2,8 dihydroxy-adenine urolithiasis
Encyclopedia
Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency (also called APRT deficiency or 2,8 dihydroxyadenine urolithiasis) is an autosomal
recessive metabolic disorder associated with a mutation in the enzyme adenine phosphoribosyltransferase
.
2,8-dihydroxyadenine.
It can result in nephrolithiasis, acute renal failure
and permanent kidney
damage.

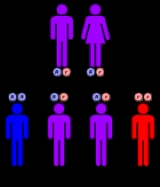
APRT deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
, and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
recessive metabolic disorder associated with a mutation in the enzyme adenine phosphoribosyltransferase
Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase
Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the APRT gene.- Function :APRTase is an enzyme involved in the purine nucleotide salvage pathway...
.
Characteristics
The disorder results in accumulation of the insoluble purinePurine
A purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, consisting of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring. Purines, including substituted purines and their tautomers, are the most widely distributed kind of nitrogen-containing heterocycle in nature....
2,8-dihydroxyadenine.
It can result in nephrolithiasis, acute renal failure
Acute renal failure
Acute kidney injury , previously called acute renal failure , is a rapid loss of kidney function. Its causes are numerous and include low blood volume from any cause, exposure to substances harmful to the kidney, and obstruction of the urinary tract...
and permanent kidney
Kidney
The kidneys, organs with several functions, serve essential regulatory roles in most animals, including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and...
damage.
Genetics

APRT deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
Genetic carrier
A genetic carrier , is a person or other organism that has inherited a genetic trait or mutation, but who does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. They are, however, able to pass the gene onto their offspring, who may then express the gene...
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.

