3-beta-HSD
Encyclopedia
3-β-HSD is an enzyme
that catalyses the synthesis of progesterone
from pregnenolone
, 17-hydroxyprogesterone from 17-hydroxypregnenolone, and androstenedione
from dehydroepiandrosterone
in the adrenal gland. It is the only enzyme in the adrenal pathway of corticosteroid
synthesis that is not a member of the Cytochrome P450 family. In humans, there are two 3-β-HSD isozyme
s encoded by the HSD3B1
and HSD3B2
genes, respectively.
It is also known as delta 5-delta 4-isomerase, which catalyzes the oxidative conversion of delta 5-3 beta- hydroxysteroid
s to the delta 4-3-keto configuration and is, therefore, essential for the biosynthesis
of all classes of hormonal steroid
s, namely progesterone
, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgen
s, and estrogen
s.
The 3-beta HSD complex is responsible for the conversion of:
s, to be specific, those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. This enzyme participates in c21-steroid hormone metabolism and androgen and estrogen metabolism.
3-β-HSD catalyzes
the chemical reaction
:
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-steroid and NAD+
, whereas its 3 products
are 3-oxo-Δ5-steroid, NADH
, and H+
.
s, HSD3B1
(type I) and HSD3B2
(type II). The type I isoenzyme is expressed in placenta and peripheral tissues, whereas the type II 3β-HSD isoenzyme is expressed in the adrenal gland, ovary, and testis.
. No human condition has yet been linked to a deficiency in the type I enzyme. Its importance in placental progesterone production expression suggests that such a mutation would be embryonically lethal.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyses the synthesis of progesterone
Progesterone
Progesterone also known as P4 is a C-21 steroid hormone involved in the female menstrual cycle, pregnancy and embryogenesis of humans and other species...
from pregnenolone
Pregnenolone
Pregnenolone is a steroid hormone involved in the steroidogenesis of progesterone, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. As such it is a prohormone. Pregnenolone sulfate is a GABAA antagonist and increases neurogenesis in the hippocampus.-Chemistry:Like other steroids,...
, 17-hydroxyprogesterone from 17-hydroxypregnenolone, and androstenedione
Androstenedione
Androstenedione is a 19-carbon steroid hormone produced in the adrenal glands and the gonads as an intermediate step in the biochemical pathway that produces the androgen testosterone and the estrogens estrone and estradiol.-Synthesis:Androstenedione is the common precursor of male and female sex...
from dehydroepiandrosterone
Dehydroepiandrosterone
5-Dehydroepiandrosterone is a 19-carbon endogenous steroid hormone. It is the major secretory steroidal product of the adrenal glands and is also produced by the gonads and the brain. DHEA is the most abundant circulating steroid in humans....
in the adrenal gland. It is the only enzyme in the adrenal pathway of corticosteroid
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex. Corticosteroids are involved in a wide range of physiologic systems such as stress response, immune response and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte...
synthesis that is not a member of the Cytochrome P450 family. In humans, there are two 3-β-HSD isozyme
Isozyme
Isozymes are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. These enzymes usually display different kinetic parameters Isozymes (also known as isoenzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. These enzymes...
s encoded by the HSD3B1
HSD3B1
HSD3B1 is a human gene that encodes for a 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta-deltaisomerase type I or hydroxy-delta-5-steroid dehydrogenase, 3 beta- and steroid delta-isomerase 1. While it can carry out the same function as HSD3B2, it primarily localizes to different tissues, such as the...
and HSD3B2
HSD3B2
HSD3B2 is a human gene that encodes for 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta-deltaisomerase type II or hydroxy-delta-5-steroid dehydrogenase, 3 beta- and steroid delta-isomerase 2. It is principally expressed in steroidogenic tissues and is essential for steroid hormone production...
genes, respectively.
It is also known as delta 5-delta 4-isomerase, which catalyzes the oxidative conversion of delta 5-3 beta- hydroxysteroid
Hydroxysteroid
A hydroxysteroid is a molecule derived from a steroid with a hydrogen replaced with a hydroxy group....
s to the delta 4-3-keto configuration and is, therefore, essential for the biosynthesis
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
of all classes of hormonal steroid
Steroid
A steroid is a type of organic compound that contains a characteristic arrangement of four cycloalkane rings that are joined to each other. Examples of steroids include the dietary fat cholesterol, the sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, and the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone.The core...
s, namely progesterone
Progesterone
Progesterone also known as P4 is a C-21 steroid hormone involved in the female menstrual cycle, pregnancy and embryogenesis of humans and other species...
, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgen
Androgen
Androgen, also called androgenic hormone or testoid, is the generic term for any natural or synthetic compound, usually a steroid hormone, that stimulates or controls the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors...
s, and estrogen
Estrogen
Estrogens , oestrogens , or œstrogens, are a group of compounds named for their importance in the estrous cycle of humans and other animals. They are the primary female sex hormones. Natural estrogens are steroid hormones, while some synthetic ones are non-steroidal...
s.
The 3-beta HSD complex is responsible for the conversion of:
- pregnenolonePregnenolonePregnenolone is a steroid hormone involved in the steroidogenesis of progesterone, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. As such it is a prohormone. Pregnenolone sulfate is a GABAA antagonist and increases neurogenesis in the hippocampus.-Chemistry:Like other steroids,...
to progesteroneProgesteroneProgesterone also known as P4 is a C-21 steroid hormone involved in the female menstrual cycle, pregnancy and embryogenesis of humans and other species... - 17-alpha-pregnenolone to 17-alpha-progesterone
- dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) to androstenedioneAndrostenedioneAndrostenedione is a 19-carbon steroid hormone produced in the adrenal glands and the gonads as an intermediate step in the biochemical pathway that produces the androgen testosterone and the estrogens estrone and estradiol.-Synthesis:Androstenedione is the common precursor of male and female sex...
- androstenediolAndrostenediolAndrostenediol may refer to:* 4-Androstenediol, the steroid androgen that can be converted to testosterone* 5-Androstenediol, steroid* Methandriol, a synthetic androstenediol derivative...
to testosteroneTestosteroneTestosterone is a steroid hormone from the androgen group and is found in mammals, reptiles, birds, and other vertebrates. In mammals, testosterone is primarily secreted in the testes of males and the ovaries of females, although small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands...
Reaction
3-β-HSD belongs to the family of oxidoreductaseOxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another...
s, to be specific, those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. This enzyme participates in c21-steroid hormone metabolism and androgen and estrogen metabolism.
3-β-HSD catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
:
- a 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-steroid + NAD+
 a 3-oxo-Δ5-steroid + NADH + H+
a 3-oxo-Δ5-steroid + NADH + H+
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-steroid and NAD+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
, whereas its 3 products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are 3-oxo-Δ5-steroid, NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
, and H+
Hydrogen ion
Hydrogen ion is recommended by IUPAC as a general term for all ions of hydrogen and its isotopes.Depending on the charge of the ion, two different classes can be distinguished: positively charged ions and negatively charged ions....
.
Isozymes
Humans express two 3-β-HSD isozymeIsozyme
Isozymes are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. These enzymes usually display different kinetic parameters Isozymes (also known as isoenzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. These enzymes...
s, HSD3B1
HSD3B1
HSD3B1 is a human gene that encodes for a 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta-deltaisomerase type I or hydroxy-delta-5-steroid dehydrogenase, 3 beta- and steroid delta-isomerase 1. While it can carry out the same function as HSD3B2, it primarily localizes to different tissues, such as the...
(type I) and HSD3B2
HSD3B2
HSD3B2 is a human gene that encodes for 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta-deltaisomerase type II or hydroxy-delta-5-steroid dehydrogenase, 3 beta- and steroid delta-isomerase 2. It is principally expressed in steroidogenic tissues and is essential for steroid hormone production...
(type II). The type I isoenzyme is expressed in placenta and peripheral tissues, whereas the type II 3β-HSD isoenzyme is expressed in the adrenal gland, ovary, and testis.
Nomenclature
The systematic name of this enzyme class is 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-steroid:NAD+ 3-oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include:- progesterone reductase
- Δ5-3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
- 3β-hydroxy-5-ene steroid dehydrogenase
- 3β-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase/isomerase
- 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-C27-steroid dehydrogenase/isomerase
- 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-C27-steroid oxidoreductase
- 3β-hydroxy-5-ene-steroid oxidoreductase
- steroid-Δ5-3β-ol dehydrogenase
- 3β-HSDH
- 5-ene-3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
- 3β-hydroxy-5-ene-steroid dehydrogenase
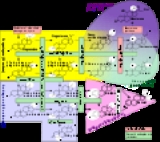
Biosynthetic pathway
Clinical significance
A deficiency in the type II form through mutations in HSD3B2 is responsible for a rare form of congenital adrenal hyperplasiaCongenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency
3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase II deficient congenital adrenal hyperplasia is an uncommon form of CAH resulting from a mutation in the gene for one of the key enzymes in cortisol synthesis by the adrenal gland, 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II...
. No human condition has yet been linked to a deficiency in the type I enzyme. Its importance in placental progesterone production expression suggests that such a mutation would be embryonically lethal.
See also
- 3-β(or 20-α)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase3beta(or 20alpha)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenaseIn enzymology, a 3-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase is a putative enzyme that possesses the combined activities of the 3-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Δ-5-4 isomerase and 20-α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzymes....

