
AQUAL
Encyclopedia
AQUAL is a theory of gravity based on Modified Newtonian Dynamics
(MOND), but using a Lagrangian
. It was developed by Jacob Bekenstein
and Mordehai Milgrom
in their 1984 paper, "Does the missing mass problem signal the breakdown of Newtonian gravity?". "AQUAL" stands for "AQUAdratic Lagrangian".
The gravitational force law obtained from MOND,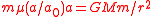 ,
,
has a serious defect: it violates Newton's third law of motion, and therefore fails to conserve
momentum and energy. To see this, consider two objects with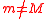 ; then we have
; then we have
but the third law gives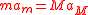 , so we would get
, so we would get  even though
even though 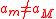 , and
, and 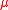 would therefore be constant, contrary to the MOND assumption that it is linear for small arguments.
would therefore be constant, contrary to the MOND assumption that it is linear for small arguments.
This problem can be rectified by deriving the force law from a Lagrangian, at the cost of possibly modifying the general form of the force law. Then conservation laws could then be derived from the Lagrangian by the usual means.
The AQUAL Lagrangian is: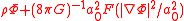 ;
;
this leads to a modified Poisson equation: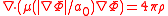 .
.
Here,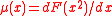 and the predicted acceleration is
and the predicted acceleration is 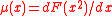 . These equations reduce to the MOND equations in the spherically symmetric case, although they differ somewhat in the disc case needed for modelling spiral or lenticular galaxies. However, the difference is only 10-15%, so does not seriously impact the results.
. These equations reduce to the MOND equations in the spherically symmetric case, although they differ somewhat in the disc case needed for modelling spiral or lenticular galaxies. However, the difference is only 10-15%, so does not seriously impact the results.
Modified Newtonian dynamics
In physics, Modified Newtonian dynamics is a hypothesis that proposes a modification of Newton's law of gravity to explain the galaxy rotation problem. When the uniform velocity of rotation of galaxies was first observed, it was unexpected because Newtonian theory of gravity predicts that objects...
(MOND), but using a Lagrangian
Lagrangian
The Lagrangian, L, of a dynamical system is a function that summarizes the dynamics of the system. It is named after Joseph Louis Lagrange. The concept of a Lagrangian was originally introduced in a reformulation of classical mechanics by Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton known as...
. It was developed by Jacob Bekenstein
Jacob Bekenstein
Jacob David Bekenstein is an Israeli theoretical physicist who has contributed to the foundation of black hole thermodynamics and to other aspects of the connections between information and gravitation.-Biography:...
and Mordehai Milgrom
Mordehai Milgrom
Mordehai Milgrom is an Israeli physicist and professor in the department of Condensed Matter Physics at the Weizmann Institute in Rehovot, Israel. He is most famous for his proposal of Modified Newtonian dynamics as an alternative to the dark matter and galaxy rotation curve problems, in 1981...
in their 1984 paper, "Does the missing mass problem signal the breakdown of Newtonian gravity?". "AQUAL" stands for "AQUAdratic Lagrangian".
The gravitational force law obtained from MOND,
 ,
,has a serious defect: it violates Newton's third law of motion, and therefore fails to conserve
Conservation law
In physics, a conservation law states that a particular measurable property of an isolated physical system does not change as the system evolves....
momentum and energy. To see this, consider two objects with
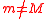 ; then we have
; then we have
but the third law gives
 , so we would get
, so we would get  even though
even though 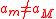 , and
, and  would therefore be constant, contrary to the MOND assumption that it is linear for small arguments.
would therefore be constant, contrary to the MOND assumption that it is linear for small arguments.This problem can be rectified by deriving the force law from a Lagrangian, at the cost of possibly modifying the general form of the force law. Then conservation laws could then be derived from the Lagrangian by the usual means.
The AQUAL Lagrangian is:
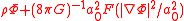 ;
;this leads to a modified Poisson equation:
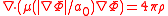 .
.Here,
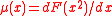 and the predicted acceleration is
and the predicted acceleration is 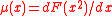 . These equations reduce to the MOND equations in the spherically symmetric case, although they differ somewhat in the disc case needed for modelling spiral or lenticular galaxies. However, the difference is only 10-15%, so does not seriously impact the results.
. These equations reduce to the MOND equations in the spherically symmetric case, although they differ somewhat in the disc case needed for modelling spiral or lenticular galaxies. However, the difference is only 10-15%, so does not seriously impact the results.

