
UTOPIA (Bioinformatics tools)
Encyclopedia
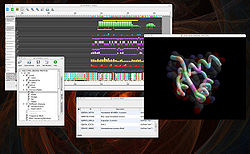
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics is the application of computer science and information technology to the field of biology and medicine. Bioinformatics deals with algorithms, databases and information systems, web technologies, artificial intelligence and soft computing, information and computation theory, software...
data. Based on an ontology
Ontology (computer science)
In computer science and information science, an ontology formally represents knowledge as a set of concepts within a domain, and the relationships between those concepts. It can be used to reason about the entities within that domain and may be used to describe the domain.In theory, an ontology is...
-driven data model, it contains applications for viewing and aligning protein sequences, rendering complex molecular structures in 3D, and for finding and using resources such as web services and data objects.
Between 2003 and 2005 work on UTOPIA was funded via The e-Science North West Centre based at The University of Manchester by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council, UK Department of Trade And Industry, and the European Molecular Biology Network. Since 2005 work continues under the EMBRACE European Network of Excellence.
History
UTOPIA's CINEMA (Colour INteractive Editor for Multiple Alignments), a tool for Sequence AlignmentSequence alignment
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are...
, is the latest incarnation of software originally developed at The University of Leeds
University of Leeds
The University of Leeds is a British Redbrick university located in the city of Leeds, West Yorkshire, England...
to aid the analysis of GPCRs. SOMAP, a Screen Orientated Multiple Alignment Procedure was developed in the late 1980s on the VMS
OpenVMS
OpenVMS , previously known as VAX-11/VMS, VAX/VMS or VMS, is a computer server operating system that runs on VAX, Alpha and Itanium-based families of computers. Contrary to what its name suggests, OpenVMS is not open source software; however, the source listings are available for purchase...
computer operating system, used a monochrome text-based VT100
VT100
The VT100 is a video terminal that was made by Digital Equipment Corporation . Its detailed attributes became the de facto standard for terminal emulators.-History:...
video terminal, and featured context-sensitive help
Context-sensitive help
Context-sensitive help is a kind of online help that is obtained from a specific point in the state of the software, providing help for the situation that is associated with that state....
and pulldown menus some time before these were standard operating system features.
SOMAP was followed by a Unix
Unix
Unix is a multitasking, multi-user computer operating system originally developed in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs, including Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Brian Kernighan, Douglas McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna...
tool called VISTAS (VIsualizing STructures And Sequences) which included the ability to render 3D molecular structure and generate plots and statistical representations of sequence properties.
The first tool under the CINEMA banner developed at The University of Manchester was a Java
Java (programming language)
Java is a programming language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems and released in 1995 as a core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but has a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities...
-based applet launched via web pages, which is still available but is no longer maintained. A standalone Java version, called CINEMA-MX, was also released but is no longer readily available.
A C++
C++
C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
version of CINEMA, called CINEMA5 was developed early on as part of the UTOPIA project, and was released as a stand-alone sequence alignment application. It has now been replaced by a version of the tool integrated with UTOPIA's other visualisation applications, and its name has reverted simply to CINEMA.
People
Pre UTOPIA alignment tools: T.K. Attwood, D.J.Parry-Smith, D.N.Perkins, A.W. Payne, A.D. Michie, P.W.Lord, J.N.Selley.UTOPIA: T.K.Attwood, P.McDermott, J.Marsh, S.Pettifer, J.Sinnott, D.Thorne,
External links
Peer reviewed publications on UTOPIA

