Achalasia
Encyclopedia
Achalasia also known as esophageal achalasia, achalasia cardiae, cardiospasm, and esophageal aperistalsis, is an esophageal motility disorder
involving the smooth muscle layer of the esophagus
and the lower esophageal sphincter. It is characterized by incomplete LES relaxation, increased LES tone, and lack of peristalsis
of the esophagus (inability of smooth muscle to move food down the esophagus) in the absence of other explanations like cancer or fibrosis.
Achalasia is characterized by difficulty swallowing
, regurgitation
, and sometimes chest pain
. Diagnosis is reached with esophageal manometry and barium swallow
radiographic studies. Various treatments are available, although none cure the condition. Certain medications or Botox
may be used in some cases, but more permanent relief is brought by esophageal dilatation
and surgical cleaving of the muscle (Heller myotomy
).
The most common form is primary achalasia, which has no known underlying cause. It is due to the failure of distal esophageal inhibitory neurons. However, a small proportion occurs secondary to other conditions, such as esophageal cancer
or Chagas disease
(an infectious disease common in South America). Achalasia affects about one person in 100,000 per year.
(difficulty in swallowing), regurgitation
of undigested food, chest pain
behind the sternum, and weight loss. Dysphagia tends to become progressively worse over time and to involve both fluids and solids. Some people may also experience cough
ing when lying in a horizontal position.
The chest pain experienced, also known as cardio spasm and non-cardiac chest pain can often be mistaken for a heart attack. It can be extremely painful in some sufferers. Food and liquid, including saliva, are retained in the esophagus and may be inhaled into the lungs (aspiration
).
(GERD), hiatus hernia
, and even psychosomatic disorders.
Specific tests for achalasia are barium swallow
and esophageal manometry. In addition, endoscopy
of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum (esophagogastroduodenoscopy
or EGD), with or without endoscopic ultrasound
, is typically performed to rule out the possibility of cancer. The internal tissue of the esophagus generally appears normal in endoscopy
, although a "pop" may be observed as the scope is passed through the non-relaxing lower esophageal sphincter with some difficulty, and food debris may be found above the LES.
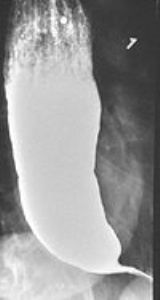
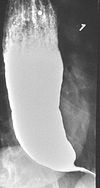 The patient swallows a barium solution, with continuous fluoroscopy
The patient swallows a barium solution, with continuous fluoroscopy
(X-ray recording) to observe the flow of the fluid through the esophagus. Normal peristaltic movement of the esophagus is not seen. There is acute tapering at the lower esophageal sphincter and narrowing at the gastro-esophageal junction
, producing a "bird's beak" or "rat's tail" appearance. The esophagus above the narrowing is often dilated (enlarged) to varying degrees as the esophagus is gradually stretched over time. An air-fluid margin is often seen over the barium column due to the lack of peristalsis. A five-minutes timed barium swallow can provide a useful benchmark to measure the effectiveness of treatment.
 Because of its sensitivity, manometry (esophageal motility study) is considered the key test for establishing the diagnosis. A thin tube is inserted through the nose, and the patient is instructed to swallow several times. The probe measures muscle contractions in different parts of the esophagus during the act of swallowing. Manometry reveals failure of the LES to relax with swallowing and lack of functional peristalsis in the smooth muscle esophagus.
Because of its sensitivity, manometry (esophageal motility study) is considered the key test for establishing the diagnosis. A thin tube is inserted through the nose, and the patient is instructed to swallow several times. The probe measures muscle contractions in different parts of the esophagus during the act of swallowing. Manometry reveals failure of the LES to relax with swallowing and lack of functional peristalsis in the smooth muscle esophagus.
, the removal of a tissue sample during endoscopy, is not typically necessary in achalasia, but if performed shows hypertrophied
musculature and absence of certain nerve cells of the myenteric plexus, a network of nerve fibers that controls esophageal peristalsis.
significantly improves outcomes in 75% of people with mild or moderate disease. Surgical myotomy provides greater benefit than either botulinum toxin or dilation in those who fail medical management.
