
Wigner-Seitz radius
Encyclopedia
The Wigner–Seitz radius 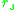 , named after Eugene Wigner and Frederick Seitz
, named after Eugene Wigner and Frederick Seitz
, is a parameter used frequently in condensed matter physics
to describe the density of a system. The formula for 3-D system is
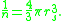
Solving for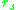 we obtain
we obtain
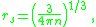
where is the particle density
is the particle density
of the valence electrons.
For a non-interacting system, the average separation between two particles will be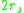 . The radius can also be calculated as
. The radius can also be calculated as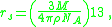
where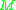 is molar mass
is molar mass
,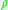 is mass density, and
is mass density, and
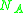 is the Avogadro number.
is the Avogadro number.
This parameter is normally reported in atomic units
, i.e., in units of the Bohr radius
.
 , named after Eugene Wigner and Frederick Seitz
, named after Eugene Wigner and Frederick SeitzFrederick Seitz
Frederick Seitz was an American physicist and a pioneer of solid state physics. Seitz was president of Rockefeller University, and president of the United States National Academy of Sciences 1962–1969. He was the recipient of the National Medal of Science, NASA's Distinguished Public Service...
, is a parameter used frequently in condensed matter physics
Condensed matter physics
Condensed matter physics deals with the physical properties of condensed phases of matter. These properties appear when a number of atoms at the supramolecular and macromolecular scale interact strongly and adhere to each other or are otherwise highly concentrated in a system. The most familiar...
to describe the density of a system. The formula for 3-D system is
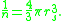
Solving for
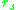 we obtain
we obtain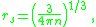
where
 is the particle density
is the particle densityParticle density
The particle density or true density of a particulate solid or powder, is the density of the particles that make up the powder, in contrast to the bulk density, which measures the average density of a large volume of the powder in a specific medium .The particle density is a relatively well-defined...
of the valence electrons.
For a non-interacting system, the average separation between two particles will be
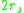 . The radius can also be calculated as
. The radius can also be calculated as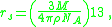
where
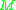 is molar mass
is molar massMolar mass
Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
,
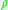 is mass density, and
is mass density, and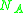 is the Avogadro number.
is the Avogadro number.This parameter is normally reported in atomic units
Atomic units
Atomic units form a system of natural units which is especially convenient for atomic physics calculations. There are two different kinds of atomic units, which one might name Hartree atomic units and Rydberg atomic units, which differ in the choice of the unit of mass and charge. This article...
, i.e., in units of the Bohr radius
Bohr radius
The Bohr radius is a physical constant, approximately equal to the most probable distance between the proton and electron in a hydrogen atom in its ground state. It is named after Niels Bohr, due to its role in the Bohr model of an atom...
.

