
Urocanate hydratase
Encyclopedia
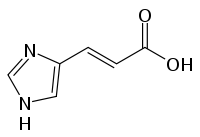

- urocanate + H2O
 4,5-dihydro-4-oxo-5-imidazolepropanoateImidazol-4-one-5-propionic acidImidazol-4-one-5-propionic acid is an intermediate in the metabolism of histidine.-See also:* Urocanate hydratase* Urocanate* Formiminoglutamic acid...
4,5-dihydro-4-oxo-5-imidazolepropanoateImidazol-4-one-5-propionic acidImidazol-4-one-5-propionic acid is an intermediate in the metabolism of histidine.-See also:* Urocanate hydratase* Urocanate* Formiminoglutamic acid...
Inherited deficiency of urocanase leads to elevated levels of urocanic acid in the urine, a condition known as urocanic aciduria
Urocanic aciduria
Urocanic aciduria, also called urocanate hydratase deficiency or urocanase deficiency, is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme urocanase. It is a secondary disorder of histidine metabolism.-Pathophysiology:...
.
Urocanase is found in some bacteria (gene hutU), in the liver of many vertebrates and has also been found in the plant Trifolium repens (white clover). Urocanase is a protein of about 60 Kd, it binds tightly to NAD+ and uses it as an electrophil cofactor. A conserved cysteine has been found to be important for the catalytic mechanism and could be involved in the binding of the NAD+.

