
Variation ratio
Encyclopedia
The variation ratio is a simple measure of statistical dispersion
in nominal distributions; it is the simplest measure of qualitative variation
.
It is defined as the proportion of cases which are not the mode
: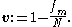
While a simple measure, it is notable in that some texts and guides suggest or imply that the dispersion of nominal measurements cannot be ascertained. It is defined for instance by .
Just as with the range
or standard deviation
, the larger the variation ratio, the more differentiated or dispersed the data are; and the smaller the variation ratio, the more concentrated and similar the data are.
For example, a group which is 55% female and 45% male has a proportion of 0.55 females and therefore variation ratio of (1.0- 0.55) = 0.45; and is more dispersed in terms of gender than a group which is 95% female and has a variation ratio of only 0.05. Similarly, a group which is 25% Catholic (where Catholic is the modal religious preference) has a variation ratio of 0.75 and is much more dispersed religiously than a group which is 85% Catholic and has a variation ratio of only 0.15.
Statistical dispersion
In statistics, statistical dispersion is variability or spread in a variable or a probability distribution...
in nominal distributions; it is the simplest measure of qualitative variation
Qualitative variation
An index of qualitative variation is a measure of statistical dispersion in nominal distributions. There are a variety of these, but they have been relatively little-studied in the statistics literature...
.
It is defined as the proportion of cases which are not the mode
Mode (statistics)
In statistics, the mode is the value that occurs most frequently in a data set or a probability distribution. In some fields, notably education, sample data are often called scores, and the sample mode is known as the modal score....
:
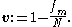
While a simple measure, it is notable in that some texts and guides suggest or imply that the dispersion of nominal measurements cannot be ascertained. It is defined for instance by .
Just as with the range
Range (statistics)
In the descriptive statistics, the range is the length of the smallest interval which contains all the data. It is calculated by subtracting the smallest observation from the greatest and provides an indication of statistical dispersion.It is measured in the same units as the data...
or standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
, the larger the variation ratio, the more differentiated or dispersed the data are; and the smaller the variation ratio, the more concentrated and similar the data are.
For example, a group which is 55% female and 45% male has a proportion of 0.55 females and therefore variation ratio of (1.0- 0.55) = 0.45; and is more dispersed in terms of gender than a group which is 95% female and has a variation ratio of only 0.05. Similarly, a group which is 25% Catholic (where Catholic is the modal religious preference) has a variation ratio of 0.75 and is much more dispersed religiously than a group which is 85% Catholic and has a variation ratio of only 0.15.
See also
- Qualitative variationQualitative variationAn index of qualitative variation is a measure of statistical dispersion in nominal distributions. There are a variety of these, but they have been relatively little-studied in the statistics literature...
, for a number of other measures of dispersion in nominal variables

