Acceptor (semiconductors)
Encyclopedia
In semiconductor physics, an acceptor is a dopant
atom that when added to a semiconductor
can form p-type
regions.
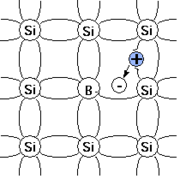 For example, when silicon
For example, when silicon
(Si), having four valence electron
s, needs to be doped as a p-type semiconductor
, elements from group III
like boron
(B) or aluminium
(Al), having three valence electrons, can be used. The latter elements are also called trivalent impurities. Other trivalent dopants include indium
(In) and gallium
(Ga).
When substituting an Si atom in the crystal lattice, the three valence electrons of boron form covalent bond
s with three of the Si neighbours but the bond with the fourth neighbour remains unsatisfied. The unsatisfied bond attracts electrons from the neighbouring bonds. At room temperature
, an electron from the neighbouring bond will jump to repair the unsatisfied bond thus leaving a hole
(a place where an electron is deficient). The hole will again attract an electron from the neighbouring bond to repair this unsatisfied bond. This chain-like process results in the hole acting as a charge carrier
, moving around the crystal and can carry a current. The initially electroneutral acceptor becomes negatively charged (ionised).
Dopant
A dopant, also called a doping agent, is a trace impurity element that is inserted into a substance in order to alter the electrical properties or the optical properties of the substance. In the case of crystalline substances, the atoms of the dopant very commonly take the place of elements that...
atom that when added to a semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
can form p-type
P-type semiconductor
A P-type semiconductor is obtained by carrying out a process of doping: that is, adding a certain type of atoms to the semiconductor in order to increase the number of free charge carriers ....
regions.

Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
(Si), having four valence electron
Valence electron
In chemistry, valence electrons are the electrons of an atom that can participate in the formation of chemical bonds with other atoms. Valence electrons are the "own" electrons, present in the free neutral atom, that combine with valence electrons of other atoms to form chemical bonds. In a single...
s, needs to be doped as a p-type semiconductor
P-type semiconductor
A P-type semiconductor is obtained by carrying out a process of doping: that is, adding a certain type of atoms to the semiconductor in order to increase the number of free charge carriers ....
, elements from group III
Boron group
The boron group is the series of elements in group 13 of the periodic table, comprising boron , aluminium , gallium , indium , thallium , and ununtrium . The elements in the boron group are characterized by having three electrons in their outer energy levels...
like boron
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
(B) or aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
(Al), having three valence electrons, can be used. The latter elements are also called trivalent impurities. Other trivalent dopants include indium
Indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two...
(In) and gallium
Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies...
(Ga).
When substituting an Si atom in the crystal lattice, the three valence electrons of boron form covalent bond
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a form of chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding....
s with three of the Si neighbours but the bond with the fourth neighbour remains unsatisfied. The unsatisfied bond attracts electrons from the neighbouring bonds. At room temperature
Room temperature
-Comfort levels:The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers has listings for suggested temperatures and air flow rates in different types of buildings and different environmental circumstances. For example, a single office in a building has an occupancy ratio per...
, an electron from the neighbouring bond will jump to repair the unsatisfied bond thus leaving a hole
Electron hole
An electron hole is the conceptual and mathematical opposite of an electron, useful in the study of physics, chemistry, and electrical engineering. The concept describes the lack of an electron at a position where one could exist in an atom or atomic lattice...
(a place where an electron is deficient). The hole will again attract an electron from the neighbouring bond to repair this unsatisfied bond. This chain-like process results in the hole acting as a charge carrier
Charge carrier
In physics, a charge carrier is a free particle carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric currents in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons and ions...
, moving around the crystal and can carry a current. The initially electroneutral acceptor becomes negatively charged (ionised).

