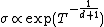Variable range hopping
Encyclopedia
Introduction
Variable range hopping or Mott variable range hopping, is a model describing low temperature conduction in strongly disordered systems with localizedAnderson localization
In condensed matter physics, Anderson localization, also known as strong localization, is the absence of diffusion of waves in a disordered medium. This phenomenon is named after the American physicist P. W...
states.
It has a characteristic temperature dependence of

for three dimensional conductance, and in general for
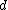 -dimensions
-dimensions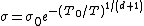 .
.Hopping conduction at low temperatures is of great interest because of the savings the semiconductor industry could achieve if they were able to replace single-crystal devices with glass layers.
Derivation
The original Mott paper introduced a simplifying assumption that the hopping energy depends inversely on the cube of the hopping distance (in the three dimensional case). Later it was shown that this assumption was unnecessary, and this proof is followed here. In the original paper, the hopping probability at a given temperature was seen to depend on two parameters, R the spatial separation of the sites, and W, their energy separation. Apsley and Hughes noted that in a truly amorphous system, these variables are random and independent and so can be combined into a single parameter, the range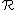 between two sites, which determines the probability of hopping between them.
between two sites, which determines the probability of hopping between them.Mott showed that the probability of hopping between two states of spatial separation
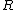 and energy separation W has the form:
and energy separation W has the form: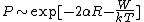
where α−1 is the attenuation length for a hydrogen-like localised wave-function. This assumes that hopping to a state with a higher energy is the rate limiting process.
We now define
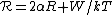 , the range between two states, so
, the range between two states, so 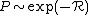 . The states may be regarded as points in a four-dimensional random array (three spatial coordinates and one energy coordinate), with the `distance' between them given by the range
. The states may be regarded as points in a four-dimensional random array (three spatial coordinates and one energy coordinate), with the `distance' between them given by the range 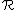 .
.Conduction is the result of many series of hops through this four-dimensional array and as short-range hops are favoured, it is the average nearest-neighbour `distance' between states which determines the overall conductivity. Thus the conductivity has the form
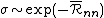
where
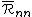 is the `average nearest-neighbour range'. The problem is therefore to calculate this quantity.
is the `average nearest-neighbour range'. The problem is therefore to calculate this quantity.The first step is to obtain
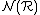 , the total number of states within a range
, the total number of states within a range 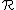 of some initial state at the Fermi level. For
of some initial state at the Fermi level. For 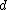 -dimensions, and under particular assumptions this turns out to be
-dimensions, and under particular assumptions this turns out to be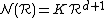
where
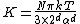 .
.The particular assumptions are simply that
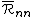 is well less than the band-width and comfortably bigger than the interatomic spacing.
is well less than the band-width and comfortably bigger than the interatomic spacing.Then the probability that a state with range
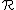 is the nearest neighbour in the four-dimensional space (or in general the
is the nearest neighbour in the four-dimensional space (or in general the 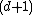 -dimensional space) is
-dimensional space) is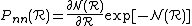
the nearest-neighbour distribution.
For the
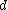 -dimensional case then
-dimensional case then .
.This can be evaluated by making a simple substitution of
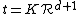 into the Gamma function
into the Gamma functionGamma function
In mathematics, the gamma function is an extension of the factorial function, with its argument shifted down by 1, to real and complex numbers...
,
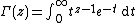
After some algebra this gives
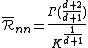
and hence that