, including ketchup, citrus, chocolate, alcohol, and caffeine, may need to be avoided.
, and nitrates such as isosorbide dinitrate
and nitroglycerin. However, many patients experience unpleasant side effects such as headache
and swollen feet, and these drugs often stop helping after several months.
Botulinum toxin
(Botox) may be injected into the lower esophageal sphincter to paralyze the muscles holding it shut. As in the case of cosmetic Botox, the effect is only temporary and lasts about 6 months. Botox injections cause scarring in the sphincter which may increase the difficulty of later Heller myotomy
. This therapy is only recommended for patients who cannot risk surgery, such as elderly persons in poor health.
or dilatation, the muscle fibers are stretched and slightly torn by forceful inflation of a balloon placed inside the lower esophageal sphincter. Gastroenterologists who specialize in achalasia have performed many of these forceful balloon dilatations achieve better results and fewer perforations. There is always a small risk of a perforation which requires immediate surgical repair. Pneumatic dilatation causes some scarring which may increase the difficulty of Heller myotomy
if the surgery is needed later. Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
occurs after pneumatic dilatation in some patients. Pneumatic dilatation is most effective on the long term in patients over the age of 40; the benefits tend to be shorter-lived in younger patients. It may need to be repeated with larger balloons for maximum effectiveness.
helps 90% of achalasia patients. It can usually be performed by a keyhole approach
, or laparoscopically. The myotomy is a lengthwise cut along the esophagus, starting above the LES and extending down onto the stomach a little way. The esophagus is made of several layers, and the myotomy only cuts through the outside muscle layers which are squeezing it shut, leaving the inner muscosal layer intact. A partial fundoplication
or "wrap" is generally added in order to prevent excessive reflux
, which can cause serious damage to the esophagus over time. After surgery, patients should keep to a soft diet
for several weeks to a month, avoiding foods that can aggravate reflux.
Most recommended fundoplication along with Heller's myotomy is Dor's fundoplication. It consists of 180 to 200 degree anterior wrap around the esophagus. It provides excellent result as compared to Nissen's fundoplication which is associated with higher incidence of the post surgery dysphagia.
after many years. In addition, some physicians recommend pH testing and endoscopy to check for reflux damage, which may lead to a premalignant condition known as Barrett's esophagus
or a stricture if untreated.
Esophageal motility disorder
An esophageal motility disorder is a medical disorder causing difficulty in swallowing, regurgitation of food and a spasm-type pain which can be brought on by an allergic reaction to certain foods and by autoimmune disease affecting the muscles such as myositis.- Anatomy :The tubular esophagus is a...
involving the smooth muscle layer of the esophagus
Esophagus
The esophagus is an organ in vertebrates which consists of a muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach. During swallowing, food passes from the mouth through the pharynx into the esophagus and travels via peristalsis to the stomach...
and the lower esophageal sphincter. It is characterized by incomplete LES relaxation, increased LES tone, and lack of peristalsis
Peristalsis
Peristalsis is a radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles which propagates in a wave down the muscular tube, in an anterograde fashion. In humans, peristalsis is found in the contraction of smooth muscles to propel contents through the digestive tract. Earthworms use a similar...
of the esophagus (inability of smooth muscle to move food down the esophagus) in the absence of other explanations like cancer or fibrosis.
Achalasia is characterized by difficulty swallowing
Dysphagia
Dysphagia is the medical term for the symptom of difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, the term is sometimes used as a condition in its own right. Sufferers are sometimes unaware of their dysphagia....
, regurgitation
Regurgitation (digestion)
Regurgitation is the expulsion of material from the mouth, pharynx, or esophagus, usually characterized by the presence of undigested food or blood.Regurgitation is used by a number of species to feed their young...
, and sometimes chest pain
Chest pain
Chest pain may be a symptom of a number of serious conditions and is generally considered a medical emergency. Even though it may be determined that the pain is non-cardiac in origin, this is often a diagnosis of exclusion made after ruling out more serious causes of the pain.-Differential...
