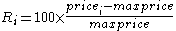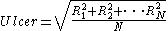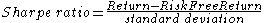Ulcer Index
Encyclopedia
The Ulcer Index is a stock market risk measure or technical analysis
indicator devised by Peter Martin in 1987, and published by him and Byron McCann in their 1989 book The Investors Guide to Fidelity Funds. It's designed as a measure of volatility, but only volatility in the downward direction, i.e. the amount of drawdown or retracement occurring over a period.
Other volatility measures like standard deviation
treat up and down movement equally, but a trader doesn't mind upward movement, it's the downside that causes stress
and stomach ulcers that the index's name suggests. (The name pre-dates the discovery, described in the ulcer article, that most gastric ulcers are actually caused by a bacterium.)
The term Ulcer Index has also been used (later) by Steve Shellans, editor and publisher of MoniResearch Newsletter for a different calculation, also based on the ulcer causing potential of drawdowns. Shellans index is not described in this article.
For example if the high so far is $5.00 then a price of $4.50 is a retracement of -10%. The first R is always 0, there being no drawdown from a single price. The quadratic mean (or root mean square
) of these values is taken, similar to a standard deviation calculation.
The squares mean it doesn't matter if the R values are expressed as positives or negatives, both come out as a positive Ulcer Index.
The calculation is relatively immune to the sampling rate used. It gives similar results when calculated on weekly prices as it does on daily prices. Martin advises against sampling less often than weekly though, since for instance with quarterly prices a fall and recovery could take place entirely within such a period and thereby not appear in the index.
, which rates an investment's excess return (return above a safe cash rate) against risk, is
The ulcer index can replace the SD to make an Ulcer Performance Index (UPI) or Martin ratio,
In both cases annualized rates of return would be used (net of costs, inclusive of dividend reinvestment, etc.).
The index can also be charted over time and used as a kind of technical analysis
indicator, to show stocks going into ulcer-forming territory (for one's chosen time-frame), or to compare volatility in different stocks. As with the Sharpe Ratio, a higher value is better than a lower value (investors prefer more return for less risk).
Books
Technical analysis
In finance, technical analysis is security analysis discipline for forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. Behavioral economics and quantitative analysis incorporate technical analysis, which being an aspect of active management stands...
indicator devised by Peter Martin in 1987, and published by him and Byron McCann in their 1989 book The Investors Guide to Fidelity Funds. It's designed as a measure of volatility, but only volatility in the downward direction, i.e. the amount of drawdown or retracement occurring over a period.
Other volatility measures like standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
treat up and down movement equally, but a trader doesn't mind upward movement, it's the downside that causes stress
Stress (medicine)
Stress is a term in psychology and biology, borrowed from physics and engineering and first used in the biological context in the 1930s, which has in more recent decades become commonly used in popular parlance...
and stomach ulcers that the index's name suggests. (The name pre-dates the discovery, described in the ulcer article, that most gastric ulcers are actually caused by a bacterium.)
The term Ulcer Index has also been used (later) by Steve Shellans, editor and publisher of MoniResearch Newsletter for a different calculation, also based on the ulcer causing potential of drawdowns. Shellans index is not described in this article.
Calculation
The index is based on a given past period of N days. Working from oldest to newest a highest price (highest closing price) seen so-far is maintained, and any close below that is a retracement, expressed as a percentageFor example if the high so far is $5.00 then a price of $4.50 is a retracement of -10%. The first R is always 0, there being no drawdown from a single price. The quadratic mean (or root mean square
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
) of these values is taken, similar to a standard deviation calculation.
The squares mean it doesn't matter if the R values are expressed as positives or negatives, both come out as a positive Ulcer Index.
The calculation is relatively immune to the sampling rate used. It gives similar results when calculated on weekly prices as it does on daily prices. Martin advises against sampling less often than weekly though, since for instance with quarterly prices a fall and recovery could take place entirely within such a period and thereby not appear in the index.
Usage
Martin recommends his index as a measure of risk in various contexts where usually the standard deviation (SD) is used for that purpose. For example the Sharpe ratioSharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
, which rates an investment's excess return (return above a safe cash rate) against risk, is
The ulcer index can replace the SD to make an Ulcer Performance Index (UPI) or Martin ratio,
In both cases annualized rates of return would be used (net of costs, inclusive of dividend reinvestment, etc.).
The index can also be charted over time and used as a kind of technical analysis
Technical analysis
In finance, technical analysis is security analysis discipline for forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. Behavioral economics and quantitative analysis incorporate technical analysis, which being an aspect of active management stands...
indicator, to show stocks going into ulcer-forming territory (for one's chosen time-frame), or to compare volatility in different stocks. As with the Sharpe Ratio, a higher value is better than a lower value (investors prefer more return for less risk).
Further reading
Related topics- Hindenburg OmenHindenburg omenThe Hindenburg Omen is a technical analysis pattern that is said to portend a stock market crash. It is named after the Hindenburg disaster of May 6, 1937, during which the German Zeppelin Hindenburg was destroyed.- History :...
- The "Gilt Dragon" Omen
Books
- The Investors Guide to Fidelity Funds, Peter Martin and Byron McCann, John Wiley & SonsJohn Wiley & SonsJohn Wiley & Sons, Inc., also referred to as Wiley, is a global publishing company that specializes in academic publishing and markets its products to professionals and consumers, students and instructors in higher education, and researchers and practitioners in scientific, technical, medical, and...
, 1989. Now out of print, but offered for sale in electronic form by Martin at his web site http://www.tangotools.com/ui/igff.htm.