
Welch's t test
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, Welch's t test is an adaptation of Student's t-test
intended for use with two samples having possibly unequal variance
s. As such, it is an approximate solution to the Behrens–Fisher problem.
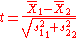
where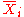 ,
, 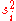 and
and 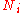 are the
are the 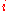 th sample mean
th sample mean
, sample variance
and sample size
, respectively. Unlike in Student's t-test, the denominator is not based on a pooled variance
estimate.
The degrees of freedom associated with this variance estimate is approximated using the Welch-Satterthwaite equation
associated with this variance estimate is approximated using the Welch-Satterthwaite equation
:
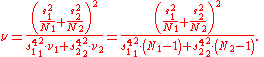
Here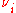 =
= 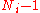 , the degrees of freedom associated with the
, the degrees of freedom associated with the 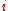 th variance estimate.
th variance estimate.
 have been computed, these statistics can be used with the t-distribution to test the null hypothesis
have been computed, these statistics can be used with the t-distribution to test the null hypothesis
that the two population means are equal (using a two-tailed test
), or the null hypothesis that one of the population means is greater than or equal to the other (using a one-tailed test). In particular, the test will yield a p-value
which might or might not give evidence sufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, Welch's t test is an adaptation of Student's t-test
Student's t-test
A t-test is any statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's t distribution if the null hypothesis is supported. It is most commonly applied when the test statistic would follow a normal distribution if the value of a scaling term in the test statistic were known...
intended for use with two samples having possibly unequal variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
s. As such, it is an approximate solution to the Behrens–Fisher problem.
Formulas
Welch's t-test defines the statistic t by the following formula: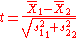
where
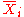 ,
, 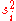 and
and 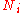 are the
are the 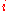 th sample mean
th sample meanMean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
, sample variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
and sample size
Sample size
Sample size determination is the act of choosing the number of observations to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences about a population from a sample...
, respectively. Unlike in Student's t-test, the denominator is not based on a pooled variance
Pooled variance
In statistics, many times, data are collected for a dependent variable, y, over a range of values for the independent variable, x. For example, the observation of fuel consumption might be studied as a function of engine speed while the engine load is held constant...
estimate.
The degrees of freedom
 associated with this variance estimate is approximated using the Welch-Satterthwaite equation
associated with this variance estimate is approximated using the Welch-Satterthwaite equationWelch-Satterthwaite equation
In statistics and uncertainty analysis, the Welch–Satterthwaite equation is used to calculate an approximation to the effective degrees of freedom of a linear combination of independent sample variances....
:
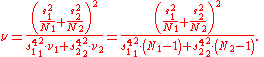
Here
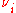 =
= 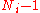 , the degrees of freedom associated with the
, the degrees of freedom associated with the 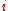 th variance estimate.
th variance estimate.Statistical test
Once t and have been computed, these statistics can be used with the t-distribution to test the null hypothesis
have been computed, these statistics can be used with the t-distribution to test the null hypothesisNull hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
that the two population means are equal (using a two-tailed test
Two-tailed test
The two-tailed test is a statistical test used in inference, in which a given statistical hypothesis, H0 , will be rejected when the value of the test statistic is either sufficiently small or sufficiently large...
), or the null hypothesis that one of the population means is greater than or equal to the other (using a one-tailed test). In particular, the test will yield a p-value
P-value
In statistical significance testing, the p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic at least as extreme as the one that was actually observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. One often "rejects the null hypothesis" when the p-value is less than the significance level α ,...
which might or might not give evidence sufficient to reject the null hypothesis.