. Diagnosis is reached with esophageal manometry and barium swallow
Barium swallow
A barium swallow is a medical imaging procedure used to examine the upper GI tract, which includes the esophagus and, to a lesser extent, the stomach.-Principle:...
radiographic studies. Various treatments are available, although none cure the condition. Certain medications or Botox
Botulinum toxin
Botulinum toxin is a protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, and is considered the most powerful neurotoxin ever discovered. Botulinum toxin causes Botulism poisoning, a serious and life-threatening illness in humans and animals...
may be used in some cases, but more permanent relief is brought by esophageal dilatation
Esophageal dilatation
Esophageal dilatation is a therapeutic endoscopic procedure that enlarges the lumen of the esophagus.-Indications:It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions that result in narrowing of the esophageal lumen, or decrease motility in the distal esophagus...
and surgical cleaving of the muscle (Heller myotomy
Heller myotomy
Heller myotomy is a surgical procedure in which the muscles of the cardia are cut, allowing food and liquids to pass to the stomach...
).
The most common form is primary achalasia, which has no known underlying cause. It is due to the failure of distal esophageal inhibitory neurons. However, a small proportion occurs secondary to other conditions, such as esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer is malignancy of the esophagus. There are various subtypes, primarily squamous cell cancer and adenocarcinoma . Squamous cell cancer arises from the cells that line the upper part of the esophagus...
or Chagas disease
Chagas disease
Chagas disease is a tropical parasitic disease caused by the flagellate protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi. T. cruzi is commonly transmitted to humans and other mammals by an insect vector, the blood-sucking insects of the subfamily Triatominae most commonly species belonging to the Triatoma, Rhodnius,...
(an infectious disease common in South America). Achalasia affects about one person in 100,000 per year.
Signs and symptoms
The main symptoms of achalasia are dysphagiaDysphagia
Dysphagia is the medical term for the symptom of difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, the term is sometimes used as a condition in its own right. Sufferers are sometimes unaware of their dysphagia....
(difficulty in swallowing), regurgitation
Regurgitation (digestion)
Regurgitation is the expulsion of material from the mouth, pharynx, or esophagus, usually characterized by the presence of undigested food or blood.Regurgitation is used by a number of species to feed their young...
of undigested food, chest pain
Chest pain
Chest pain may be a symptom of a number of serious conditions and is generally considered a medical emergency. Even though it may be determined that the pain is non-cardiac in origin, this is often a diagnosis of exclusion made after ruling out more serious causes of the pain.-Differential...
behind the sternum, and weight loss. Dysphagia tends to become progressively worse over time and to involve both fluids and solids. Some people may also experience cough
Cough
A cough is a sudden and often repetitively occurring reflex which helps to clear the large breathing passages from secretions, irritants, foreign particles and microbes...
ing when lying in a horizontal position.
The chest pain experienced, also known as cardio spasm and non-cardiac chest pain can often be mistaken for a heart attack. It can be extremely painful in some sufferers. Food and liquid, including saliva, are retained in the esophagus and may be inhaled into the lungs (aspiration
Pulmonary aspiration
Pulmonary aspiration is the entry of material from the oropharynx or gastrointestinal tract into the larynx and lower respiratory tract...
).
Diagnosis
Due to the similarity of symptoms, achalasia can be mistaken for more common disorders such as gastroesophageal reflux diseaseGastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease , gastro-oesophageal reflux disease , gastric reflux disease, or acid reflux disease is chronic symptoms or mucosal damage caused by stomach acid coming up from the stomach into the esophagus...
(GERD), hiatus hernia
Hiatus hernia
A hiatus hernia or hiatal hernia is the protrusion of the upper part of the stomach into the thorax through a tear or weakness in the diaphragm.- Classification :There are two major kinds of hiatus hernia:...
, and even psychosomatic disorders.
Specific tests for achalasia are barium swallow
Barium swallow
A barium swallow is a medical imaging procedure used to examine the upper GI tract, which includes the esophagus and, to a lesser extent, the stomach.-Principle:...
and esophageal manometry. In addition, endoscopy
Endoscopy
Endoscopy means looking inside and typically refers to looking inside the body for medical reasons using an endoscope , an instrument used to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike most other medical imaging devices, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ...
of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum (esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
For other expansions of the initialism "OGD", see the disambiguation page.In medicine , esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract up to the duodenum...
or EGD), with or without endoscopic ultrasound
Endoscopic ultrasound
Endoscopic ultrasound or echo-endoscopy is a medical procedure in endoscopy is combined with ultrasound to obtain images of the internal organs in the chest and abdomen. It can be used to visualize the wall of these organs, or to look at adjacent structures...
