
2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey
Encyclopedia
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, the 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey (Two-degree-Field Galaxy Redshift Survey), 2dF or 2dFGRS is a redshift survey
Redshift survey
In astronomy, a redshift survey, or galaxy survey, is a survey of a section of the sky to measure the redshift of astronomical objects. Using Hubble's law, the redshift can be used to calculate the distance of an object from Earth. By combining redshift with angular position data, a redshift...
conducted by the Anglo-Australian Observatory
Anglo-Australian Observatory
The Australian Astronomical Observatory , formerly the Anglo-Australian Observatory, is an optical/near-infrared astronomy observatory with its headquarters in suburban Sydney, Australia...
(AAO) with the 3.9m Anglo-Australian Telescope
Anglo-Australian Telescope
The Anglo-Australian Telescope is a 3.9 m equatorially mounted telescope operated by the Australian Astronomical Observatory and situated at the Siding Spring Observatory, Australia at an altitude of a little over 1100 m...
between 1997 and 11 April 2002. The data from this survey were made public on 30 June 2003. The survey determined the large-scale structure in one section of the local Universe. As of July 2009, it is the second largest redshift survey next to the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
Sloan Digital Sky Survey
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-filter imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project was named after the Alfred P...
which began in 2000. Matthew Colless, Steve Maddox and John Peacock were in charge of the project.
Description
The 2dF survey covered an area of about 1500 square degreeSquare degree
A square degree is a non-SI unit measure of solid angle. It is denoted in various ways, including deg2, sq.deg. and ². Just as degrees are used to measure parts of a circle, square degrees are used to measure parts of a sphere. Analogous to one degree being equal to π /180 radians, a...
s, surveying regions in both the north and the south galactic poles. The name derives from the fact that the survey instrument covers an area of approximately two square degrees.
The areas selected for observation were previously surveyed by the massive APM Galaxy Survey (on which Steve Maddox also worked). The regions surveyed cover roughly 75 degrees of right ascension
Right ascension
Right ascension is the astronomical term for one of the two coordinates of a point on the celestial sphere when using the equatorial coordinate system. The other coordinate is the declination.-Explanation:...
for both bands, and the declination
Declination
In astronomy, declination is one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and...
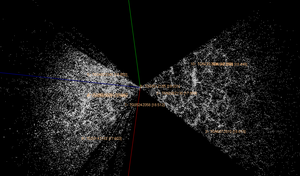
of the North Polar band was about 7.5 degrees while the declination of the South Polar band was about 15 degrees. Hundreds of isolated two degree fields near the South Polar band were also surveyed (see this illustration, where black circles represent survey fields, and the red grid represents the earlier APM survey).
In total, the photometry
Photometry (astronomy)
Photometry is a technique of astronomy concerned with measuring the flux, or intensity of an astronomical object's electromagnetic radiation...
of 382,323 objects were measured, which includes spectra
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
for 245,591 objects, of which 232,155 were galaxies (221,414 with good quality spectra), 12,311 are star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s, and 125 are quasi-stellar objects (quasars). The survey necessitated 272 required nights of observation, spread over 5 years.
The survey was carried out with the 4 metre Anglo-Australian Telescope
Anglo-Australian Telescope
The Anglo-Australian Telescope is a 3.9 m equatorially mounted telescope operated by the Australian Astronomical Observatory and situated at the Siding Spring Observatory, Australia at an altitude of a little over 1100 m...
, with the 2dF instrument installed at the primary focus permitting the observation of a field of 2 degrees per pointing. The instrument possesses a spectrograph
Spectrograph
A spectrograph is an instrument that separates an incoming wave into a frequency spectrum. There are several kinds of machines referred to as spectrographs, depending on the precise nature of the waves...
equipped with two banks each of 200 optical fibres, permitting the simultaneous measurement of 400 spectra. The limiting apparent magnitude of the survey is 19.5, covering objects with a redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
mostly within less than z=0.3 and a median redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
of 0.11. The volume of the Universe covered by the survey is approximately 108 h-1 Mpc3, where h corresponds to the value of the Hubble constant, H0, divided by 100. H0 is approximately 70 km/s/Mpc. The largest redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
observed by the survey corresponds to a distance of 600 h-1 Mpc.
