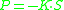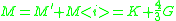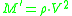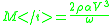Acoustic rheometer
Encyclopedia
An acoustic rheometer employs piezo-electric crystal
that can easily launch a successive wave
of extensions and contractions into the fluid
. It applies an oscillating extensional stress to the system. System response can be interpreted in terms of extensional rheology.
It is well known that properties of viscoelastic fluid are characterised in shear rheology with a shear modulus G, which links shear stress
Tij and shear strain Sij
There is similar linear relationship in extensional rheology between extensional stress P, extensional strain S and extensional modulus K:
Detail theoretical analysis indicates that propagation of sound
or ultrasound
through a viscoelastic fluid depends on both shear modulus G and extensional modulus K,. It is convenient to introduce a combined longitudinal modulus M:
There are simple equations that express longitudinal modulus in terms of acoustic properties, sound speed V and attenuation
α
Acoustic rheometer measures sound speed and attenuation
of ultrasound
for a set of frequencies in the megahertz range. These measurable parameters can be converted into real and imaginary components of longitudinal modulus.
This type of rheometer works at much higher frequencies than others. It is suitable for studying effects with much shorter relaxation time
s than any other rheometer.
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
that can easily launch a successive wave
Wave
In physics, a wave is a disturbance that travels through space and time, accompanied by the transfer of energy.Waves travel and the wave motion transfers energy from one point to another, often with no permanent displacement of the particles of the medium—that is, with little or no associated mass...
of extensions and contractions into the fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
. It applies an oscillating extensional stress to the system. System response can be interpreted in terms of extensional rheology.
- This interpretation is based on a link between shear rheology, extensional rheology and acousticsAcousticsAcoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of all mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics...
. Relationship between these scientific disciplines was described in details by Litovitz and Davis in 1964 .
It is well known that properties of viscoelastic fluid are characterised in shear rheology with a shear modulus G, which links shear stress
Shear stress
A shear stress, denoted \tau\, , is defined as the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. Shear stress arises from the force vector component parallel to the cross section...
Tij and shear strain Sij
There is similar linear relationship in extensional rheology between extensional stress P, extensional strain S and extensional modulus K:
Detail theoretical analysis indicates that propagation of sound
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
or ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
through a viscoelastic fluid depends on both shear modulus G and extensional modulus K,. It is convenient to introduce a combined longitudinal modulus M:
There are simple equations that express longitudinal modulus in terms of acoustic properties, sound speed V and attenuation
Attenuation
In physics, attenuation is the gradual loss in intensity of any kind of flux through a medium. For instance, sunlight is attenuated by dark glasses, X-rays are attenuated by lead, and light and sound are attenuated by water.In electrical engineering and telecommunications, attenuation affects the...
α
Acoustic rheometer measures sound speed and attenuation
Attenuation
In physics, attenuation is the gradual loss in intensity of any kind of flux through a medium. For instance, sunlight is attenuated by dark glasses, X-rays are attenuated by lead, and light and sound are attenuated by water.In electrical engineering and telecommunications, attenuation affects the...
of ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
for a set of frequencies in the megahertz range. These measurable parameters can be converted into real and imaginary components of longitudinal modulus.
- Sound speed determines M', which is a measure of system elasticityElasticity (physics)In physics, elasticity is the physical property of a material that returns to its original shape after the stress that made it deform or distort is removed. The relative amount of deformation is called the strain....
. It can be converted into fluid compressibility. - Attenuation determines M", which is a measure of viscous properties, energy dissipationDissipationIn physics, dissipation embodies the concept of a dynamical system where important mechanical models, such as waves or oscillations, lose energy over time, typically from friction or turbulence. The lost energy converts into heat, which raises the temperature of the system. Such systems are called...
. This parameter can be considered as extensional viscosityExtensional viscosityExtensional viscosity is a viscosity coefficient when applied stress is extensional stress.Extensional viscosity can be measured using rheometers that apply extensional stress... - In the case of Newtonian liquid attenuation yields information on the volume viscosityVolume viscosityVolume viscosity becomes important only for such effects where fluid compressibility is essential. Examples would include shock waves and sound propagation...
. Stokes' law (sound attenuation) provides relationship among attenuationAttenuationIn physics, attenuation is the gradual loss in intensity of any kind of flux through a medium. For instance, sunlight is attenuated by dark glasses, X-rays are attenuated by lead, and light and sound are attenuated by water.In electrical engineering and telecommunications, attenuation affects the...
, dynamic viscosity and volume viscosityVolume viscosityVolume viscosity becomes important only for such effects where fluid compressibility is essential. Examples would include shock waves and sound propagation...
of the Newtonian fluid.
This type of rheometer works at much higher frequencies than others. It is suitable for studying effects with much shorter relaxation time
Relaxation time
In the physical sciences, relaxation usually means the return of a perturbed system into equilibrium.Each relaxation process can be characterized by a relaxation time τ...
s than any other rheometer.