, is typically performed to rule out the possibility of cancer. The internal tissue of the esophagus generally appears normal in endoscopy
Endoscopy
Endoscopy means looking inside and typically refers to looking inside the body for medical reasons using an endoscope , an instrument used to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike most other medical imaging devices, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ...
, although a "pop" may be observed as the scope is passed through the non-relaxing lower esophageal sphincter with some difficulty, and food debris may be found above the LES.
Barium swallow

Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy is an imaging technique commonly used by physicians to obtain real-time moving images of the internal structures of a patient through the use of a fluoroscope. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and fluorescent screen between which a patient is placed...
(X-ray recording) to observe the flow of the fluid through the esophagus. Normal peristaltic movement of the esophagus is not seen. There is acute tapering at the lower esophageal sphincter and narrowing at the gastro-esophageal junction
Cardia
The cardia is the anatomical term for the part of the stomach attached to the esophagus. The cardia begins immediately distal to the z-line of the gastroesophageal junction, where the squamous epithelium of the esophagus gives way to the columnar epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract.Just...
, producing a "bird's beak" or "rat's tail" appearance. The esophagus above the narrowing is often dilated (enlarged) to varying degrees as the esophagus is gradually stretched over time. An air-fluid margin is often seen over the barium column due to the lack of peristalsis. A five-minutes timed barium swallow can provide a useful benchmark to measure the effectiveness of treatment.
Esophageal manometry

Biopsy
BiopsyBiopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
, the removal of a tissue sample during endoscopy, is not typically necessary in achalasia, but if performed shows hypertrophied
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It should be distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number...
musculature and absence of certain nerve cells of the myenteric plexus, a network of nerve fibers that controls esophageal peristalsis.
Treatment
Sublingual nifedipineNifedipine
Nifedipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker...
significantly improves outcomes in 75% of people with mild or moderate disease. Surgical myotomy provides greater benefit than either botulinum toxin or dilation in those who fail medical management.
Lifestyle changes
Both before and after treatment, achalasia patients may need to eat slowly, chew very well, drink plenty of water with meals, and avoid eating near bedtime. Raising the head of the bed or sleeping with a wedge pillow promotes emptying of the esophagus by gravity. After surgery or pneumatic dilatation, proton pump inhibitors can help prevent reflux damage by inhibiting gastric acid secretion; and foods that can aggravate refluxGastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease , gastro-oesophageal reflux disease , gastric reflux disease, or acid reflux disease is chronic symptoms or mucosal damage caused by stomach acid coming up from the stomach into the esophagus...
, including ketchup, citrus, chocolate, alcohol, and caffeine, may need to be avoided.
Medication
Drugs that reduce LES pressure are useful. These include calcium channel blockers such as nifedipineNifedipine
Nifedipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker...
, and nitrates such as isosorbide dinitrate
Isosorbide dinitrate
Isosorbide dinitrate is a nitrate used pharmacologically as a vasodilator, e.g. in angina pectoris but also for anal fissure, a condition which is known to involve decreased blood supply leading to poor healing...
and nitroglycerin. However, many patients experience unpleasant side effects such as headache
Headache
A headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
and swollen feet, and these drugs often stop helping after several months.
Botulinum toxin
Botulinum toxin
Botulinum toxin is a protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, and is considered the most powerful neurotoxin ever discovered. Botulinum toxin causes Botulism poisoning, a serious and life-threatening illness in humans and animals...
(Botox) may be injected into the lower esophageal sphincter to paralyze the muscles holding it shut. As in the case of cosmetic Botox, the effect is only temporary and lasts about 6 months. Botox injections cause scarring in the sphincter which may increase the difficulty of later Heller myotomy
Heller myotomy
Heller myotomy is a surgical procedure in which the muscles of the cardia are cut, allowing food and liquids to pass to the stomach...
