
4-8-0
Encyclopedia

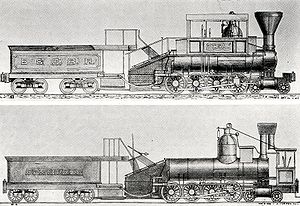
Whyte notation
The Whyte notation for classifying steam locomotives by wheel arrangement was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte and came into use in the early twentieth century encouraged by an editorial in American Engineer and Railroad Journal...
for the classification of steam locomotive
Steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a railway locomotive that produces its power through a steam engine. These locomotives are fueled by burning some combustible material, usually coal, wood or oil, to produce steam in a boiler, which drives the steam engine...
s, 4-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement
Wheel arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed beneath a locomotive.. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country...
of four leading wheel
Leading wheel
The leading wheel or leading axle of a steam locomotive is an unpowered wheel or axle located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located in a truck...
s on two axles (usually in a leading truck), eight powered and coupled driving wheel
Driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons...
s on four axles, and no trailing wheel
Trailing wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels was usually located on a trailing truck...
s. The type was nicknamed the Mastodon or Twelve-wheeler in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. Mastodon
Mastodon (steam locomotive)
Mastodon was the unofficial name of the Central Pacific Railroad's number 229, the world's first successful 4-8-0 steam locomotive.-History and career:...
(No. 229) was the unofficial name of Central Pacific Railroad
Central Pacific Railroad
The Central Pacific Railroad is the former name of the railroad network built between California and Utah, USA that formed part of the "First Transcontinental Railroad" in North America. It is now part of the Union Pacific Railroad. Many 19th century national proposals to build a transcontinental...
's first 4-8-0, which was built in 1882 at the Sacramento Locomotive Works.
Other equivalent classifications are:
UIC classification
UIC classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is set out in the International Union of Railways "Leaflet 650 - Standard designation of axle arrangement on locomotives and multiple-unit sets". It is used in much...
: 2′D (also known as German classification and Italian classification)
French classification: 240
Turkish classification
Turkish classification
In the Turkish classification system for railway locomotives, the number of powered axles are followed by the total number of axles. It is identical to the Swiss system except that the latter places a slash between the two numbers.Thus0-6-0 becomes 33...
: 46
Swiss classification: 4/6
Russian classification: 2-4-0
The very first 4-8-0 is believed to be the Centipede, a "Winans Camel" built in 1855 for the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad. It entered service in 1864 and ran on the B&O for nearly 20 years.
Australia
The 4-8-0 saw service in Australia from 1900.In Tasmania the private railway company of Emu Bay ordered 4 of these 4-8-0 tendered locomotives for their narrow (1,066 mm) gauge system. In 1910 another locomotive was delivered from the now reformed North British Coy. Two examples of these engines are preserved.
Initially designed in South Australia for use on its narrow gauge 3 ft 6 in (1,066 mm) system, a new class of 4-8-0 engine proved suitable workhorses and by 1917 there were seventy eight locomotives in the class. During 1922-23 five of the class were converted to state's broad gauge system (1,600 mm) and then reconverted during 1949 back to narrow gauge. In 1921-22 the Tasmanian Government purchased six of the SAR narrow gauged engines. During the Second World War the Commonwealth Railways also obtained four SAR narrow gauge locomotives for a period. Several ex-SAR engines are preserved.
In Queensland the QR which also operates a narrow gauge system a 4-8-0 class was introduced in 1903 as C16 class locomotives. A total of 152 engines were in service by 1917. During the Second World War (1939–45) the Commonwealth Government acquired eleven C16s on loan. Only one example of this class was preserved. From 1920, as the Queensland 4-8-0s acquired super heaters they were classed as C17
Queensland C17 class locomotive
The C17 class locomotive was a 4-8-0 locomotive of the Queensland Railways. . The locomotives operated on narrow gauge.The design was so successful that 227 locomotives were built from 1920 when the first engine N° 15 entering service through until 1953 when N° 1000 was delivered. The 22 NM...
