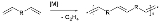
Acyclic diene metathesis
Encyclopedia
Acyclic diene metathesis or ADMET is a special type of olefin metathesis
used to polymerize certain terminal diene
s to polyene
s:
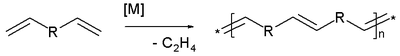 The new double bonds formed can be in cis- or trans-configuation.
The new double bonds formed can be in cis- or trans-configuation.
It is a type of step growth
condensation reaction
whereas the other metathesis reaction, ring-opening metathesis polymerization is a chain-growth polymerization.
ADMET was introduced by K. B. Wagener in 1991 . He successfully polymerized 1,5-hexadiene to polybutadiene
with 70% trans double bonds and Weight average molar mass of 28000.
ADMET has been applied in the synthesis of new supramolecular structures .
Olefin metathesis
Olefin metathesis or transalkylidenation is an organic reaction that entails redistribution of alkylene fragments by the scission of carbon - carbon double bonds in olefins . Its advantages include the creation of fewer sideproducts and hazardous wastes. Yves Chauvin, Robert H. Grubbs, and Richard R...
used to polymerize certain terminal diene
Diene
In organic chemistry a diene or diolefin is a hydrocarbon that contains two carbon double bonds.Conjugated dienes are functional groups, with a general formula of CnH2n-2. Dienes and alkynes are functional isomers...
s to polyene
Polyene
Polyenes are poly-unsaturated organic compounds that contain one or more sequences of alternating double and single carbon-carbon bonds. These double carbon-carbon bonds interact in a process known as conjugation, which results in an overall lower energy state of the molecule.Organic compounds with...
s:
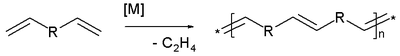
It is a type of step growth
Step-growth polymerization
Step-growth polymerization refers to a type of polymerization mechanism in which bi-functional or multifunctional monomers react to form first dimers, then trimers, longer oligomers and eventually long chain polymers. Many naturally occurring and some synthetic polymers are produced by step-growth...
condensation reaction
Condensation reaction
A condensation reaction is a chemical reaction in which two molecules or moieties combine to form one single molecule, together with the loss of a small molecule. When this small molecule is water, it is known as a dehydration reaction; other possible small molecules lost are hydrogen chloride,...
whereas the other metathesis reaction, ring-opening metathesis polymerization is a chain-growth polymerization.
ADMET was introduced by K. B. Wagener in 1991 . He successfully polymerized 1,5-hexadiene to polybutadiene
Polybutadiene
Polybutadiene is a synthetic rubber that is a polymer formed from the polymerization process of the monomer 1,3-butadiene.It has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tires, which consumes about 70% of the production...
with 70% trans double bonds and Weight average molar mass of 28000.
ADMET has been applied in the synthesis of new supramolecular structures .

