
Ultrarelativistic limit
Encyclopedia
In physics
, a particle is called ultrarelativistic when its speed is very close to the speed of light .
.
Max Planck
showed that the relativistic expression for the energy of a particle whose rest mass is and momentum is
and momentum is 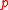 is given by
is given by 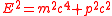 . The energy of an ultrarelativistic particle is almost completely due to its momentum (
. The energy of an ultrarelativistic particle is almost completely due to its momentum (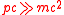 ), and thus can be approximated by
), and thus can be approximated by 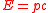 . This can result from holding the mass fixed and increasing p to very large values (the usual case); or by holding the energy E fixed and shrinking the mass m to negligible values. The latter is used to derive orbits of massless particles such as the photon
. This can result from holding the mass fixed and increasing p to very large values (the usual case); or by holding the energy E fixed and shrinking the mass m to negligible values. The latter is used to derive orbits of massless particles such as the photon
from those of massive particles (cf. Kepler problem in general relativity
).
In general, the ultrarelativistic limit of an expression is the resulting simplified expression when is assumed. Or, similarly, in the limit where the Lorentz factor
is assumed. Or, similarly, in the limit where the Lorentz factor
is very large (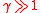 ).
).
 is about 10%, and for
is about 10%, and for 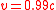 it is just 2%. For particles such as neutrinos, whose γ (Lorentz factor
it is just 2%. For particles such as neutrinos, whose γ (Lorentz factor
) are usually above 106 ( very close to c), the approximation is essentially exact.
very close to c), the approximation is essentially exact.
 and so its energy can be approximated by
and so its energy can be approximated by 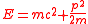 .
.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, a particle is called ultrarelativistic when its speed is very close to the speed of light
 .
.Max Planck
Max Planck
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, ForMemRS, was a German physicist who actualized the quantum physics, initiating a revolution in natural science and philosophy. He is regarded as the founder of the quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918.-Life and career:Planck came...
showed that the relativistic expression for the energy of a particle whose rest mass is
 and momentum is
and momentum is 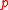 is given by
is given by 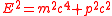 . The energy of an ultrarelativistic particle is almost completely due to its momentum (
. The energy of an ultrarelativistic particle is almost completely due to its momentum (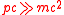 ), and thus can be approximated by
), and thus can be approximated by  . This can result from holding the mass fixed and increasing p to very large values (the usual case); or by holding the energy E fixed and shrinking the mass m to negligible values. The latter is used to derive orbits of massless particles such as the photon
. This can result from holding the mass fixed and increasing p to very large values (the usual case); or by holding the energy E fixed and shrinking the mass m to negligible values. The latter is used to derive orbits of massless particles such as the photonPhoton
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
from those of massive particles (cf. Kepler problem in general relativity
Kepler problem in general relativity
The two-body problem in general relativity is to determine the motion and gravitational field of two bodies interacting with one another by gravitation, as described by the field equations of general relativity. Solving the Kepler problem is essential to calculate the bending of light by gravity...
).
In general, the ultrarelativistic limit of an expression is the resulting simplified expression when
 is assumed. Or, similarly, in the limit where the Lorentz factor
is assumed. Or, similarly, in the limit where the Lorentz factorLorentz factor
The Lorentz factor or Lorentz term appears in several equations in special relativity, including time dilation, length contraction, and the relativistic mass formula. Because of its ubiquity, physicists generally represent it with the shorthand symbol γ . It gets its name from its earlier...
is very large (
 ).
).Accuracy of the approximation
For calculations of the energy of a particle, the relative error of the ultrarelativistic limit for a speed is about 10%, and for
is about 10%, and for  it is just 2%. For particles such as neutrinos, whose γ (Lorentz factor
it is just 2%. For particles such as neutrinos, whose γ (Lorentz factorLorentz factor
The Lorentz factor or Lorentz term appears in several equations in special relativity, including time dilation, length contraction, and the relativistic mass formula. Because of its ubiquity, physicists generally represent it with the shorthand symbol γ . It gets its name from its earlier...
) are usually above 106 (
 very close to c), the approximation is essentially exact.
very close to c), the approximation is essentially exact.Other limits
The opposite case is a so-called classical particle, where its speed is much smaller than and so its energy can be approximated by
and so its energy can be approximated by 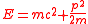 .
.