—and all up 227 engines were in this class. The Commonwealth Railways also ordered 22 engines of the same class for their narrow gauge rail system. Twenty examples of the class are preserved.
In 1922 the QR ordered 22 new 4-8-0s as class C19 engines. (all Australian details: Oberg)
New Zealand
New Zealand's first 4-8-0 was built in the Addington Railway Workshops in 1899 and classified B classNZR B class (1899)
The B class of 1899 was a class of steam locomotives that operated on New Zealand's national rail network. An earlier B class of Double Fairlies had entered service in 1874, but as they had departed from the ownership of the New Zealand Railways by the end of 1896, the B classification was free...
. Four more were completed the same year, and one more in 1901. Sharp Stewart and Company built four more over the next two years. Ten BA class
NZR Ba class
The BA class was a class of steam locomotive built by the New Zealand Railways Department for use on New Zealand's national rail network. The first BA entered service in November 1911, with the last of the 11 class members introduced on 14 May 1913....
were built at Addington between 1911–1913; and 30 BB class
NZR Bb class
The BB class of steam locomotives comprised 30 engines operated by New Zealand Railways in the North Island of New Zealand. Similar in design and appearance to the preceding B and BA classes, the first BB class locomotive entered service in February 1915, with the last to commence operations doing...
were built by A & G Price
A & G Price
A & G Price Limited is an engineering firm and locomotive manufacturer in Thames, New Zealand, established in 1868. In 2004 a precision formed yacht keel division was formed to make the Maximus canting keel...
in New Zealand between 1915 and 1918. 1 BB and 1 BA have been preserved being BB 144 and BA 552. Both are at Mainline Steam
Mainline Steam
Mainline Steam is a New Zealand organisation devoted to the restoration and operation of historic New Zealand Railways mainline steam locomotives. Regular day excursions and multi-day tours are operated over rail lines throughout New Zealand...
's Parnell Depot.
Austria
In AustriaAustria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, the wheel arrangement was used for some express locomotives: class 570 of 1915 and class 113
BBÖ Class 113
The steam locomotive class BBÖ 113 was an express train, tender locomotive class operated by the Federal Railway of Austria .-History:After World War I new locomotives had to be built for the Austrian Western Railway due to increasing train loads and the replacement of old, wooden, passenger...
of 1923, both numbered as class 33 from 1938 on.
Britain and Ireland
In the United KingdomUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, there were two classes of 4-8-0 tank locomotives, both built for hump shunting. Ten were built by the North Eastern Railway
North Eastern Railway (UK)
The North Eastern Railway , was an English railway company. It was incorporated in 1854, when four existing companies were combined, and was absorbed into the London and North Eastern Railway at the Grouping in 1923...
in 1909–10, designated NER Class X
NER Class X
The NER Class X was a class of 4-8-0T tank locomotive designed by Wilson Worsdell for the North Eastern Railway. They were intended for use as powerful shunting engines to arrange and move coal wagons for loading into ships. In total 15 were built, 10 by the NER between 1909 and 1910, and a...
(later LNER Class T1), to which the LNER added a further five in 1925. These had three cylinders, following Robinson's 0-8-4 design for the Great Central
Great Central
Great Central or Great Central Railway may refer to:*Great Central Railway, a historical railway company in the UK*Great Central Railway , a modern heritage railway in Leicestershire and Nottinghamshire, England...
. The London and South Western Railway
London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Its network extended from London to Plymouth via Salisbury and Exeter, with branches to Ilfracombe and Padstow and via Southampton to Bournemouth and Weymouth. It also had many routes connecting towns in...
also built four G16 class
LSWR G16 class
The LSWR G16 class is a steam tank locomotive class of 4-8-0T wheel arrangement. It was designed by Robert Urie and introduced in 1921 specifically for heavy shunting over humps at Feltham marshalling yard, on the London and South Western Railway...
two-cylinder machines in 1921 to Urie's design for Feltham marshalling yard
Feltham marshalling yard
Feltham marshalling yard, also known as Feltham hump yard, was a large railway marshalling yard designed for the concentration of freight traffic to and from South West London, and for transfer to other marshalling yards in London. It was built on the Waterloo to Reading Line...