. This therapy is only recommended for patients who cannot risk surgery, such as elderly persons in poor health.
Pneumatic dilatation
In balloon (pneumatic) dilationEsophageal dilatation
Esophageal dilatation is a therapeutic endoscopic procedure that enlarges the lumen of the esophagus.-Indications:It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions that result in narrowing of the esophageal lumen, or decrease motility in the distal esophagus...
or dilatation, the muscle fibers are stretched and slightly torn by forceful inflation of a balloon placed inside the lower esophageal sphincter. Gastroenterologists who specialize in achalasia have performed many of these forceful balloon dilatations achieve better results and fewer perforations. There is always a small risk of a perforation which requires immediate surgical repair. Pneumatic dilatation causes some scarring which may increase the difficulty of Heller myotomy
Heller myotomy
Heller myotomy is a surgical procedure in which the muscles of the cardia are cut, allowing food and liquids to pass to the stomach...
if the surgery is needed later. Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease , gastro-oesophageal reflux disease , gastric reflux disease, or acid reflux disease is chronic symptoms or mucosal damage caused by stomach acid coming up from the stomach into the esophagus...
occurs after pneumatic dilatation in some patients. Pneumatic dilatation is most effective on the long term in patients over the age of 40; the benefits tend to be shorter-lived in younger patients. It may need to be repeated with larger balloons for maximum effectiveness.
Surgery
Heller myotomyHeller myotomy
Heller myotomy is a surgical procedure in which the muscles of the cardia are cut, allowing food and liquids to pass to the stomach...
helps 90% of achalasia patients. It can usually be performed by a keyhole approach
Laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive surgery , bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique in which operations in the abdomen are performed through small incisions as opposed to the larger incisions needed in laparotomy.Keyhole surgery makes use of images...
, or laparoscopically. The myotomy is a lengthwise cut along the esophagus, starting above the LES and extending down onto the stomach a little way. The esophagus is made of several layers, and the myotomy only cuts through the outside muscle layers which are squeezing it shut, leaving the inner muscosal layer intact. A partial fundoplication
Nissen fundoplication
Nissen fundoplication is a surgical procedure to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease and hiatus hernia. In GERD it is usually performed when medical therapy has failed, but with paraesophageal hiatus hernia, it is the first-line procedure...
or "wrap" is generally added in order to prevent excessive reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease , gastro-oesophageal reflux disease , gastric reflux disease, or acid reflux disease is chronic symptoms or mucosal damage caused by stomach acid coming up from the stomach into the esophagus...
, which can cause serious damage to the esophagus over time. After surgery, patients should keep to a soft diet
Soft diet
A soft diet is recommended in many situations, including some types of dysphagia , surgery involving the jaw, mouth or gastrointestinal tract, and pain from newly adjusted dental braces....
for several weeks to a month, avoiding foods that can aggravate reflux.
Most recommended fundoplication along with Heller's myotomy is Dor's fundoplication. It consists of 180 to 200 degree anterior wrap around the esophagus. It provides excellent result as compared to Nissen's fundoplication which is associated with higher incidence of the post surgery dysphagia.
Follow-up
Follow-up monitoring: Even after successful treatment of achalasia, swallowing may still deteriorate over time. The esophagus should be checked every year or two with a timed barium swallow because some may need pneumatic dilatations, a repeat myotomy, or even esophagectomyEsophagectomy
Esophagectomy or Oesophagectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the esophagus .-Purpose:...
after many years. In addition, some physicians recommend pH testing and endoscopy to check for reflux damage, which may lead to a premalignant condition known as Barrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus refers to an abnormal change in the cells of the inferior portion of the esophagus. A positive diagnosis generally requires observing specific macroscopic and microscopic changes...
or a stricture if untreated.
Epidemiology
Incidence of achalasia is 1 to 2 per 200,000. Disease affects young adults in their 20s and 30s.External links
- Center for Esophageal Disorders Website of UCLA Health System
- U.S. Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract - Achalasia treatment guidelines.
- Patient.co.uk - Achalasia patient information.
- Barium Swallow of Achalasia - from MedPix Images

