
Zilla Parishad
Encyclopedia
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
. It looks after the administration of the rural area of the district and its office is located at the district headquarters. The Hindi word Parishad means Council and Zilla Parishad translates to District Council
Constitution
Members of the Zilla Parishad are elected from the district on the basis of adult franchise for a term of five years. Zilla Parishad has minimum of 50 and maximum of 75 members. There are seats reserved for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, backward classes and women.The Chairmen of all the Panchayat Samiti
Panchayat samiti
Panchayat samiti is a local government body at the tehsil or Taluka level in India. It works for the villages of the Tehsil or Taluka that together are called a Development Block. The Panchayat Samiti is the link between the Gram Panchayat and the district administration. There are a number of...
s form the members of Zilla Parishad
Zilla Parishad
Zilla Parishad is a local government body at the district level in India. It looks after the administration of the rural area of the district and its office is located at the district headquarters...
. The Parishad is headed by a President and a Vice-President.
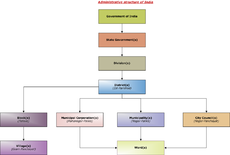
Administrative structure
The Chief Executive Officer (CEO), who is an IASIndian Administrative Service
The Indian Administrative Service is the administrative civil service of the Government of India. It is one of the three All India Services....
officer, heads the administrative machinery of the Zilla Parishad. The CEO supervises the divisions of the Parishad and executes its development schemes.
Functions
- Provide essential services and facilities to the rural population and the planning and execution of the development programmes for the district.
- Supply improved seeds to farmers. Inform them of new techniques of training. Undertake construction of small-scale irrigation projects and percolation tanks. Maintain pastures and grazing lands.
- Set up and run schools in villages. Execute programmes for adult literacy. Run libraries.
- Start Primary Health Centers and hospitals in villages. Start mobile hospitals for hamlets, vaccination drives against epidemics and family welfare campaigns.
- Construct bridges and roads.
- Execute plans for the development of the scheduled castes and tribes. Run ashramshalas for adivasi children. Set up free hostels for scheduled caste students.
- Encourage entrepreneurs to start small-scale industries like cottage industries, handicraft, agriculture produce processing mills, dairy farms, etc. Implement rural employment schemes.
- They construct roads,schools,& public properties.And they take care of the public properties.
- They even supply work for the poor people.(tribes,scheduled caste,lower caste)
Sources of Income
- Taxes on water, pilgrimage, markets, etc.
- Fixed grant from the State Government in proportion with the land revenue and money for works and schemes assigned to the Parishad.

