
Void (astronomy)
Encyclopedia
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
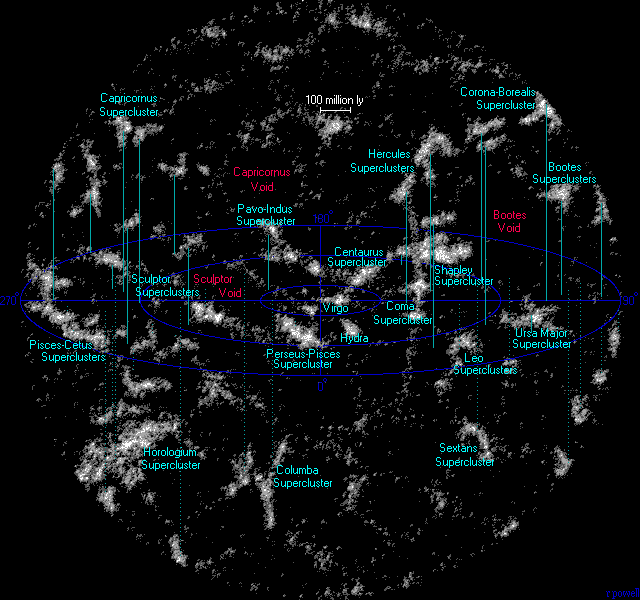
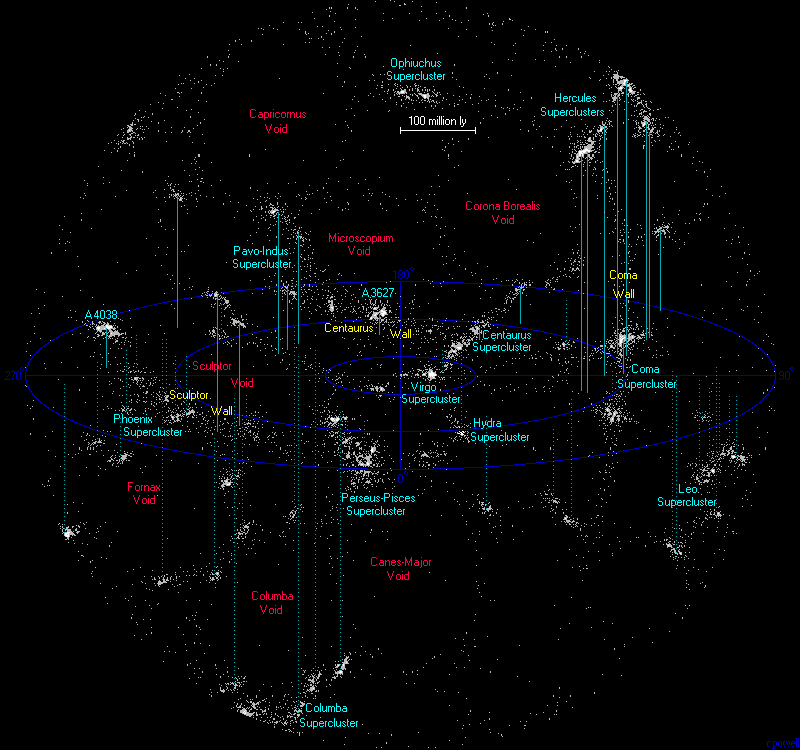
, voids are the empty spaces between filaments
Galaxy filament
In physical cosmology, galaxy filaments, also called supercluster complexes or great walls, are, so far, the largest known cosmic structures in the universe. They are massive, thread-like structures with a typical length of 50 to 80 megaparsecs h-1 that form the boundaries between large voids in...
, the largest-scale structures in the Universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
, that contain very few
Void galaxy
Void galaxies are galaxies which exist in cosmological voids. Few galaxies exist in voids; most galaxies exist in sheets, walls and filaments that surround voids and supervoids. Many of the void galaxies are connected through void filaments, lightweight versions of the regular galaxy filaments that...
, or no, galaxies. They were first discovered in 1978 during a pioneering study by Stephen Gregory and Laird A. Thompson
Laird A. Thompson
Laird A. Thompson , is a professor of astronomy at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Thompson graduated with a B.A. in both physics and astronomy from the University of California, Los Angeles in 1969. He received his Ph.D...
at the Kitt Peak National Observatory
Kitt Peak National Observatory
The Kitt Peak National Observatory is a United States astronomical observatory located on 2,096 m Kitt Peak of the Quinlan Mountains in the Arizona-Sonoran Desert on the Tohono O'odham Nation, southwest of Tucson...
. Voids typically have a diameter of 11 to 150 megaparsecs; particularly large voids, defined by the absence of rich supercluster
Supercluster
Superclusters are large groups of smaller galaxy groups and clusters and are among the largest known structures of the cosmos. They are so large that they are not gravitationally bound and, consequently, partake in the Hubble expansion.-Existence:...
s, are sometimes called "supervoids". Voids located in high-density environments are smaller than voids situated in low-density spaces of the universe.
Voids were formed by baryon acoustic oscillations in the Big Bang
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
by collapses of mass followed by implosions of the compressed baryonic matter. The shells of the voids are the remnants of shock fronts left by this process. The decoupling of matter from radiation when the universe became transparent "froze" the voids and shock fronts in place.
See also
- List of voids
- List of superclusters
- Large-scale structure of the universe
External links
- Universe family tree: Void
- Animated views of voids and their distribution from Hume Feldman with Sergei Shandarin, Dept. Physics and Astronomy, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, USA.
- Visualization of Nearby Large-Scale Structures Fairall, A. P., Paverd, W. R., & Ashley, R. P.