. The Great Southern and Western Railway
Great Southern and Western Railway
The Great Southern and Western Railway was the largest Irish gauge railway company in Ireland in the late 19th and early 20th centuries...
in Ireland similarly had a small class of inside-cylinder shunting machines.
Both the London Midland and Scottish Railway and the Southern Railway
Southern Railway (Great Britain)
The Southern Railway was a British railway company established in the 1923 Grouping. It linked London with the Channel ports, South West England, South coast resorts and Kent...
however contemplated 4-8-0 tender freight engines, but these never materialised.
France
In France this wheel arrangement came into use twice. The first was in 1907, for the Chemins de fer de Paris à Lyon et à la MéditerranéeChemins de fer de Paris à Lyon et à la Méditerranée
The Compagnie des chemins de fer de Paris à Lyon et à la Méditerranée was a French railway company ....
. They were intended for both for goods trains, and passenger trains on difficult routes. They were Baudry type compounds, which was similar to the de Glehn type, but the low pressure cylinders were fixed at 60% cut-off. All were originally saturated, but some later had superheaters; all others were provided with feedwater heaters. These locomotives had a speed limit of 52.8 mph, and were designed to hail 1,177 long tons at 22.4 mph. A total of 282 were built. The PLM had prepared designs for another, much larger 4-8-0 in about 1913, but nothing materialized due to the outbreak of World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
.
The second appeared was the famous 240P
SNCF 240P
The SNCF 4-240A class and SNCF 5-240P class was a group of 37 4-8-0 steam locomotives designed by André Chapelon, and regarded by some, as one of his best designs....
, 2-4-0 referring to the number and arrangement of axles rather than wheels. These machines were technically rebuilds of some of the earliest Pacifics
4-6-2
4-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .These locomotives are also known as Pacifics...
in Europe, built for the Chemin de Fer de Paris à Orléans. The 240P was considered to be one of André Chapelon
André Chapelon
André Chapelon was a noted French mechanical engineer and designer of advanced steam locomotives. Engineer of Ecole Centrale Paris, he was one of very few locomotive designers who brought a rigorous scientific method to their design, and he sought to apply up-to-date knowledge and theories in...
's finest works and benefited from his thorough understanding of thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
and his appreciation of the need to consider the entirety of the steam circuit. The locomotive was a 4 cylinder compound fitted with Lentz-Dabeg poppet valves. With a power output of 4700 horsepower* the 240P was reported to have the highest power-to-weight ratio of any steam locomotive. Discussion continues as to how robust they were mechanically - whether the size of the bearings was too near the bone, or whether they were simply worked to death during the difficult war years. Coupled with the elegant French style tender the second batch at least was also a very aesthetic locomotive. Unfortunately none have survived into preservation.
- http://thierry.stora.free.fr/english/techdat2.htm
Hungary
MAV (Hungarian Railways) adopted the 4-8-0 type as their standard mixed-traffic locomotive in the shape of the 424 class which was built between 1924 and 1958. Of these 365 were built for Hungary, and 149 for foreign systems, including Yugoslavia, the USSR and North Korea. The last of the Hungarian examples were withdrawn from service in 1984.Spain
RENFE, the Spanish rail system nationalised in 1938, inherited 4-8-0s from the Madrid, Zaragoza and Alicante Railway, and continued to construct the class as standard. The last survivors, all oil-burners, were concentrated at Salamanca shed around 1970.Soviet Union
In Soviet Union 4-8-0 were the first passenger locomotives built by the new state. They were represented by one hundred M-class locomotives built by Putilov Works in Leningrad (Saint Petersburg) in 1927. Initially built as a 3-cylinder machines they were later rebuilt as a 2-cylinder ones and re-designated as Mr (Мр in Cyrillic). The M series were not considered a great success.South Africa
Locomotives of the 4-8-0 wheel arrangement used in South Africa included the following:- The Cape Government RailwaysCape Government RailwaysThe Cape Government Railways was the government-owned railway operator in the Cape Colony from 1874 until the creation of the South African Railways in 1910.-Private railways:...
