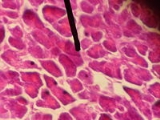
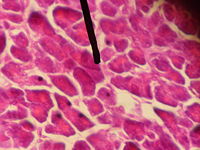
Acinus
Encyclopedia
An acinus refers to any cluster of cells that resembles a many-lobed "berry," such as a raspberry
(acinus is Latin
for berry). The berry-shaped termination of an exocrine gland
, where the secretion is produced, is acinar in form, as is the alveolar sac containing multiple alveoli in the lungs.
The thyroid
follicles can also be considered of acinar formation but in this case the follicles, being part of an endocrine gland, act as a hormonal deposit rather than to facilitate secretion.
Mucous acini usually stain pale, while serous acini usually stain dark.
The term "acinus" is considered synonymous with alveolus
by some sources, but not all.
Raspberry
The raspberry or hindberry is the edible fruit of a multitude of plant species in the genus Rubus, most of which are in the subgenus Idaeobatus; the name also applies to these plants themselves...
(acinus is Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
for berry). The berry-shaped termination of an exocrine gland
Exocrine gland
Exocrine glands are a type of ductal glands that secrete their products into ducts that lead directly into the external environment...
, where the secretion is produced, is acinar in form, as is the alveolar sac containing multiple alveoli in the lungs.
Exocrine glands
Acinar exocrine glands are found in many organs, including:- the stomachStomachThe stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
- the sebaceous glandSebaceous glandThe sebaceous glands are microscopic glands in the skin that secrete an oily/waxy matter, called sebum, to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair of mammals...
of the scalpScalpThe scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the face anteriorly and the neck to the sides and posteriorly.-Layers:It is usually described as having five layers, which can conveniently be remembered as a mnemonic:... - the salivary glands of the tongueTongueThe tongue is a muscular hydrostat on the floors of the mouths of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication. It is the primary organ of taste , as much of the upper surface of the tongue is covered in papillae and taste buds. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly...
- the liverLiverThe liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
- the lacrimal glands
- the mammary glands
- the pancreasPancreasThe pancreas is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine system of vertebrates. It is both an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin, as well as a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist...
- the bulbourethral (Cowper's) glandsBulbourethral glandA bulbourethral gland, also called a Cowper's gland for anatomist William Cowper, is one of two small exocrine glands present in the reproductive system of human males...
The thyroid
Thyroid
The thyroid gland or simply, the thyroid , in vertebrate anatomy, is one of the largest endocrine glands. The thyroid gland is found in the neck, below the thyroid cartilage...
follicles can also be considered of acinar formation but in this case the follicles, being part of an endocrine gland, act as a hormonal deposit rather than to facilitate secretion.
Mucous acini usually stain pale, while serous acini usually stain dark.
The term "acinus" is considered synonymous with alveolus
Alveolus (disambiguation)
Alveolus is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.Alveolus may refer to:In anatomy and zoology in general* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs* Alveolar gland...
by some sources, but not all.