Survey Results
The principal results obtained for the field of cosmologyCosmology
Cosmology is the discipline that deals with the nature of the Universe as a whole. Cosmologists seek to understand the origin, evolution, structure, and ultimate fate of the Universe at large, as well as the natural laws that keep it in order...
by the 2dF survey are:
- The measurement of the density parameter of non-relativistic matter (baryonic matter plus dark matterDark matterIn astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
plus massive neutrinos) - The detection of Baryon acoustic oscillationsBaryon acoustic oscillationsIn cosmology, baryon acoustic oscillations refers to an overdensity or clustering of baryonic matter at certain length scales due to acoustic waves which propagated in the early universe. In the same way that supernova experiments provide a "standard candle" for astronomical observations, BAO...
, and as a consequence the relationship between the density of baryonic matter and dark matter - Limits on the contribution of massive neutrinos to dark matter, putting a limit on the sum of the masses of the three families of neutrinos at 1.8 eV.
All these results are in agreement with the measurements of other experiments, notably those of WMAP. They confirm the standard cosmological model
Lambda-CDM model
ΛCDM or Lambda-CDM is an abbreviation for Lambda-Cold Dark Matter, which is also known as the cold dark matter model with dark energy...
.
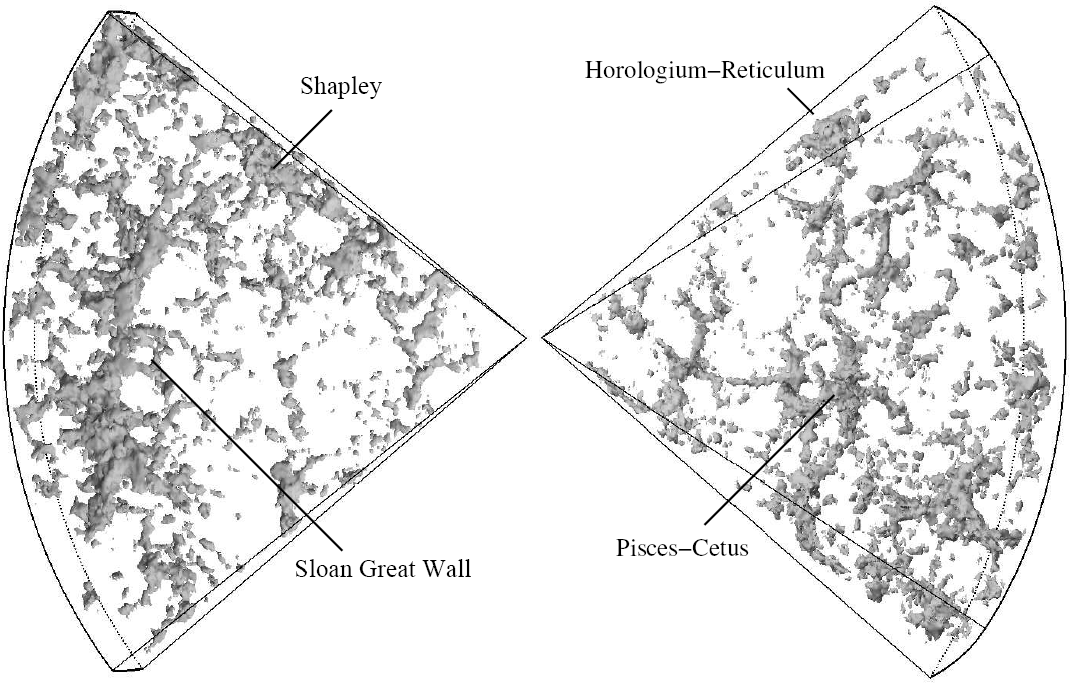
Sloan Great Wall
The Sloan Great Wall is a cosmic structure formed by a giant wall of galaxies , and to the present day it is the largest known structure in the universe. Its discovery was announced on October 20, 2003 by J. Richard Gott III of Princeton University and Mario Jurić and their colleagues, based on...
, the largest structure in the universe known to date.
External links
- Official site of the 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey
- The 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey: spectra and redshifts − 2001 Royal Astronomical SocietyRoyal Astronomical SocietyThe Royal Astronomical Society is a learned society that began as the Astronomical Society of London in 1820 to support astronomical research . It became the Royal Astronomical Society in 1831 on receiving its Royal Charter from William IV...
paper describing the survey - Official site of the Two Degree Field instrument system

