
Wolffenstein-Böters reaction
Encyclopedia
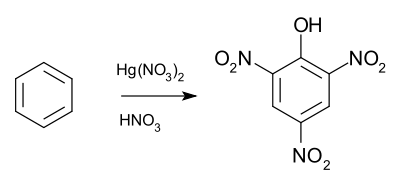
The Wolffenstein-Böters reaction is an organic reaction
converting benzene
to picric acid
by a mixture of aqueous nitric acid
and mercury(II) nitrate
.
 According to one series of studies the mercury nitrate first takes benzene to the corresponding nitroso
According to one series of studies the mercury nitrate first takes benzene to the corresponding nitroso
compound and through the diazonium salt to the phenol
. The presence of nitrite
is essential for the reaction; picric acid formation is prevented when urea
, a trap for nitrous acid, is added to the mixture. From then on the reaction proceeds as a regular aromatic nitration
.
A conceptually related reaction at one time of interest to the pigment industry is the Bohn-Schmidt reaction (1889) involving the hydroxylation of hydroxyantraquinone with sulfuric acid
and lead
or selenium
to a polyhydroxylated anthraquinone
.
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
converting benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
to picric acid
Picric acid
Picric acid is the chemical compound formally called 2,4,6-trinitrophenol . This yellow crystalline solid is one of the most acidic phenols. Like other highly nitrated compounds such as TNT, picric acid is an explosive...
by a mixture of aqueous nitric acid
Nitric acid
Nitric acid , also known as aqua fortis and spirit of nitre, is a highly corrosive and toxic strong acid.Colorless when pure, older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation of oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% nitric acid, it is referred to as fuming...
and mercury(II) nitrate
Mercury(II) nitrate
Mercury nitrate is a toxic colorless or white soluble crystalline mercury salt of nitric acid. It was also used to treat fur to make felt in a process called 'carroting'. The phrase 'mad as a hatter' is associated with psychological illness brought on by excessive exposure to mercury nitrate...
.

Nitroso
Nitroso refers to a functional group in organic chemistry which has the general formula RNO. Nitroso compounds are a class of organic compounds containing the nitroso functional group, R−N=O....
compound and through the diazonium salt to the phenol
Phenol
Phenol, also known as carbolic acid, phenic acid, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid. The molecule consists of a phenyl , bonded to a hydroxyl group. It is produced on a large scale as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds...
. The presence of nitrite
Nitrite
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula NO2−. The anion is symmetric with equal N-O bond lengths and a O-N-O bond angle of ca. 120°. On protonation the unstable weak acid nitrous acid is produced. Nitrite can be oxidised or reduced, with product somewhat dependent on the oxidizing/reducing agent...
is essential for the reaction; picric acid formation is prevented when urea
Urea
Urea or carbamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO2. The molecule has two —NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl functional group....
, a trap for nitrous acid, is added to the mixture. From then on the reaction proceeds as a regular aromatic nitration
Nitration
Nitration is a general chemical process for the introduction of a nitro group into a chemical compound. The dominant application of nitration is for the production of nitrobenzene, the precursor to methylene diphenyl diisocyanate...
.
A conceptually related reaction at one time of interest to the pigment industry is the Bohn-Schmidt reaction (1889) involving the hydroxylation of hydroxyantraquinone with sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
and lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
or selenium
Selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with atomic number 34, chemical symbol Se, and an atomic mass of 78.96. It is a nonmetal, whose properties are intermediate between those of adjacent chalcogen elements sulfur and tellurium...
to a polyhydroxylated anthraquinone
Anthraquinone
Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene is an aromatic organic compound with formula . Several isomers are possible, each of which can be viewed as a quinone derivative...
.
External links
- The Bohn-Schmidt reaction @ Institute of Chemistry, Skopje, Macedonia Link