(CGR) Class 7South African Class 7 4-8-0In 1892 the Cape Government Railways placed six Class 7 steam locomotives with a 4-8-0 Mastodon wheel arrangement in service and between 1892 and 1893 another thirty-two were acquired. They were initially placed in service on the Cape Midland System, but were later distributed between the Cape...
and Class 8South African Class 8A 4-8-0In 1902 the Central South African Railways placed forty Class 8-L1 4-8-0 Mastodon steam locomotives in service. In 1912, when they were assimilated into the South African Railways, they were renumbered and reclassified to Class 8A.-Manufacturers:...
, later South African Railways (SAR) Class 7 and 8. - The Natal Government RailwaysNatal government railwaysThe Natal Government Railways was formed in January 1877 in the Colony of Natal.In 1877 the Natal Government Railways acquired the Natal Railway Company for the sum of £40,000, gaining the line from the Point to Durban and from Durban to Umgeni...
(NGR) Class Hendrie BSouth African Class 1 4-8-0In 1904 the Natal Government Railways placed fifty Class Hendrie B 4-8-0 Mastodon steam locomotives in service. Six of them were modified to a 4-8-2 Mountain wheel arrangement in 1906...
, later SAR Class 1. - The SAR also created the Class 13 by rebuilding the Central South African RailwaysCentral South African RailwaysFrom 1902 to 1904, the area of power of Lieutenant-Colonel Sir Percy Girouard later also included the lines of The Netherlands-South African Railway Company; together this dominion covered all lines in the Transvaal that belonged to NZASM ....
(CSAR) Class H1 and H2 4-8-2T. - In 1926 twenty-one ex NGR Class A 4-8-2TSouth African Class A 4-8-2TIn 1888 the Natal Government Railways placed the first five of its eventual one hundred Class Dübs A 4-8-2T tank steam locomotives in service. The last of the one hundred was delivered in 1899. In 1912, when these locomotives were assimilated into the South African Railways, they were renumbered...
locomotives, known as the "Improved Dübs A" on the NGR or “Class A Belpaire” on the SAR, were rebuilt to Class 17 4-8-0 tender locomotives.
North America
In the United States the 4-8-0 was essentially a freight locomotive - a marginal development of the 2-8-0. Most US 4-8-0s were built in the late 19th century or early 20th century, but the type never achieved great popularity, although there were four occasions where a 4-8-0 was claimed as the "heaviest and/or most powerful locomotive in the world." Those locomotives were Lehigh Valley #20 "Champion" of 1880, Central Pacific #229 "Mastodon" of 1882, Great Northern's G5 class of 1897, and Illinois Central #640 of 1899. It is worth noting that the G5's had 16 inches (406.4 mm) piston valves (most railways used slide valves until superheating caused lubrication difficulties), which was as large as the cylinders on some other locomotives.The wide-firebox 2-8-2 Mikado had much more potential as far as speed but the Norfolk & Western's class M
N&W "M" Series 4-8-0
The Norfolk and Western Railway's M, M1 and M2 classes were a series of 4-8-0 steam locomotives owned and operated by the Norfolk and Western Railway. These were the last significant deliveries of 4-8-0s in the United States. The N&W needed to get coal shipments over a mountain range, and powerful...
4-8-0s needed the short wheelbase and 4 wheel lead or engine truck for stability and the ability to have over 90 percent of the engines weight on the drivers. N&W's class M2 4-8-0s were the largest built and many lasted into the 1950s. Two were even converted into a high availability-low maintenance automatic type locomotive for switching (shunting) service. In continental Europe, notably France and Austria, the type was used for heavy passenger work. In Britain the type was use in small numbers for shunting tanks.

