atoms on the double bond of two ester molecules. - (2) Free radical coupling between two molecules of the homolytic ester derivative (A Würtz type couplingWurtz reactionThe Wurtz reaction, named after Charles-Adolphe Wurtz, is a coupling reaction in organic chemistry, organometallic chemistry and recently inorganic main group polymers, whereby two alkyl halides are reacted with sodium to form a new carbon-carbon bond:...
). Alkoxy-eliminations in both sides occur, producing a 1,2-diketone. - (3) Oxidative ionizationIonizationIonization is the process of converting an atom or molecule into an ion by adding or removing charged particles such as electrons or other ions. This is often confused with dissociation. A substance may dissociate without necessarily producing ions. As an example, the molecules of table sugar...
of two sodium atoms on both diketone double bonds. The sodium enodiolate is formed. - (4) NeutralizationNeutralizationIn chemistry, neutralization, or neutralisation is a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react to form a salt. Water is frequently, but not necessarily, produced as well. Neutralizations with Arrhenius acids and bases always produce water:Y and X represent a monovalent cation and anion...
with water to form the enodiol, which tautomerizesKeto-enol tautomerismIn organic chemistry, keto-enol tautomerism refers to a chemical equilibrium between a keto form and an enol . The enol and keto forms are said to be tautomers of each other...
to acyloin.
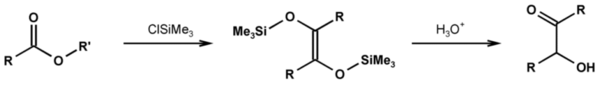
Rühlmann-method
The method according to Rühlmann employs trimethylchlorosilaneTrimethylsilyl chloride
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is a silyl halide, with a variety of different uses in chemistry. It has the formula 3SiCl, and under standard conditions it is a colourless liquid, which is stable in the absence of water...
as a trapping reagent; by this, competing reactions are efficiently subdued. Generally, yields increase considerably. The hydrolytic cleavage of the silylether gives the acyloin. To achieve a mild cleavage methanol can be used in several cases.

Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
, dioxane, tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity at standard temperature and pressure. This heterocyclic compound has the chemical formula 4O. As one of the most polar ethers with a wide liquid range, it is a useful solvent. Its main use, however, is as a precursor...
or acyclic dialkylethers are employed as solvents. Advantageously also N-methyl-morpholine
Morpholine
Morpholine is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula O2NH. This heterocycle, pictured at right, features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base; its conjugate acid is called morpholinium...
has been used. It allowed in some cases a successful reaction, in which otherwise the reaction failed in less polar media.
See also
- Benzoin condensationBenzoin condensationThe benzoin condensation is a reaction between two aromatic aldehydes, particularly benzaldehyde. The reaction is catalyzed by a nucleophile such as the cyanide anion or an N-heterocyclic carbene. The reaction product is an aromatic acyloin with benzoin as the parent compound...
- Bouveault-Blanc reductionBouveault-Blanc reductionThe Bouveault-Blanc reduction is a chemical reaction in which an ester is reduced to primary alcohols using absolute ethanol and sodium metal.This reaction is an inexpensive and large-scale alternative to lithium aluminium hydride reduction of esters....
- Claisen condensationClaisen condensationThe Claisen condensation is a carbon–carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base, resulting in a β-keto ester or a β-diketone...
- Dieckmann condensationDieckmann condensationThe Dieckmann condensation is the intramolecular chemical reaction of diesters with base to give β-ketoesters. It is named after the German chemist Walter Dieckmann . The equivalent intermolecular reaction is the Claisen condensation....

