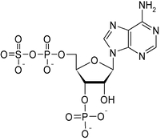
3'-Phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate
Encyclopedia
3'-Phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate is a derivative of adenosine monophosphate
that is phosphorylated at the 3' position and has a sulfate
group attached to the 5' phosphate
. This anion, abbreviated PAPS, serves as a coenzyme in sulfotransferase
reactions. A related anion is adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (APS), which is not phosphorylated at the 3' position.
, an exothermic conversion that is carried out by sulfate-reducing bacteria
. In these organisms, sulfate serves as an electron acceptor, akin to the use of O2 as an electron acceptor by aerobic organisms. Sulfate is not reduced directly but must be activated by the formation of APS or PAPS. These carriers of activated sulfate are produced by reaction with ATP. The first reaction is catalysed by ATP sulfurase:
The conversion of APS to PAPS is catalysed by APS kinase
:
Reduction of APS leads to sulfite, which is further reduced to hydrogen sulfide
, which is excreted. This process is called dissimilatory sulfate reduction. Reduction of PAPS, a more elaborated sulfate ester, leads also to hydrogen sulfide. But in this case, the product is used in biosynthesis, e.g. for the production of cysteine
. The latter process is called assimilatory sulfate reduction because the sulfate sulfur is assimilated.
Adenosine monophosphate
Adenosine monophosphate , also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine...
that is phosphorylated at the 3' position and has a sulfate
Sulfate
In inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:...
group attached to the 5' phosphate
Phosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
. This anion, abbreviated PAPS, serves as a coenzyme in sulfotransferase
Sulfotransferase
Sulfotransferases are transferase enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a sulfate group from a donor molecule to an acceptor alcohol or amine. The most common sulfate donor is 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate...
reactions. A related anion is adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (APS), which is not phosphorylated at the 3' position.
Formation and reduction
APS and PAPS are intermediates in the reduction of sulfate to sulfiteSulfite
Sulfites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion SO. The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although the acid itself is elusive, its salts are widely used.-Structure:...
, an exothermic conversion that is carried out by sulfate-reducing bacteria
Sulfate-reducing bacteria
Sulfate-reducing bacteria are those bacteria and archaea that can obtain energy by oxidizing organic compounds or molecular hydrogen while reducing sulfate to hydrogen sulfide...
. In these organisms, sulfate serves as an electron acceptor, akin to the use of O2 as an electron acceptor by aerobic organisms. Sulfate is not reduced directly but must be activated by the formation of APS or PAPS. These carriers of activated sulfate are produced by reaction with ATP. The first reaction is catalysed by ATP sulfurase:
- SO42- + ATP → APS + PPi
The conversion of APS to PAPS is catalysed by APS kinase
Adenylyl-sulfate kinase
In enzymology, an adenylyl-sulfate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and adenylyl sulfate, whereas its two products are ADP and 3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate....
:
- APS + ATP → PAPS + ADP
Reduction of APS leads to sulfite, which is further reduced to hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless, very poisonous, flammable gas with the characteristic foul odor of expired eggs perceptible at concentrations as low as 0.00047 parts per million...
, which is excreted. This process is called dissimilatory sulfate reduction. Reduction of PAPS, a more elaborated sulfate ester, leads also to hydrogen sulfide. But in this case, the product is used in biosynthesis, e.g. for the production of cysteine
Cysteine
Cysteine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2SH. It is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans. Its codons are UGU and UGC. The side chain on cysteine is thiol, which is polar and thus cysteine is usually classified as a hydrophilic amino acid...
. The latter process is called assimilatory sulfate reduction because the sulfate sulfur is assimilated.

