
Zyablov bound
Encyclopedia
In coding theory, the Zyablov bound, is a lower bound on the rate  and relative distance
and relative distance 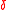 of the concatenated codes.
of the concatenated codes.
 be the rate of the outer code
be the rate of the outer code  and
and 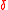 be the relative distance, then the rate of the concatenated codes satisfies the following bound.
be the relative distance, then the rate of the concatenated codes satisfies the following bound.
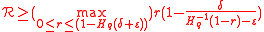
where is the rate of the inner code
is the rate of the inner code 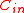 .
.
 be the outer code,
be the outer code, 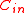 be the inner code.
be the inner code.
Consider meets the Singleton bound
meets the Singleton bound
with rate of , i.e.
, i.e.  has relative distance
has relative distance 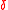 >
>  . In order for
. In order for 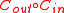 to be an asymptotically good code,
to be an asymptotically good code, 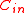 also needs to be an asymptotically good code which means,
also needs to be an asymptotically good code which means, 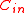 needs to have rate
needs to have rate  >
> 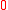 and relative distance
and relative distance 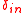 >
> 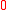 .
.
Suppose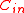 meets the Gilbert-Varshamov bound
meets the Gilbert-Varshamov bound
with rate of and thus with relative distance
and thus with relative distance 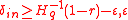 >
> 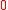 , then
, then 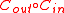 has rate of
has rate of 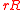 and
and 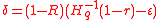 .
.
Expressing as a function of
as a function of 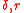 ,:
,: 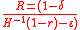
Then optimizing over the choice of r, we get that rate of the Concatenated error correction code satisfies,
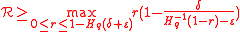
This lower bound is called Zyablov bound (the bound of <
< 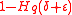 is necessary to ensure that
is necessary to ensure that  >
>  ). See Figure 2 for a plot of this bound.
). See Figure 2 for a plot of this bound.
Note that the Zyablov bound implies that for every >
>  , there exists a (concatenated) code with rate
, there exists a (concatenated) code with rate
 >
> 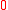 .
.
Linear Codes will help us complete the proof of the above statement since linear codes have polynomial representation. Let Cout be an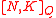 Reed-Solomon error correction code where
Reed-Solomon error correction code where 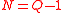 (evaluation points being
(evaluation points being 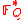 with
with 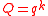 , then
, then 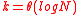 .
.
We need to construct the Inner code that lies on Gilbert-Varshamov bound
. This can be done in two ways
can be achieved by using the method of conditional expectation on the proof that random linear code lies on the bound with high probability.
Thus we can construct a code that achieves the Zyablov bound in polynomial time.
 and relative distance
and relative distance 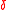 of the concatenated codes.
of the concatenated codes.Statement of the bound
Let be the rate of the outer code
be the rate of the outer code  and
and 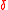 be the relative distance, then the rate of the concatenated codes satisfies the following bound.
be the relative distance, then the rate of the concatenated codes satisfies the following bound.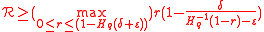
where
 is the rate of the inner code
is the rate of the inner code 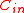 .
.Description
Let be the outer code,
be the outer code, 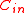 be the inner code.
be the inner code.Consider
 meets the Singleton bound
meets the Singleton boundSingleton bound
In coding theory, the Singleton bound, named after Richard Collom Singleton, is a relatively crude bound on the size of a block code C with block length n, size r and minimum distance d.-Statement of the Bound:...
with rate of
 , i.e.
, i.e.  has relative distance
has relative distance 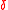 >
>  . In order for
. In order for 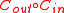 to be an asymptotically good code,
to be an asymptotically good code, 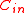 also needs to be an asymptotically good code which means,
also needs to be an asymptotically good code which means, 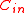 needs to have rate
needs to have rate  >
>  and relative distance
and relative distance 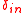 >
>  .
.Suppose
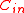 meets the Gilbert-Varshamov bound
meets the Gilbert-Varshamov boundGilbert-Varshamov bound
In coding theory, the Gilbert–Varshamov bound is a bound on the parameters of a code . It is occasionally known as the Gilbert–Shannon–Varshamov bound , but the Gilbert–Varshamov bound is by far the most popular name...
with rate of
 and thus with relative distance
and thus with relative distance 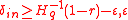 >
>  , then
, then 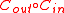 has rate of
has rate of  and
and 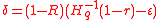 .
.Expressing
 as a function of
as a function of 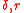 ,:
,: 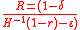
Then optimizing over the choice of r, we get that rate of the Concatenated error correction code satisfies,
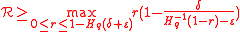
This lower bound is called Zyablov bound (the bound of
 <
< 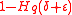 is necessary to ensure that
is necessary to ensure that  >
>  ). See Figure 2 for a plot of this bound.
). See Figure 2 for a plot of this bound.Note that the Zyablov bound implies that for every
 >
>  , there exists a (concatenated) code with rate
, there exists a (concatenated) code with rate >
>  .
.Remarks
We can construct a code that achieves the Zyablov bound in polynomial time. In particular, we can construct explicit asymptotically good code (over some alphabets) in polynomial time.Linear Codes will help us complete the proof of the above statement since linear codes have polynomial representation. Let Cout be an
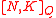 Reed-Solomon error correction code where
Reed-Solomon error correction code where  (evaluation points being
(evaluation points being 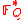 with
with  , then
, then 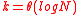 .
.We need to construct the Inner code that lies on Gilbert-Varshamov bound
Gilbert-Varshamov bound
In coding theory, the Gilbert–Varshamov bound is a bound on the parameters of a code . It is occasionally known as the Gilbert–Shannon–Varshamov bound , but the Gilbert–Varshamov bound is by far the most popular name...
. This can be done in two ways
- To perform an exhaustive search on all generator matrices until the required property is satisfied for
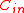 . This is because Varshamovs bound states that there exists a linear code that lies on Gilbert-Varshamon bound which will take
. This is because Varshamovs bound states that there exists a linear code that lies on Gilbert-Varshamon bound which will take 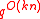 time.Using
time.Using 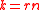 we get
we get 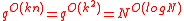 , which is upper bounded by
, which is upper bounded by 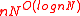 , a quasi-polynomial time bound.
, a quasi-polynomial time bound.
- To construct
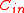 in
in 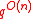 time and use
time and use 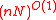 time overall. This
time overall. This
can be achieved by using the method of conditional expectation on the proof that random linear code lies on the bound with high probability.
Thus we can construct a code that achieves the Zyablov bound in polynomial time.

