
Actinomycosis in animals
Encyclopedia


Actinomycosis
Actinomycosis is an infectious bacterial disease caused by Actinomyces species such as Actinomyces israelii or A. gerencseriae. It can also be caused by Propionibacterium propionicus, and the condition is likely to be polymicrobial aerobic anaerobic infection.Actinomycosis occurs rarely in humans...
are usually due to A. israelii).
It is a quite common condition in cattle, where it is referred to as lumpy jaw (English) or senfed (moroccan arabic
Moroccan Arabic
Moroccan Arabic is the variety of Arabic spoken in the Arabic-speaking areas of Morocco. For official communications, the government and other public bodies use Modern Standard Arabic, as is the case in most Arabic-speaking countries. A mixture of French and Moroccan Arabic is used in business...
).
But it can also occur in horse
Horse
The horse is one of two extant subspecies of Equus ferus, or the wild horse. It is a single-hooved mammal belonging to the taxonomic family Equidae. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature into the large, single-toed animal of today...
s, swine, and dog
Dog
The domestic dog is a domesticated form of the gray wolf, a member of the Canidae family of the order Carnivora. The term is used for both feral and pet varieties. The dog may have been the first animal to be domesticated, and has been the most widely kept working, hunting, and companion animal in...
s (rarely in sheep).
In all these species, it results in cold abscess, with granulomatous formations on the fistulised place.
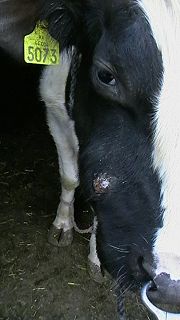
Actinomycosis in cattle
It is a common conditions in weaned calves and young bulls and heifers.The disease has a chronic course, and the general condition can remain quite good.
There is a swelling of the maxilla
Maxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
and mandible
Mandible
The mandible pronunciation or inferior maxillary bone forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place...
. Fistulisation
Fistula
In medicine, a fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between two epithelium-lined organs or vessels that normally do not connect. It is generally a disease condition, but a fistula may be surgically created for therapeutic reasons.-Locations:Fistulas can develop in various parts of the...
occurs after some days, leaving a thick, yellowish, non-odorous pus
Pus
Pus is a viscous exudate, typically whitish-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammatory during infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection of pus within or beneath the epidermis is known as a pustule or...
, with mineralised, 2 to 5 mm grains therein.
Later on, a granuloma will form in the place of fistulisation.
The bony lesions are followed by periostitis
Periostitis
Periostitis, also known as periostalgia, is a medical condition caused by inflammation of the periosteum, a layer of connective tissue that surrounds bone...
, with permanent deformation of the facial bones.

