
Vympel R-73
Encyclopedia
The Vympel R-73 developed by Vympel
machine-building design bureau, is the most modern Russian short-range air-to-air missile
.
weapon for short-range use by Soviet
fighter aircraft
. Work began in 1973, and the first missiles entered service in 1982.
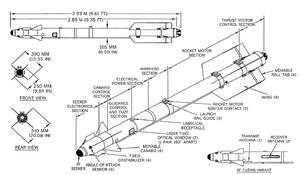
The R-73 is an infrared-guided (heat-seeking) missile with a sensitive, cryogenic cooled seeker with a substantial "off-boresight" capability: the seeker can "see" targets up to 60° off the missile's centerline. It can be targeted by a helmet-mounted sight (HMS) allowing pilots to designate targets by looking at them. Minimum engagement range is about 300 meters, with maximum aerodynamic range of nearly 30 km (18.6 mi) at altitude.
The R-73 is a highly maneuverable missile and mock dogfights have indicated that the high degree of "off-boresight" capability of the R-73 would make a significant difference in combat. The missile also has a mechanically simple but effective system for thrust-vectoring. Altogether this prompted the development of the Sidewinder
and other SRM successors like AIM-132 ASRAAM
, IRIS-T
, MICA IR, Python IV and the latest Sidewinder variant, AIM-9X, that entered squadron service in 2003.
From 1994 the R-73 has been upgraded in production to the R-73M standard, which entered CIS
service in 1997. The R-73M has greater range and a wider seeker angle (to 60° off-boresight), as well as improved IRCCM (Infra-Red Counter-Counter-Measures).
An improved version of the R-73M, the R-74M features fully digital and re-programmable systems, and is intended for use on the MiG-35 or MiG-29K/M/M2 and Su-27SM, Su-30MK and Su-35BM.
The weapon is used by the MiG-29, MiG-31, Su-27, Su-34 and Su-35, and can be carried by newer versions of the MiG-21, MiG-23, Sukhoi Su-24
, and Su-25 aircraft. India is looking to use the missile on their HAL Tejas
. It can also be carried by Russian attack helicopters, including the Mil Mi-24
, Mil Mi-28
, and Kamov Ka-50
.
were shot down by a Cuban Air Force MiG-29UB. Each of the aircraft was downed by a R-73 missile.
During Eritrean-Ethiopian War
from May 1998 to June 2000, R-73 missiles were used in combat by both Ethiopian Su-27s and Eritrean MiG-29s. It was the IR-homing R-60 and the R-73 that were used in all but two of the kills (one having been scored with 30mm cannon fire, while one of the no less than 24 R-27 medium-range missiles resulted in the other).
On 21 April 2008, a Russian MIG-29 shot down
a Georgian UAV with an IR guided missile, most likely an R-73. The downing was recorded by the shot down UAV itself.
Vympel NPO
Vympel NPO is a Russian research and production company based near Moscow, mostly known for their air-to-air missiles. Other projects include SAM and ABM defenses. It was started in the Soviet era as an OKB .-OKB-134 Toropov:...
machine-building design bureau, is the most modern Russian short-range air-to-air missile
Air-to-air missile
An air-to-air missile is a missile fired from an aircraft for the purpose of destroying another aircraft. AAMs are typically powered by one or more rocket motors, usually solid fuelled but sometimes liquid fuelled...
.
Development
The R-73 was developed to replace the earlier R-60 (AA-8 'Aphid')Molniya R-60
The Molniya R-60 is a lightweight air-to-air missile designed for use by Soviet fighter aircraft. It has been widely exported, and remains in service with the CIS and many other nations....
weapon for short-range use by Soviet
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
fighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft
A fighter aircraft is a military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat with other aircraft, as opposed to a bomber, which is designed primarily to attack ground targets...
. Work began in 1973, and the first missiles entered service in 1982.
The R-73 is an infrared-guided (heat-seeking) missile with a sensitive, cryogenic cooled seeker with a substantial "off-boresight" capability: the seeker can "see" targets up to 60° off the missile's centerline. It can be targeted by a helmet-mounted sight (HMS) allowing pilots to designate targets by looking at them. Minimum engagement range is about 300 meters, with maximum aerodynamic range of nearly 30 km (18.6 mi) at altitude.
The R-73 is a highly maneuverable missile and mock dogfights have indicated that the high degree of "off-boresight" capability of the R-73 would make a significant difference in combat. The missile also has a mechanically simple but effective system for thrust-vectoring. Altogether this prompted the development of the Sidewinder
AIM-9 Sidewinder
The AIM-9 Sidewinder is a heat-seeking, short-range, air-to-air missile carried mostly by fighter aircraft and recently, certain gunship helicopters. The missile entered service with United States Air Force in the early 1950s, and variants and upgrades remain in active service with many air forces...
and other SRM successors like AIM-132 ASRAAM
AIM-132 ASRAAM
The AIM-132 Advanced Short Range Air-to-Air Missile is an infrared homing air-to-air missile, produced by MBDA. It is currently in service in the Royal Air Force and Royal Australian Air Force , replacing the AIM-9 Sidewinder...
, IRIS-T
IRIS-T
The IRIS-T is a German-led program to develop a short-range air-to-air missile to replace the venerable AIM-9 Sidewinder found in some of the NATO member countries...
, MICA IR, Python IV and the latest Sidewinder variant, AIM-9X, that entered squadron service in 2003.
From 1994 the R-73 has been upgraded in production to the R-73M standard, which entered CIS
Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States is a regional organization whose participating countries are former Soviet Republics, formed during the breakup of the Soviet Union....
service in 1997. The R-73M has greater range and a wider seeker angle (to 60° off-boresight), as well as improved IRCCM (Infra-Red Counter-Counter-Measures).
An improved version of the R-73M, the R-74M features fully digital and re-programmable systems, and is intended for use on the MiG-35 or MiG-29K/M/M2 and Su-27SM, Su-30MK and Su-35BM.
The weapon is used by the MiG-29, MiG-31, Su-27, Su-34 and Su-35, and can be carried by newer versions of the MiG-21, MiG-23, Sukhoi Su-24
Sukhoi Su-24
The Sukhoi Su-24 is a supersonic, all-weather attack aircraft developed in the Soviet Union. This variable-sweep wing, twin-engined two-seater carried the USSR's first integrated digital navigation/attack system...
, and Su-25 aircraft. India is looking to use the missile on their HAL Tejas
HAL Tejas
The HAL Tejas is a lightweight multirole fighter developed by India. It is a tailless, compound delta-wing design powered by a single engine. It came from the Light Combat Aircraft programme, which began in the 1980s to replace India's ageing MiG-21 fighters...
. It can also be carried by Russian attack helicopters, including the Mil Mi-24
Mil Mi-24
The Mil Mi-24 is a large helicopter gunship and attack helicopter and low-capacity troop transport with room for 8 passengers. It is produced by Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant and operated since 1972 by the Soviet Air Force, its successors, and by over thirty other nations.In NATO circles the export...
, Mil Mi-28
Mil Mi-28
The Mil Mi-28 is a Russian all-weather day-night military tandem two-seat anti-armour attack helicopter. It is a dedicated attack helicopter with no intended secondary transport capability, better optimized than the Mil Mi-24 for the role...
, and Kamov Ka-50
Kamov Ka-50
The Kamov Ka-50 "Black Shark" is a single-seat Russian attack helicopter with the distinctive coaxial rotor system of the Kamov design bureau. It was designed in the 1980s and adopted for service in the Russian army in 1995...
.

Operational history
On 24 February 1996, two Cessna 337 of the Brothers to the RescueBrothers to the Rescue
Brothers to the Rescue is a Miami-based activist organization headed by José Basulto. Formed by Cuban exiles, the group is widely known for its opposition to the Cuban government and, then President, Fidel Castro...
were shot down by a Cuban Air Force MiG-29UB. Each of the aircraft was downed by a R-73 missile.
During Eritrean-Ethiopian War
Eritrean-Ethiopian War
The Eritrean–Ethiopian War took place from May 1998 to June 2000 between Ethiopia and Eritrea, forming one of the conflicts in the Horn of Africa...
from May 1998 to June 2000, R-73 missiles were used in combat by both Ethiopian Su-27s and Eritrean MiG-29s. It was the IR-homing R-60 and the R-73 that were used in all but two of the kills (one having been scored with 30mm cannon fire, while one of the no less than 24 R-27 medium-range missiles resulted in the other).
On 21 April 2008, a Russian MIG-29 shot down
2008 Georgian spy plane shootdowns
2008 Georgian spy plane shootdowns refers to seven occasions during the course of March, April and May 2008 where Georgia's breakaway republic of Abkhazia claimed to have shot down unmanned Georgian reconnaissance aircraft...
a Georgian UAV with an IR guided missile, most likely an R-73. The downing was recorded by the shot down UAV itself.

